Question: A schematic of a clutch - testing machine is shown. The steel shaft rotates at a constant speed. An axial load is applied to the
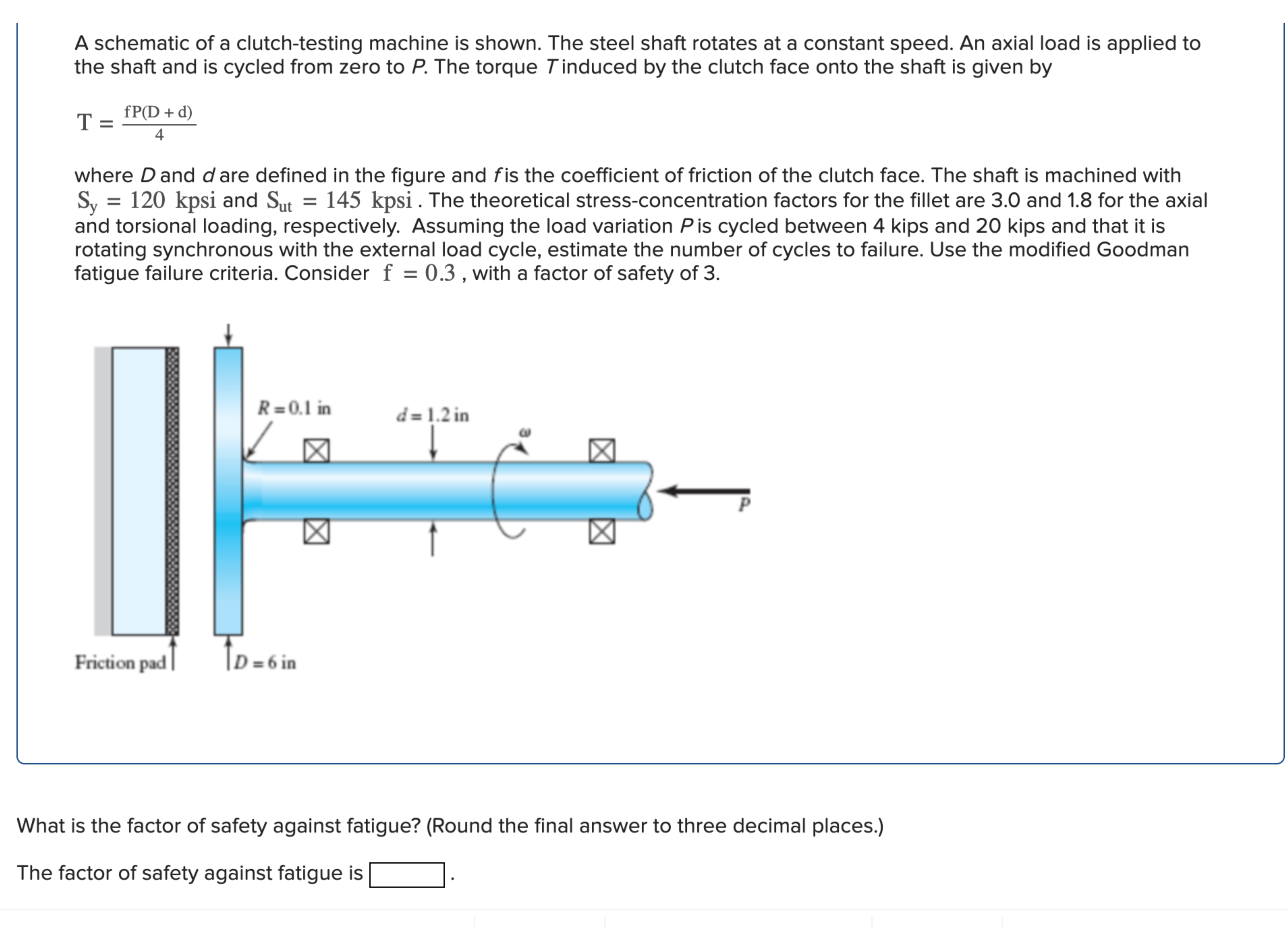
A schematic of a clutchtesting machine is shown. The steel shaft rotates at a constant speed. An axial load is applied to the shaft and is cycled from zero to P The torque T induced by the clutch face onto the shaft is given by
mathrmTfracmathrmfPmathrmDmathrmd
where D and d are defined in the figure and f is the coefficient of friction of the clutch face. The shaft is machined with mathrmSmathrmymathrmkpsi and mathrmSmathrmutmathrmkpsi The theoretical stressconcentration factors for the fillet are and for the axial and torsional loading, respectively. Assuming the load variation P is cycled between kips and kips and that it is rotating synchronous with the external load cycle, estimate the number of cycles to failure. Use the modified Goodman fatigue failure criteria. Consider mathrmf with a factor of safety of
What is the factor of safety against fatigue? Round the final answer to three decimal places.
The factor of safety against fatigue is
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


