Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
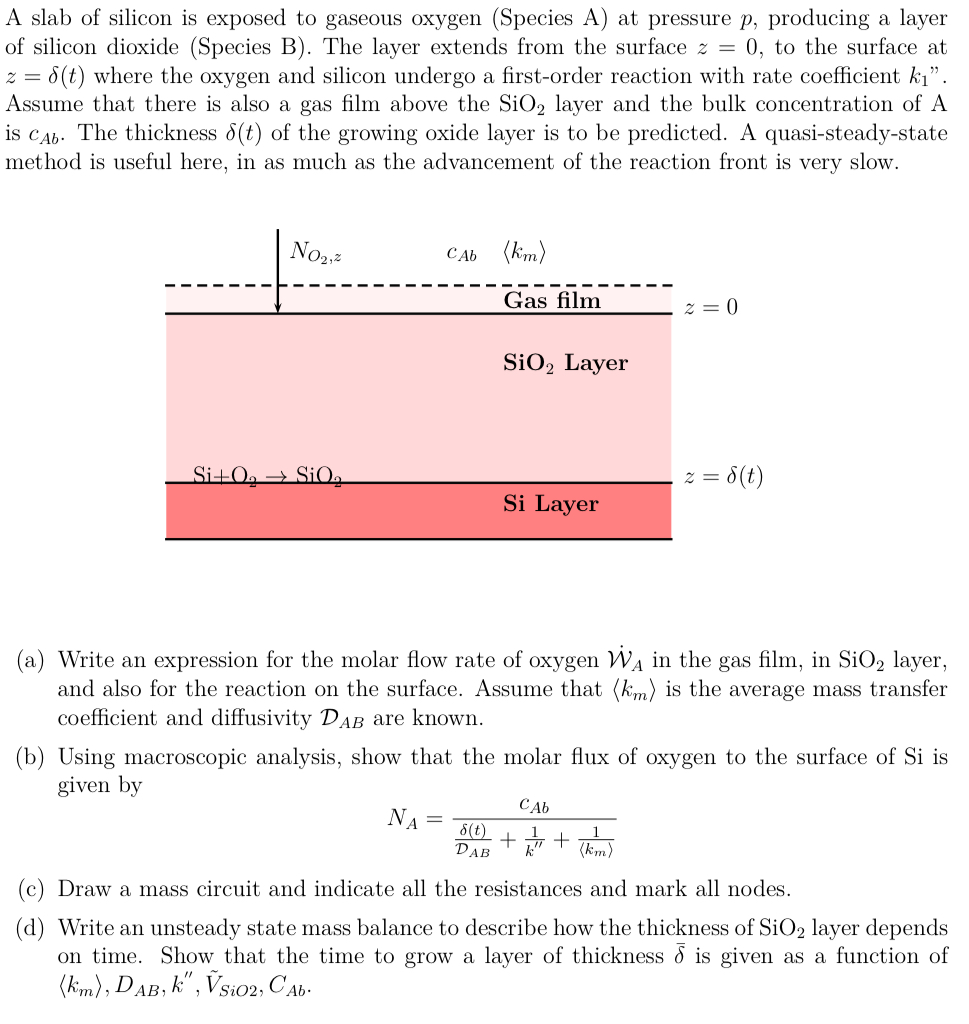
A slab of silicon is exposed to gaseous oxygen ( Species A ) at pressure p , producing a layer of silicon dioxide ( Species
A slab of silicon is exposed to gaseous oxygen Species A at pressure producing a layer
of silicon dioxide Species B The layer extends from the surface to the surface at
where the oxygen and silicon undergo a firstorder reaction with rate coefficient
Assume that there is also a gas film above the layer and the bulk concentration of
is The thickness of the growing oxide layer is to be predicted. A quasisteadystate
method is useful here, in as much as the advancement of the reaction front is very slow.
a Write an expression for the molar flow rate of oxygen in the gas film, in layer,
and also for the reaction on the surface. Assume that :: is the average mass transfer
coefficient and diffusivity are known.
b Using macroscopic analysis, show that the molar flux of oxygen to the surface of is
given by
c Draw a mass circuit and indicate all the resistances and mark all nodes.
d Write an unsteady state mass balance to describe how the thickness of layer depends
on time. Show that the time to grow a layer of thickness is given as a function of
::tilde
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


