A steam condenser employed in a power plant handles 35,000 kg of dry air per hour and saturated steam at 50 C. The cooling

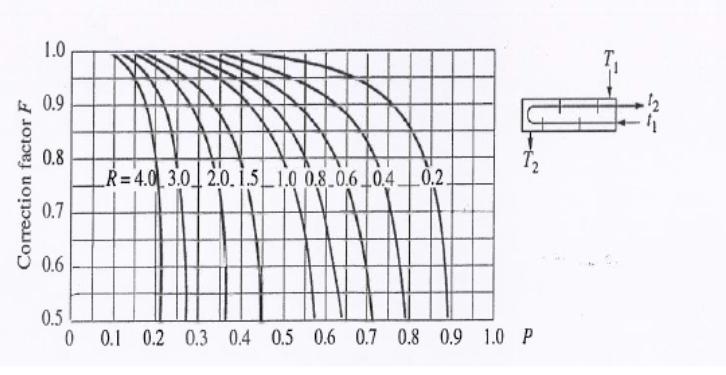
A steam condenser employed in a power plant handles 35,000 kg of dry air per hour and saturated steam at 50 C. The cooling water enters the condenser at 15 C and leaves at 25 C. The tubes (made of carbon steel with a thermal conductivity of 45 W/m K) have an inside diameter of 22.5 mm and an outside diameter of 25 mm. The water flows through the tubes at an average velocity of 2 m/s. The heat transfer coefficient on the steam side is 5000 W/mK. Assume that the condensate coming out of the condenser is saturated water. Using the heat exchanger correction factor plot below, calculate (a) Mass flow rate of water (b) Heat transfer surface area [4 points] [4 points] (e) Number of tubes required for the flow of water [14 points] (d) Number of tube passes in the condenser if the length of each tube per pass should not exceed 2.5 m [3 points] DATA: Density of water 998.8 kg/m Specific heat capacity of water = 4180 J/kg K Kinematic viscosity of water = 1.0006 x 10 m/s Thermal conductivity of water 0.59859 W/m K Latent heat of steam = 2374 kJ/kg 1.0 10 60 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 R=4.0 3.0 20.15 1.0 0.8.0.6 0.4 0.2. 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 P Correction factor F
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Heres the breakdown of the steam condenser ...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


