Question
A store assembles some segment data from their clients. The accompanying diagram sums up the age-related data they gathered: Age Number of Customers 20-30 72
A store assembles some segment data from their clients. The accompanying diagram sums up the age-related data they gathered:
Age Number of Customers
20-30 72
30-40 60
40-50 56
50-60 93
?60?60 53
One client is picked aimlessly for a prize giveaway.
What is the likelihood that the client is in any event 30 yet no more seasoned than 60?
What is the likelihood that the client is either more seasoned than 50 or more youthful than 30?
What is the likelihood that the client is at any rate 50?
Assume that in a specific country, the likelihood of having red hair is 0.20, and the likelihood of having blue eyes is 0.30. The likelihood of having the two qualities is 0.06. The probabilities are appeared in the Venn graph, where ?An is the occasion that an arbitrarily picked occupant of this nation has red hair, and ?B is the occasion that a haphazardly picked occupant has blue eyes.
A not B Both B not A
0.14 0.06 0.24
A=0.20 B= 0.30
Figure the restrictive likelihood of an individual having blue eyes given that the person has red hair, and utilize the worth to decide if having blue eyes and red hair are autonomous.
P(B/A=)
Having red hair is? of having blue eyes in light of the fact that?
i11i
a) Market research has shown that 60% of people who are acquainted with a specific item really purchase the item. An arbitrary example of 15 people were acquainted with the item.
I. Characterize the variable of interest for this situation.
ii. What likelihood circulation do you think best depicts the circumstance? Why?
iii. Compute the likelihood that precisely 9 will purchase the item.
iv. On the off chance that 80 people are acquainted with the item, decide the quantity of individual who are required to purchase the item.
b) It is realized that a normal of 5 trains go through Grand Central Terminal like clockwork. Discover the likelihood that
I. Precisely 4 trains will pass in a short time
ii. under 2 trains will pass in 60 minutes
The Chief Information Officer (CIO) at Old Dominion University - ODU-is attempting to improve the college's data network security. The CIO is attempting to assess another interruption discovery innovation on the lookout for a potential trade for the current framework. An interruption recognition framework sounds an "alert" each time conceivable malevolent assault on an organization is identified. The accompanying data is given:
Occasion of interest, A, is an assault
Proof, B, is interruption recognition framework setting off because of abnormal traffic
Likelihood of an assault is 0.01
For the right now introduced situation, the likelihood of a caution given that there is an assault is 0.9, while the likelihood of an alert given there is no assault is 0.25.
For the new innovation, the likelihood of an alert given that there is an assault is 0.8, while the likelihood of a caution given there is no assault is 0.1.
The CIO expects that there are just two sorts of occasions: either there is, or there is no assault.
The CIO is utilizing "proof proportion," depicted as P(B|A)/P(B|A') as an approach to look at the innovations. Kindly assistance the CIO contrast the new innovation and the as of now introduced framework by addressing the accompanying inquiries:
What is proof proportion for the right now introduced situation?
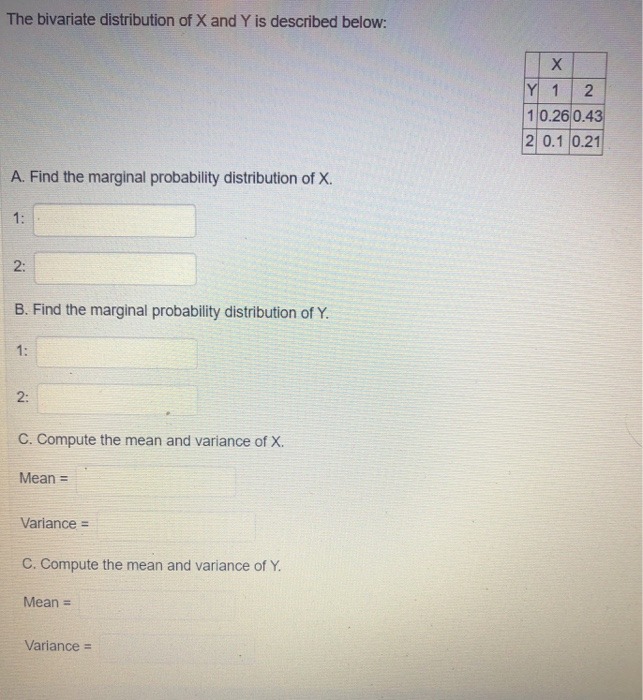
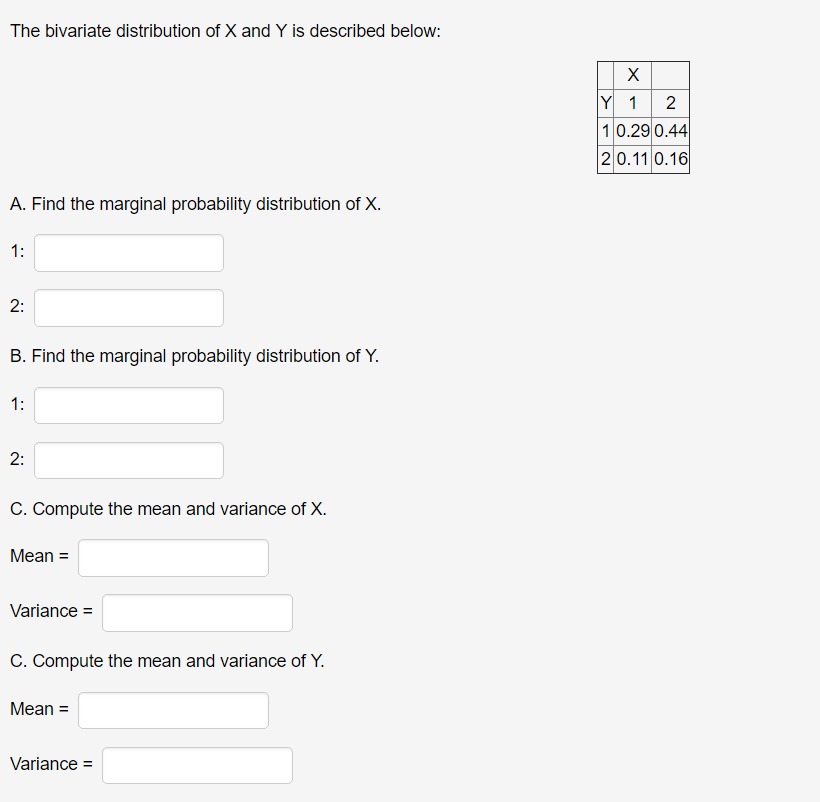

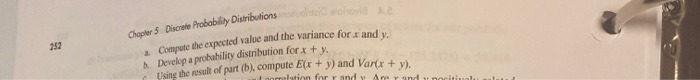
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


