Question: a) To prevent liquid-junction potential that limits the accuracy of potentiomeiry cell measurement, i. membrane electrode ii. Working electrode iii. Salt bridge of sat KCl


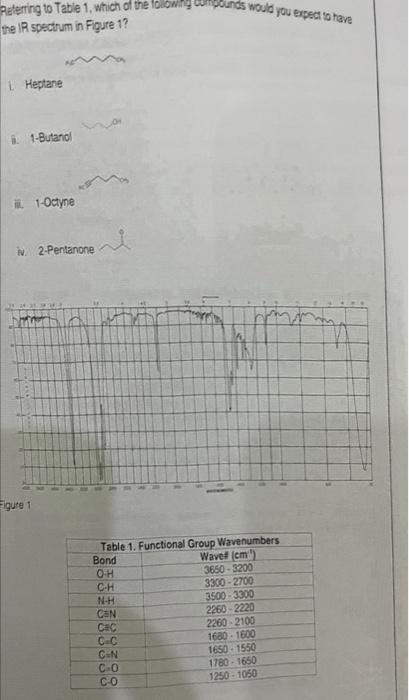


a) To prevent liquid-junction potential that limits the accuracy of potentiomeiry cell measurement, i. membrane electrode ii. Working electrode iii. Salt bridge of sat KCl iv. Reference electrode b) The auxiliary electrode uses in voltammetry cell to i. Produce the potential due to transfer of charge to and from the analyte ii. Carry the current flowing through the cell iii. provides potential to the working electrode iv. Measure current under constant applied voltage c) Calculate the potential of a lanthanum (La+3) ion-selective electrode change if the electrode is removed from La(NO3)3 solution 1105M and placed in the solution 1.0102M of La(NO3)3 ? i. 0.0197V ii. 0.059V iii. 0.450V d) Electrogravmetry analysis depends on equil for emf Response of 0.0295V, if i. Nicolsky Eisenman Equation ii. weighing the electrode before and after deposition of the metal solid on an electrode from the analyte solution. iii. measurement the quantity of electricity used to deposit the metal. iv. Nernst equation for measuring the weight of metal deposit Raquirements of the reference electrode are L. Potential of relerence electrode should be known relative to the SHE. 1. Potential of reference electrode should be constant during measurments ii. Potential of relerence electrode should be not senstive to the concentration of the analye N. Answer a and D D) DHerence betwen votammety and polarographic ceil is: i. In the voltammetry, working electrode is lithium electrode i. In the volammetry, working electrode is enzyme electrode ii. The wotking electrode in the vollammetry is glass electrode with dropping mercury electrode. v. In the polarography, dropping mercury electrode (DME) use as working electrode 9) Combination clectrode means L. Glass electrode and reference electrode in diferent body h. Incorporate three electrode glass electrode, Ag/AgCl and SCE as one electrode i. Incorporate boch glass and reference electrodes in one body . iv. Use two telerences electrodes h) Calculate the potential required to generate current of 3105. A and with resistance equal 0.2 in the reversed drection of the cell potential equal 0.53V. L. 0.52V 14. 0.39V i. 0.52V (v) 1.1V i) Before conducting voltammetric measurements, No gas is usually bubbled through solutions for a few minutes to remove dissolved _....... gas which is reduced at. working electrode to form two oxygen waves i. O2 i. Av ii. CO3 iv. N2 D) A galvanic cell employs the following hall reactions Fe213y+e=Fe2b+2e=31E=0.771VE=0.5355V 1) What would be the cell reaction? 1. 2Fe+3+3F1=2Fe+2+F5 (Cell reaction) -i. 2Fe+2+3I2=2Fe+3+F5 (Cell reaction) iii. Fe+3+I=Fe+2+2H5 (Cell reaction) iv. 2Fe33+I3=Fe+2+2F3 (Cell reaction) Retering to Table 1, which of the lollowing cunpounds would you expect to have the IR spectrum in Figute 1? L. Heptane i. 1-Butanol iii. 1-Octyne N. 2.Pentanone a) Identify the major ionic species present in an aqueous solution of Na2CO3. i. Na22,CO32 ii. Na2+C2,O3 iii. Na+,C4,O32. iv. Na+,C+,O2 v. Na+,CO32 b) What element is oxidized in the chemical reaction 3Cu+8HNO33Cu(NO3)2+2NO+4H2O? i. Cu ii. H iii. N iv. O v. H2O c) Which of these chemical equations describes an acid-base neutralization reac i. 2Al(s)+3H2SO4(aq)Al2(SO4)3(aq)+3H2(g) ii. SO2(g)+H2O(i)H2SO3(g) iii. LiOH(aq)+HNO3(aq)LiNO3(aq)+H2O(1) iv. 2KBr(aq)+Cl(g)2KCl(aq)+Br2( () v. CaBr2(aq)+H2SO4(aq)CaSO4(s)+2HBr(g) d) Which of the following is a weak Brnst-Lowry acid? i. HClO4 ii. HNO3 iii. H2S iv. H2SO4 v. HCl e) A 0.9182g sample of CaBr2 is dissolved in enough water to give 500.mL of What is the calcium ion concentration in this solution? i. 9.19103M ii. 2.30103M iii. 2.72103M iv. 4.59103M v. 1.25103M Treatment of a 0.2500g sample of impure KCl with an excess of AgNOs resulted in the formation of 0.2912g of AgCl, calculate the percentage of KCl in the sample? i. 30,04%KCl ii. 85.85%KCl ii. 65.85%KCl (v. 60.59%KCl v. 80.90%KCl Suggest a suitable indicator for a titration based on the following equation: H2SO3+2NaOHNaSO3+2H3O i. Nechylene blue ii. Phenolphthalein iii. Cresol purple iv. Bromocresol greon v. Methyene orange h) Calculate the hydronium and hydroxide ion concentration of pure water at 25C. Kn=1.01014 ? i. 1.0107M ii. 1.01071.01014M iii. 7.0104.7.0101M iv. 1.01014M v. 5.0107M i) How many grams of lead are contained in 6.0103g of blood (the amount in an average adult) id the lead content is 0.62ppm ? i. 3.7101g ii. 0.72105g iii. 3.7103g iv. 3.71049 v. 7.2102g j) Which choice gives the correct oxidation numbers for all three elements in Rb2SO3 in the order that the elements are shown in the formula? i. 2,+6,2 ii. 1,+4,3 iii. +2,+4,2 iv. +1,+4,2 v. +1,+6,6
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


