Question: ABC Framing has been hired to frame a light commercial building. The project began on July 2 and was completed on August 9. The following
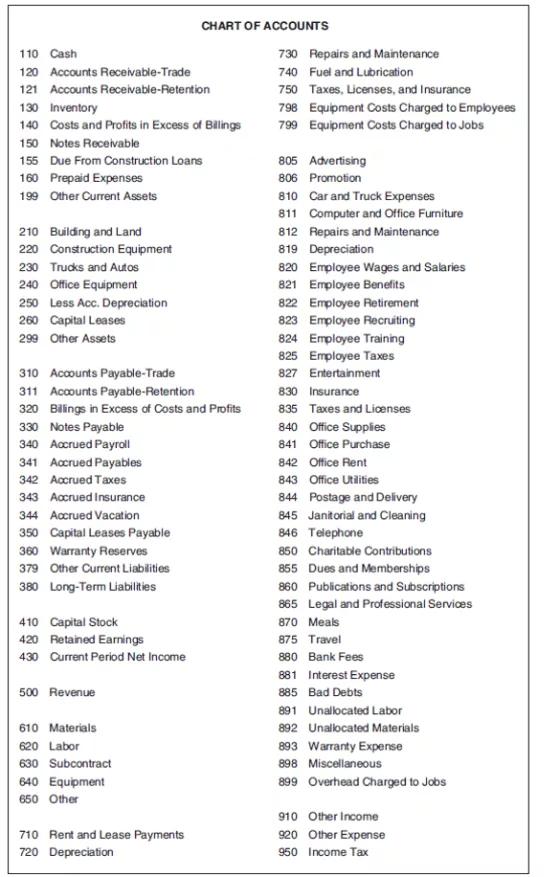
ABC Framing has been hired to frame a light commercial building. The project began on July 2 and was completed on August 9. The following is a list of accounting transactions associated with the project. For each transaction, determine the changes that occur on the balance sheet, income statement, and job cost ledger as a result of that transaction and the year-to-date totals by general ledger account and job cost code. The company uses the chart of accounts in Figure 2-1. The general contractor doesn’t withhold retention. All costs are billed to job cost code 1005.06110.
The appropriate cost type (M, L, or E) needs to be added to the job cost code. The company rents its equipment and the equipment is billed directly to the job cost ledger; therefore, they do not keep an equipment ledger. After you have entered all of the transactions, plot the daily balance of the 110 cash account and profit for the project.
a. On July 11 the time cards were entered into the ac-counting system. The following costs were recorded: wages due to employees, $4,299.52; social security, $602.88; Medicare, $142.08; SUTA, $268.16; FUTA, $5.76; workers’ compensation, $425.92; general liability, $38.08; and employer-paid health insurance, $288.00.
b. On July 13 the employees were paid for the time entered into the accounting system on July 11.
c. On July 18 the time cards were entered into the accounting system. The following costs were recorded: wages due to employees, $5,374.40; social security, $753.60; Medicare, $177.60; SUTA, $335.20; FUTA, $7.20; workers’ compensation, $532.40; general liability, $47.60; and employer-paid health insurance, $360.00.
d. On July 20 the employees were paid for the time entered into the accounting system on July 18.
e. On July 25 the time cards were entered into the ac-counting system. The following costs were recorded: wages due to employees, $5,374.40; social security, $753.60; Medicare, $177.60; SUTA, $335.20; FUTA, $7.20; workers’ compensation, $532.40; general liability, $47.60; and employer-paid health insurance, $360.00.
f. On July 27 the employees were paid for the time entered into the accounting system on July 25.
g. On July 31, the social security, Medicare, SUTA, FUTA, workers’ compensation, general liability, and employer-paid health insurance premiums recorded during July were paid.
h. On August 1 the time cards were entered into the accounting system. The following costs were record-ed: wages due to employees, $5,374.40; social secu-rity, $753.60; Medicare, $177.60; SUTA, $335.20; FUTA, $7.20; workers’ compensation, $532.40; general liability, $47.60; and employer-paid health insurance, $360.00.
i. On August 2 a bill for materials (e.g., nails, hard-ware, and small tools) in the amount of $3,846 was entered into the accounting system. A bill for the forklift rental in the amount of $6,720 was also entered.
j. On August 3 the employees were paid for the time entered into the accounting system on August 1.
k. On August 5 the general contractor was billed $45,000 for July’s work.
51
l. On August 8 the time cards were entered into the accounting system. The following costs were record-ed: wages due to employees, $5,374.40; social secu-rity, $753.60; Medicare, $177.60; SUTA, $335.20; FUTA, $7.20; workers’ compensation, $532.40; general liability, $47.60; and employer-paid health insurance, $360.00.
m. On August 10 the employees were paid for the time entered into the accounting system on August 8.
n. On August 15 the time cards were entered into the accounting system. The following costs were record-ed: wages due to employees, $5,374.40; social secu-rity, $753.60; Medicare, $177.60; SUTA, $335.20; FUTA, $7.20; workers’ compensation, $532.40; general liability, $47.60; and employer-paid health insurance, $360.00.
o. On August 15 the materials and equipment bills entered into the accounting system on August 2 were paid.
p. On August 17 the employees were paid for the time entered into the accounting system on August 15.
q. On August 17 a bill for the forklift rental in the amount of $2,240 was entered into the accounting system.
r. On August 25 payment was received from the gener-al contractor for July’s work.
s. On August 31, the social security, Medicare, SUTA, FUTA, workers’ compensation, general liability, and employer-paid health insurance premiums recorded during August were paid.
t. On August 31 the forklift rental bill recorded on Au-gust 17 was paid.
u. On September 3 the bill for materials (e.g., nails, hardware, and small tools) in the amount of $1,705 was entered into the accounting system.
v. On September 5 the general contractor was billed for $20,800 for July’s work.
w. On September 15 the materials bill recorded on September 3 was paid.
x. On September 25 payment is received from the general contractor for August’s work.
CHART OF ACCOUNTS 110 Cash 730 Repairs and Maintenance 120 Accounts Receivable-Trade 740 Fuel and Lubrication 121 Accounts Receivable-Retention 750 Taxes, Licenses, and Insurance 130 Inventory 140 Costs and Profits in Excess of Bilings 798 Equipment Costs Charged to Employees 799 Equipment Costs Charged to Jobs 150 Notes Receivable 155 Due From Construction Loans 805 Advertising 160 Prepaid Expenses 806 Promotion 199 Other Current Assets 810 Car and Truck Expenses 811 Computer and Office Furniture 210 Building and Land 220 Construction Equipment 812 Repairs and Maintenance 819 Depreciation 230 Trucks and Auos 820 Employee Wages and Salaries 821 Employee Benefits 240 Office Equipment 250 Less Acc. Depreciation 822 Employee Retirement 260 Capital Leases 823 Employee Recruiting 824 Employee Training 299 Other Assets 825 Employee Taxes 310 Accounts Payable-Trade 827 Entertainment 311 Accounts Payable-Retention 830 Insurance 835 Taxes and Licenses 320 Bilings in Excess of Costs and Profits 330 Notes Payable 840 Office Supples 340 Accrued Payroll 841 Office Purchase 341 Accrued Payables 342 Accrued Taxes 842 Office Rent 843 Office Utlities 844 Postage and Delivery 845 Janitorial and Cleaning 846 Telephone 343 Accrued Insurance 344 Accrued Vacation 350 Capital Leases Payable 360 Warranty Reserves 850 Charitable Contributions 379 Other Current Liablities 855 Dues and Memberships 860 Publications and Subscriptions 380 Long-Term Liabilities 865 Legal and Professional Services 410 Capital Stock 870 Meals 875 Travel 420 Retained Earnings 430 Current Period Net Income 880 Bank Fees 881 Interest Expense 500 Revenue 885 Bad Debts 891 Unalocated Labor 610 Materials 892 Unallocated Materials 620 Labor 893 Warranty Expense 898 Miscellaneous 630 Subcontract 640 Equipment 899 Overhead Charged to Jobs 650 Other 910 Other Income 710 Rent and Lease Payments 920 Other Expense 720 Depreciation 950 Income Tax
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Balance Sheet Income Statement Job Cost 430 Current 120 Accounts 310 Accounts 340 Accrued 343 Accrue... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts