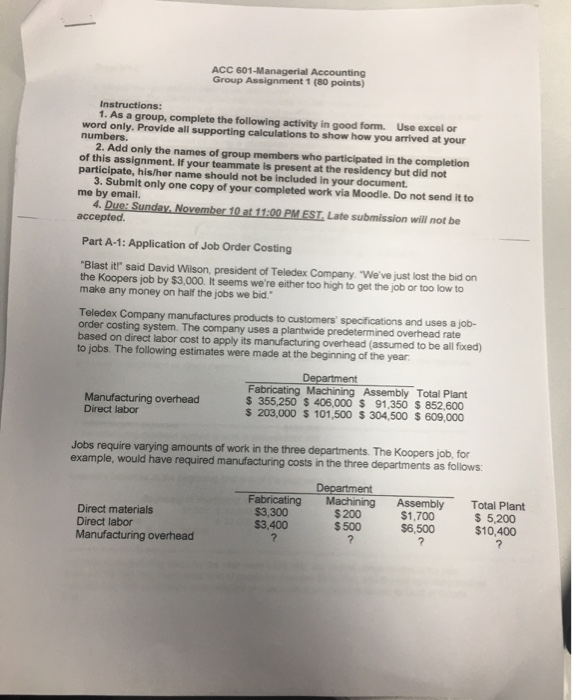
ACC 601-Managerial Accounting Group Assignment 1 (80 points) Instructions: 1. As a group, complete the following activity in good form. Use excolor word only. Provide all supporting calculations to show how you arrived at your numbers 2. Add only the names of group members who participated in the completion of this assignment. If your teammate is present at the residency but did not participate, his/her name should not be included in your document. 3. Submit only one copy of your completed work via Moodle. Do not send it to me by email. 4. Due: Sunday, November 10 at 11:00 PM EST. Late submission will not be accepted. Part A-1: Application of Job Order Costing "Blast it!" said David Wilson, president of Teledex Company. We've just lost the bid on the Koopers job by $3,000. It seems we're either too high to get the job or too low to make any money on half the jobs we bid." Toledex Company manufactures products to customers' specifications and uses a job- order costing system. The company uses a plantwide predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor cost to apply its manufacturing overhead (assumed to be all foxed) to jobs. The following estimates were made at the beginning of the year Manufacturing overhead Direct labor Department Fabricating Machining Assembly Total Plant $ 355,250 $ 406,000 $ 91,350 $ 852.600 $ 203,000 $ 101,500 $ 304,500 $ 609,000 Jobs require varying amounts of work in the three departments. The Koopers job, for example, would have required manufacturing costs in the three departments as follows: Department Machining $200 Fabricating $3,300 $3,400 Direct materials Direct labor Manufacturing overhead Assembly $1,700 $6,500 $ 500 Total Plant $ 5,200 $10,400 Required: 1. Using the company's plantwide approach: a. Compute the plantwide predetermined rate for the current year b. Determine the amount of manufacturing overhead cost that would have been applied to the Koopers job. 2. Suppose that instead of using a plantwide predetermined overhead rate, the company had used departmental predetermined overhead rates based on direct labor cost. Under these conditions: a.Compute the predetermined overhead rate for each department for the current year. b. Determine the amount of manufacturing overhead cost that would have been applied to the Koopers job. 4. Assume that it is customary in the industry to bid jobs at 150% of total manufacturing cost direct materials, direct labor, and applied overhead) a. What was the company's bid price on the Koopers job using a plantwide predetermined overhead rate? b. What would the bid price have been if departmental predetermined overhead rates had been used to apply overhead cost? Part A-2: Schedules of Cost of Goods Manufactured and cost of Goods Sold; Income Statement Superior Company provided the following data for the year ended December 31 (all raw materials are used in production as direct materials): Selling expenses $216,000 Purchases of raw materials $264,000 Direct labor Administrative expenses $159,000 Manufacturing overhead applied to work in process $368,000 Actual manufacturing overhead cost $355,000 Inventory balances at the beginning and end of the year were as follows: Beginning of YearEnd of Year Raw materials $ 51,000 $ 33,000 Work in process ? $ 32,000 Finished goods $ 34,000 The total manufacturing costs for the year were $675,000; the cost of goods available for sale totaled $735,000: the unadjusted cost of goods sold totaled $669,000, and the net operating income was $32,000. The company's underapplied or overapplied overhead is closed to cost of Goods Sold. Required: Prepare schedules of cost of goods manufactured and cost of goods sold and an income statement (Hint: Prepare the income statement and schedule of cost of goods sold first followed by the schedule of cost of goods manufactured.) Part B-1: Process Costing using Weighted Average "I think we goofed when we hired that new assistant controller," said Ruth Scarpino, president of Provost Industries. "Just look at this report that he prepared for last month for the Finishing Department. I can't understand it." Finishing Department costs: Work in process inventory, April 900 units; materials 100% complete: conversion 60% complete Costs transferred in during the month from the preceding department, 2,400 units Materials cost added during the month Conversion costs incurred during the month Total departmental costs $ 8,561 25,381 10,017 21,750 $65 709 Finishing Department costs assigned to: Units completed and transferred to finished goods, 2,700 units at $24.340 per unit Work in process inventory, April 30, 600 units materials 0% complete, conversion 50% complete Total departmental costs assigned $65,709 $65,709 *Consists of cost transferred in, $4,286; materials cost, $2,025, and conversion cost, $2,250. "He's struggling to leam our system," replied Frank Harrop, the operations manager "The problem is that he's been away from process costing for a long time, and it's coming back slowly." "It's not just the format of his report that I'm concerned about. Look at that $24.340 unit cost that he's come up with for April. Doesn't that seem high to you?" said Ms. Scarpino. "Yes, it does seem high, but on the other hand, I know we had an increase in materials prices during April, and that may be the explanation," replied Mr. Harrop. "Til get someone else to redo this report and then we can see what's going on." Provost Industries manufactures a ceramic product that goes through two processing departments-Molding and Finishing. The company uses the weighted average method in its process costing. Required: 1-a. Calculate the equivalent units of production 1-b. Calculate the cost per equivalent unit 1-c. How much cost should have been assigned to the ending work in process inventory? 1-d. How much cost should have been assigned to the units completed and transferred to finished goods? Part B-2: Break-Even Analysis Cheryl Montoya picked up the phone and called her boss, Wes Chan, the vice president of marketing at Piedmont Fasteners Corporation: "Wes, I'm not sure how to go about answering the questions that came up at the meeting with the president yesterday "What's the problem? "The president wanted to know the break-even point for each of the company's products, but I am having trouble figuring them out." "I'm sure you can handle it, Cheryl. And, by the way, I need your analysis on my desk tomorrow morning at 8:00 sharp in time for the follow-up meeting at 9:00." Piedmont Fasteners Corporation makes three different clothing fasteners in its manufacturing facility in North Carolina. Data concerning these products appear below: Velcro Metal Nylon Annual sales volume 95,000 216,000 320,000 Unit selling price $ 1.90 $ 1.30 $ 0.90 Variable expense per unit$ 0.70 $ 0.70 $ 0.70 Total fixed expenses are $262,000 per year. All three products are sold in highly competitive markets, so the company is unable to raise prices without losing an unacceptable numbers of customers. The company has an extremely effective lean production system, so there are no beginning or ending work in process or finished goods inventories Required: 1. What is the company's over-all break-even point in dollar sales? 2. Of the total fixed expenses of $262.000, $34,200 could be avoided if the Velcro product is dropped, $96,000 if the Metal product is dropped, and $38,800 if the Nylon product is dropped. The remaining fixed expenses of $93,000 consist of common fixed expenses such as administrative salaries and rent on the factory building that could be avoided only by going out of business entirely a. What is the break-even point in unit sales for each product? b. If the company sells exactly the break-even quantity of each product, what will be the overall profit of the company? ACC 601-Managerial Accounting Group Assignment 1 (80 points) Instructions: 1. As a group, complete the following activity in good form. Use excolor word only. Provide all supporting calculations to show how you arrived at your numbers 2. Add only the names of group members who participated in the completion of this assignment. If your teammate is present at the residency but did not participate, his/her name should not be included in your document. 3. Submit only one copy of your completed work via Moodle. Do not send it to me by email. 4. Due: Sunday, November 10 at 11:00 PM EST. Late submission will not be accepted. Part A-1: Application of Job Order Costing "Blast it!" said David Wilson, president of Teledex Company. We've just lost the bid on the Koopers job by $3,000. It seems we're either too high to get the job or too low to make any money on half the jobs we bid." Toledex Company manufactures products to customers' specifications and uses a job- order costing system. The company uses a plantwide predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor cost to apply its manufacturing overhead (assumed to be all foxed) to jobs. The following estimates were made at the beginning of the year Manufacturing overhead Direct labor Department Fabricating Machining Assembly Total Plant $ 355,250 $ 406,000 $ 91,350 $ 852.600 $ 203,000 $ 101,500 $ 304,500 $ 609,000 Jobs require varying amounts of work in the three departments. The Koopers job, for example, would have required manufacturing costs in the three departments as follows: Department Machining $200 Fabricating $3,300 $3,400 Direct materials Direct labor Manufacturing overhead Assembly $1,700 $6,500 $ 500 Total Plant $ 5,200 $10,400 Required: 1. Using the company's plantwide approach: a. Compute the plantwide predetermined rate for the current year b. Determine the amount of manufacturing overhead cost that would have been applied to the Koopers job. 2. Suppose that instead of using a plantwide predetermined overhead rate, the company had used departmental predetermined overhead rates based on direct labor cost. Under these conditions: a.Compute the predetermined overhead rate for each department for the current year. b. Determine the amount of manufacturing overhead cost that would have been applied to the Koopers job. 4. Assume that it is customary in the industry to bid jobs at 150% of total manufacturing cost direct materials, direct labor, and applied overhead) a. What was the company's bid price on the Koopers job using a plantwide predetermined overhead rate? b. What would the bid price have been if departmental predetermined overhead rates had been used to apply overhead cost? Part A-2: Schedules of Cost of Goods Manufactured and cost of Goods Sold; Income Statement Superior Company provided the following data for the year ended December 31 (all raw materials are used in production as direct materials): Selling expenses $216,000 Purchases of raw materials $264,000 Direct labor Administrative expenses $159,000 Manufacturing overhead applied to work in process $368,000 Actual manufacturing overhead cost $355,000 Inventory balances at the beginning and end of the year were as follows: Beginning of YearEnd of Year Raw materials $ 51,000 $ 33,000 Work in process ? $ 32,000 Finished goods $ 34,000 The total manufacturing costs for the year were $675,000; the cost of goods available for sale totaled $735,000: the unadjusted cost of goods sold totaled $669,000, and the net operating income was $32,000. The company's underapplied or overapplied overhead is closed to cost of Goods Sold. Required: Prepare schedules of cost of goods manufactured and cost of goods sold and an income statement (Hint: Prepare the income statement and schedule of cost of goods sold first followed by the schedule of cost of goods manufactured.) Part B-1: Process Costing using Weighted Average "I think we goofed when we hired that new assistant controller," said Ruth Scarpino, president of Provost Industries. "Just look at this report that he prepared for last month for the Finishing Department. I can't understand it." Finishing Department costs: Work in process inventory, April 900 units; materials 100% complete: conversion 60% complete Costs transferred in during the month from the preceding department, 2,400 units Materials cost added during the month Conversion costs incurred during the month Total departmental costs $ 8,561 25,381 10,017 21,750 $65 709 Finishing Department costs assigned to: Units completed and transferred to finished goods, 2,700 units at $24.340 per unit Work in process inventory, April 30, 600 units materials 0% complete, conversion 50% complete Total departmental costs assigned $65,709 $65,709 *Consists of cost transferred in, $4,286; materials cost, $2,025, and conversion cost, $2,250. "He's struggling to leam our system," replied Frank Harrop, the operations manager "The problem is that he's been away from process costing for a long time, and it's coming back slowly." "It's not just the format of his report that I'm concerned about. Look at that $24.340 unit cost that he's come up with for April. Doesn't that seem high to you?" said Ms. Scarpino. "Yes, it does seem high, but on the other hand, I know we had an increase in materials prices during April, and that may be the explanation," replied Mr. Harrop. "Til get someone else to redo this report and then we can see what's going on." Provost Industries manufactures a ceramic product that goes through two processing departments-Molding and Finishing. The company uses the weighted average method in its process costing. Required: 1-a. Calculate the equivalent units of production 1-b. Calculate the cost per equivalent unit 1-c. How much cost should have been assigned to the ending work in process inventory? 1-d. How much cost should have been assigned to the units completed and transferred to finished goods? Part B-2: Break-Even Analysis Cheryl Montoya picked up the phone and called her boss, Wes Chan, the vice president of marketing at Piedmont Fasteners Corporation: "Wes, I'm not sure how to go about answering the questions that came up at the meeting with the president yesterday "What's the problem? "The president wanted to know the break-even point for each of the company's products, but I am having trouble figuring them out." "I'm sure you can handle it, Cheryl. And, by the way, I need your analysis on my desk tomorrow morning at 8:00 sharp in time for the follow-up meeting at 9:00." Piedmont Fasteners Corporation makes three different clothing fasteners in its manufacturing facility in North Carolina. Data concerning these products appear below: Velcro Metal Nylon Annual sales volume 95,000 216,000 320,000 Unit selling price $ 1.90 $ 1.30 $ 0.90 Variable expense per unit$ 0.70 $ 0.70 $ 0.70 Total fixed expenses are $262,000 per year. All three products are sold in highly competitive markets, so the company is unable to raise prices without losing an unacceptable numbers of customers. The company has an extremely effective lean production system, so there are no beginning or ending work in process or finished goods inventories Required: 1. What is the company's over-all break-even point in dollar sales? 2. Of the total fixed expenses of $262.000, $34,200 could be avoided if the Velcro product is dropped, $96,000 if the Metal product is dropped, and $38,800 if the Nylon product is dropped. The remaining fixed expenses of $93,000 consist of common fixed expenses such as administrative salaries and rent on the factory building that could be avoided only by going out of business entirely a. What is the break-even point in unit sales for each product? b. If the company sells exactly the break-even quantity of each product, what will be the overall profit of the company