Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Sunshine Electric Company is a small, rapidly growing wholesaler of consumer electrical products. The firm's main product lines are small kitchen appliances and power


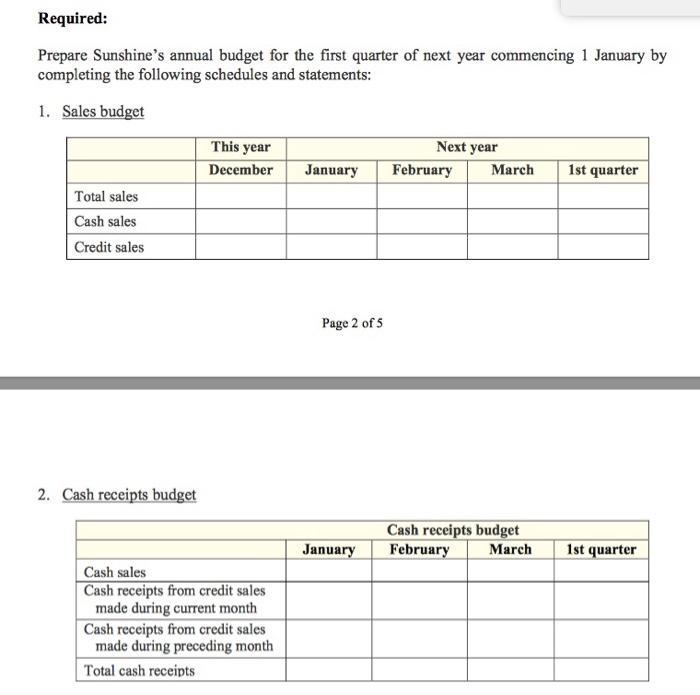
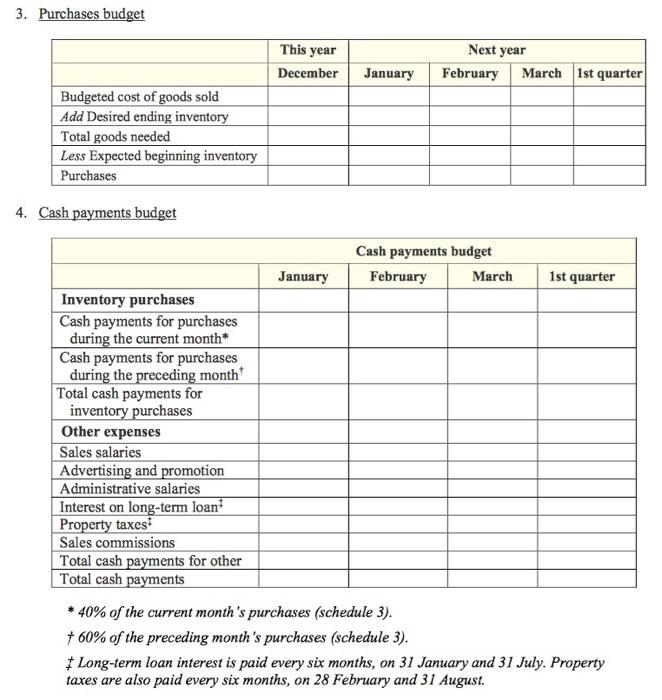
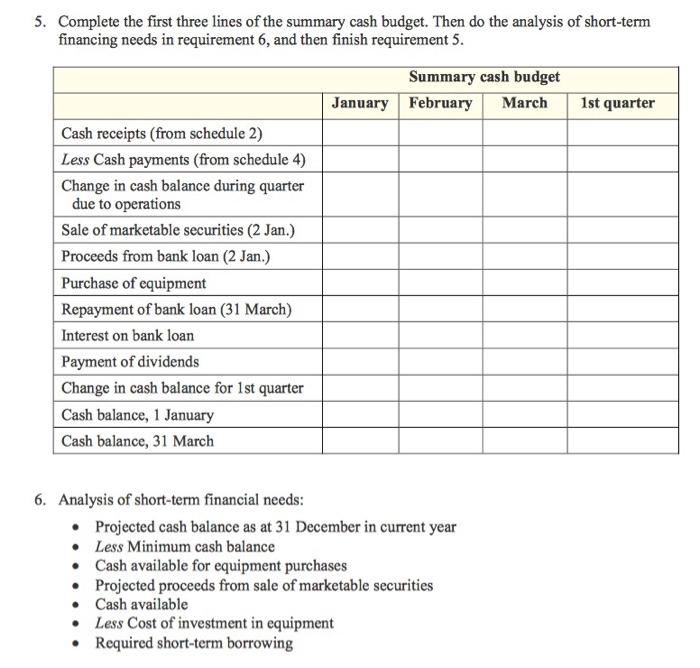

Sunshine Electric Company is a small, rapidly growing wholesaler of consumer electrical products. The firm's main product lines are small kitchen appliances and power tools. The new marketing manager, Maria Brown, has recently completed a sales forecast. She believes that the company's sales during the first quarter of next year will increase by 10 per cent each month over the previous month's sales. Brown then expects sales to remain constant for several months. Sunshine's projected balance sheet as at 31 December this year is as follows: Cash $ 35 000 Accounts receivable Marketable securities 270 000 Inventory Buildings and equipment (net of acc. depr.) Total assets 15 000 154 000 626 000 $1 100 000 Accounts payable Long-term loan interest payable Property taxes payable Long-term loan payable (10% p.a.) Share capital Retained earnings Total liabilities and shareholders' equity $176 400 12 500 3 600 300 000 500 000 107 500 $1 100 000 Peter Jackman, the management accountant, is now preparing a monthly budget for the first quarter of next year. In the budgeting process, the following information has been accumulated: Projected sales for December this year are $400 000. Credit sales typically are 75 per cent of total sales. Sunshine's credit experience indicates that 10 per cent of the credit sales are collected during the month of sale, and the remainder are collected during the following month. Sunshine's cost of goods sold generally runs at 70 per cent of sales. Inventory is purchased on credit, and 40 per cent of each month's purchases is paid during the month of purchase. The remainder is paid during the following month. In order to have adequate inventory on hand, the firm aims to have inventory at the end of each month equal to half of the next month's projected cost of goods sold. Jackman has estimated that Sunshine's other monthly expenses will be as follows: Sales salaries Advertising and promotion Administrative salaries $18 000 19 000 21 000 Depreciation Interest on long-term loan Property taxes 25 000 2 500 900 In addition, sales commissions run at the rate of 1 per cent of sales. Sunshine's managing director, Beth Johnson, has indicated that the firm should, just after the new year begins, invest $125 000 in an automated inventory-handling system to control the movement of inventory in the firm's warehouse. To the extent possible, these equipment purchases would be financed from the firm's cash and marketable securities. Johnson believes that Sunshine needs to keep a minimum cash balance of $25 000. If necessary, the remainder of the equipment purchases would be financed using short-term credit from a local bank. The minimum period for such a loan is three months. Jackman believes short-term interest rates will be 5 per cent per year at the time of the equipment purchases. If a loan is necessary, Johnson has decided it should be paid off by the end of the first quarter if possible. Sunshine's board of directors has indicated an intention to declare and pay dividends amounting to $50 000 on the last day of each quarter. The interest on any short-term borrowing would be paid when the loan is repaid. Interest on Sunshine's long-term loan is paid semi-annually, on 31 January and 31 July, for the preceding six-month period. Property taxes are paid half-yearly on 28 February and 31 August for the preceding six-month period. Required: Prepare Sunshine's annual budget for the first quarter of next year commencing 1 January by completing the following schedules and statements: 1. Sales budget This year Next year December January February March 1st quarter Total sales Cash sales Credit sales Page 2 of 5 2. Cash receipts budget Cash receipts budget February January March 1st quarter Cash sales Cash receipts from credit sales made during current month Cash receipts from credit sales made during preceding month Total cash receipts 3. Purchases budget This year Next year December January February March 1st quarter Budgeted cost of goods sold Add Desired ending inventory Total goods needed Less Expected beginning inventory Purchases 4. Cash payments budget Cash payments budget January February March 1st quarter Inventory purchases Cash payments for purchases during the current month* Cash payments for purchases during the preceding month Total cash payments for inventory purchases Other expenses Sales salaries Advertising and promotion Administrative salaries Interest on long-term loan Property taxes Sales commissions Total cash payments for other Total cash payments * 40% of the current month's purchases (schedule 3). 60% of the preceding month's purchases (schedule 3). * Long-term loan interest is paid every six months, on 31 January and 31 July. Property taxes are also paid every six months, on 28 February and 31 August. 5. Complete the first three lines of the summary cash budget. Then do the analysis of short-term financing needs in requirement 6, and then finish requirement 5. Summary cash budget January February March 1st quarter Cash receipts (from schedule 2) Less Cash payments (from schedule 4) Change in cash balance during quarter due to operations Sale of marketable securities (2 Jan.) Proceeds from bank loan (2 Jan.) Purchase of equipment Repayment of bank loan (31 March) Interest on bank loan Payment of dividends Change in cash balance for 1st quarter Cash balance, 1 January Cash balance, 31 March 6. Analysis of short-term financial needs: Projected cash balance as at 31 December in current year Less Minimum cash balance Cash available for equipment purchases Projected proceeds from sale of marketable securities Cash available Less Cost of investment in equipment Required short-term borrowing 7. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted income statement for the first quarter. (Ignore income taxes.) 8. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted statement of retained earnings for the first quarter. 9. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted balance sheet as at 31 March. (Hint: On 31 March, long-term loan interest payable is $5 000 and property taxes payable are $900.) Sunshine Electric Company is a small, rapidly growing wholesaler of consumer electrical products. The firm's main product lines are small kitchen appliances and power tools. The new marketing manager, Maria Brown, has recently completed a sales forecast. She believes that the company's sales during the first quarter of next year will increase by 10 per cent each month over the previous month's sales. Brown then expects sales to remain constant for several months. Sunshine's projected balance sheet as at 31 December this year is as follows: Cash $ 35 000 Accounts receivable Marketable securities 270 000 Inventory Buildings and equipment (net of acc. depr.) Total assets 15 000 154 000 626 000 $1 100 000 Accounts payable Long-term loan interest payable Property taxes payable Long-term loan payable (10% p.a.) Share capital Retained earnings Total liabilities and shareholders' equity $176 400 12 500 3 600 300 000 500 000 107 500 $1 100 000 Peter Jackman, the management accountant, is now preparing a monthly budget for the first quarter of next year. In the budgeting process, the following information has been accumulated: Projected sales for December this year are $400 000. Credit sales typically are 75 per cent of total sales. Sunshine's credit experience indicates that 10 per cent of the credit sales are collected during the month of sale, and the remainder are collected during the following month. Sunshine's cost of goods sold generally runs at 70 per cent of sales. Inventory is purchased on credit, and 40 per cent of each month's purchases is paid during the month of purchase. The remainder is paid during the following month. In order to have adequate inventory on hand, the firm aims to have inventory at the end of each month equal to half of the next month's projected cost of goods sold. Jackman has estimated that Sunshine's other monthly expenses will be as follows: Sales salaries Advertising and promotion Administrative salaries $18 000 19 000 21 000 Depreciation Interest on long-term loan Property taxes 25 000 2 500 900 In addition, sales commissions run at the rate of 1 per cent of sales. Sunshine's managing director, Beth Johnson, has indicated that the firm should, just after the new year begins, invest $125 000 in an automated inventory-handling system to control the movement of inventory in the firm's warehouse. To the extent possible, these equipment purchases would be financed from the firm's cash and marketable securities. Johnson believes that Sunshine needs to keep a minimum cash balance of $25 000. If necessary, the remainder of the equipment purchases would be financed using short-term credit from a local bank. The minimum period for such a loan is three months. Jackman believes short-term interest rates will be 5 per cent per year at the time of the equipment purchases. If a loan is necessary, Johnson has decided it should be paid off by the end of the first quarter if possible. Sunshine's board of directors has indicated an intention to declare and pay dividends amounting to $50 000 on the last day of each quarter. The interest on any short-term borrowing would be paid when the loan is repaid. Interest on Sunshine's long-term loan is paid semi-annually, on 31 January and 31 July, for the preceding six-month period. Property taxes are paid half-yearly on 28 February and 31 August for the preceding six-month period. Required: Prepare Sunshine's annual budget for the first quarter of next year commencing 1 January by completing the following schedules and statements: 1. Sales budget This year Next year December January February March 1st quarter Total sales Cash sales Credit sales Page 2 of 5 2. Cash receipts budget Cash receipts budget February January March 1st quarter Cash sales Cash receipts from credit sales made during current month Cash receipts from credit sales made during preceding month Total cash receipts 3. Purchases budget This year Next year December January February March 1st quarter Budgeted cost of goods sold Add Desired ending inventory Total goods needed Less Expected beginning inventory Purchases 4. Cash payments budget Cash payments budget January February March 1st quarter Inventory purchases Cash payments for purchases during the current month* Cash payments for purchases during the preceding month Total cash payments for inventory purchases Other expenses Sales salaries Advertising and promotion Administrative salaries Interest on long-term loan Property taxes Sales commissions Total cash payments for other Total cash payments * 40% of the current month's purchases (schedule 3). 60% of the preceding month's purchases (schedule 3). * Long-term loan interest is paid every six months, on 31 January and 31 July. Property taxes are also paid every six months, on 28 February and 31 August. 5. Complete the first three lines of the summary cash budget. Then do the analysis of short-term financing needs in requirement 6, and then finish requirement 5. Summary cash budget January February March 1st quarter Cash receipts (from schedule 2) Less Cash payments (from schedule 4) Change in cash balance during quarter due to operations Sale of marketable securities (2 Jan.) Proceeds from bank loan (2 Jan.) Purchase of equipment Repayment of bank loan (31 March) Interest on bank loan Payment of dividends Change in cash balance for 1st quarter Cash balance, 1 January Cash balance, 31 March 6. Analysis of short-term financial needs: Projected cash balance as at 31 December in current year Less Minimum cash balance Cash available for equipment purchases Projected proceeds from sale of marketable securities Cash available Less Cost of investment in equipment Required short-term borrowing 7. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted income statement for the first quarter. (Ignore income taxes.) 8. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted statement of retained earnings for the first quarter. 9. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted balance sheet as at 31 March. (Hint: On 31 March, long-term loan interest payable is $5 000 and property taxes payable are $900.) Sunshine Electric Company is a small, rapidly growing wholesaler of consumer electrical products. The firm's main product lines are small kitchen appliances and power tools. The new marketing manager, Maria Brown, has recently completed a sales forecast. She believes that the company's sales during the first quarter of next year will increase by 10 per cent each month over the previous month's sales. Brown then expects sales to remain constant for several months. Sunshine's projected balance sheet as at 31 December this year is as follows: Cash $ 35 000 Accounts receivable Marketable securities 270 000 Inventory Buildings and equipment (net of acc. depr.) Total assets 15 000 154 000 626 000 $1 100 000 Accounts payable Long-term loan interest payable Property taxes payable Long-term loan payable (10% p.a.) Share capital Retained earnings Total liabilities and shareholders' equity $176 400 12 500 3 600 300 000 500 000 107 500 $1 100 000 Peter Jackman, the management accountant, is now preparing a monthly budget for the first quarter of next year. In the budgeting process, the following information has been accumulated: Projected sales for December this year are $400 000. Credit sales typically are 75 per cent of total sales. Sunshine's credit experience indicates that 10 per cent of the credit sales are collected during the month of sale, and the remainder are collected during the following month. Sunshine's cost of goods sold generally runs at 70 per cent of sales. Inventory is purchased on credit, and 40 per cent of each month's purchases is paid during the month of purchase. The remainder is paid during the following month. In order to have adequate inventory on hand, the firm aims to have inventory at the end of each month equal to half of the next month's projected cost of goods sold. Jackman has estimated that Sunshine's other monthly expenses will be as follows: Sales salaries Advertising and promotion Administrative salaries $18 000 19 000 21 000 Depreciation Interest on long-term loan Property taxes 25 000 2 500 900 In addition, sales commissions run at the rate of 1 per cent of sales. Sunshine's managing director, Beth Johnson, has indicated that the firm should, just after the new year begins, invest $125 000 in an automated inventory-handling system to control the movement of inventory in the firm's warehouse. To the extent possible, these equipment purchases would be financed from the firm's cash and marketable securities. Johnson believes that Sunshine needs to keep a minimum cash balance of $25 000. If necessary, the remainder of the equipment purchases would be financed using short-term credit from a local bank. The minimum period for such a loan is three months. Jackman believes short-term interest rates will be 5 per cent per year at the time of the equipment purchases. If a loan is necessary, Johnson has decided it should be paid off by the end of the first quarter if possible. Sunshine's board of directors has indicated an intention to declare and pay dividends amounting to $50 000 on the last day of each quarter. The interest on any short-term borrowing would be paid when the loan is repaid. Interest on Sunshine's long-term loan is paid semi-annually, on 31 January and 31 July, for the preceding six-month period. Property taxes are paid half-yearly on 28 February and 31 August for the preceding six-month period. Required: Prepare Sunshine's annual budget for the first quarter of next year commencing 1 January by completing the following schedules and statements: 1. Sales budget This year Next year December January February March 1st quarter Total sales Cash sales Credit sales Page 2 of 5 2. Cash receipts budget Cash receipts budget February January March 1st quarter Cash sales Cash receipts from credit sales made during current month Cash receipts from credit sales made during preceding month Total cash receipts 3. Purchases budget This year Next year December January February March 1st quarter Budgeted cost of goods sold Add Desired ending inventory Total goods needed Less Expected beginning inventory Purchases 4. Cash payments budget Cash payments budget January February March 1st quarter Inventory purchases Cash payments for purchases during the current month* Cash payments for purchases during the preceding month Total cash payments for inventory purchases Other expenses Sales salaries Advertising and promotion Administrative salaries Interest on long-term loan Property taxes Sales commissions Total cash payments for other Total cash payments * 40% of the current month's purchases (schedule 3). 60% of the preceding month's purchases (schedule 3). * Long-term loan interest is paid every six months, on 31 January and 31 July. Property taxes are also paid every six months, on 28 February and 31 August. 5. Complete the first three lines of the summary cash budget. Then do the analysis of short-term financing needs in requirement 6, and then finish requirement 5. Summary cash budget January February March 1st quarter Cash receipts (from schedule 2) Less Cash payments (from schedule 4) Change in cash balance during quarter due to operations Sale of marketable securities (2 Jan.) Proceeds from bank loan (2 Jan.) Purchase of equipment Repayment of bank loan (31 March) Interest on bank loan Payment of dividends Change in cash balance for 1st quarter Cash balance, 1 January Cash balance, 31 March 6. Analysis of short-term financial needs: Projected cash balance as at 31 December in current year Less Minimum cash balance Cash available for equipment purchases Projected proceeds from sale of marketable securities Cash available Less Cost of investment in equipment Required short-term borrowing 7. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted income statement for the first quarter. (Ignore income taxes.) 8. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted statement of retained earnings for the first quarter. 9. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted balance sheet as at 31 March. (Hint: On 31 March, long-term loan interest payable is $5 000 and property taxes payable are $900.) Sunshine Electric Company is a small, rapidly growing wholesaler of consumer electrical products. The firm's main product lines are small kitchen appliances and power tools. The new marketing manager, Maria Brown, has recently completed a sales forecast. She believes that the company's sales during the first quarter of next year will increase by 10 per cent each month over the previous month's sales. Brown then expects sales to remain constant for several months. Sunshine's projected balance sheet as at 31 December this year is as follows: Cash $ 35 000 Accounts receivable Marketable securities 270 000 Inventory Buildings and equipment (net of acc. depr.) Total assets 15 000 154 000 626 000 $1 100 000 Accounts payable Long-term loan interest payable Property taxes payable Long-term loan payable (10% p.a.) Share capital Retained earnings Total liabilities and shareholders' equity $176 400 12 500 3 600 300 000 500 000 107 500 $1 100 000 Peter Jackman, the management accountant, is now preparing a monthly budget for the first quarter of next year. In the budgeting process, the following information has been accumulated: Projected sales for December this year are $400 000. Credit sales typically are 75 per cent of total sales. Sunshine's credit experience indicates that 10 per cent of the credit sales are collected during the month of sale, and the remainder are collected during the following month. Sunshine's cost of goods sold generally runs at 70 per cent of sales. Inventory is purchased on credit, and 40 per cent of each month's purchases is paid during the month of purchase. The remainder is paid during the following month. In order to have adequate inventory on hand, the firm aims to have inventory at the end of each month equal to half of the next month's projected cost of goods sold. Jackman has estimated that Sunshine's other monthly expenses will be as follows: Sales salaries Advertising and promotion Administrative salaries $18 000 19 000 21 000 Depreciation Interest on long-term loan Property taxes 25 000 2 500 900 In addition, sales commissions run at the rate of 1 per cent of sales. Sunshine's managing director, Beth Johnson, has indicated that the firm should, just after the new year begins, invest $125 000 in an automated inventory-handling system to control the movement of inventory in the firm's warehouse. To the extent possible, these equipment purchases would be financed from the firm's cash and marketable securities. Johnson believes that Sunshine needs to keep a minimum cash balance of $25 000. If necessary, the remainder of the equipment purchases would be financed using short-term credit from a local bank. The minimum period for such a loan is three months. Jackman believes short-term interest rates will be 5 per cent per year at the time of the equipment purchases. If a loan is necessary, Johnson has decided it should be paid off by the end of the first quarter if possible. Sunshine's board of directors has indicated an intention to declare and pay dividends amounting to $50 000 on the last day of each quarter. The interest on any short-term borrowing would be paid when the loan is repaid. Interest on Sunshine's long-term loan is paid semi-annually, on 31 January and 31 July, for the preceding six-month period. Property taxes are paid half-yearly on 28 February and 31 August for the preceding six-month period. Required: Prepare Sunshine's annual budget for the first quarter of next year commencing 1 January by completing the following schedules and statements: 1. Sales budget This year Next year December January February March 1st quarter Total sales Cash sales Credit sales Page 2 of 5 2. Cash receipts budget Cash receipts budget February January March 1st quarter Cash sales Cash receipts from credit sales made during current month Cash receipts from credit sales made during preceding month Total cash receipts 3. Purchases budget This year Next year December January February March 1st quarter Budgeted cost of goods sold Add Desired ending inventory Total goods needed Less Expected beginning inventory Purchases 4. Cash payments budget Cash payments budget January February March 1st quarter Inventory purchases Cash payments for purchases during the current month* Cash payments for purchases during the preceding month Total cash payments for inventory purchases Other expenses Sales salaries Advertising and promotion Administrative salaries Interest on long-term loan Property taxes Sales commissions Total cash payments for other Total cash payments * 40% of the current month's purchases (schedule 3). 60% of the preceding month's purchases (schedule 3). * Long-term loan interest is paid every six months, on 31 January and 31 July. Property taxes are also paid every six months, on 28 February and 31 August. 5. Complete the first three lines of the summary cash budget. Then do the analysis of short-term financing needs in requirement 6, and then finish requirement 5. Summary cash budget January February March 1st quarter Cash receipts (from schedule 2) Less Cash payments (from schedule 4) Change in cash balance during quarter due to operations Sale of marketable securities (2 Jan.) Proceeds from bank loan (2 Jan.) Purchase of equipment Repayment of bank loan (31 March) Interest on bank loan Payment of dividends Change in cash balance for 1st quarter Cash balance, 1 January Cash balance, 31 March 6. Analysis of short-term financial needs: Projected cash balance as at 31 December in current year Less Minimum cash balance Cash available for equipment purchases Projected proceeds from sale of marketable securities Cash available Less Cost of investment in equipment Required short-term borrowing 7. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted income statement for the first quarter. (Ignore income taxes.) 8. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted statement of retained earnings for the first quarter. 9. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted balance sheet as at 31 March. (Hint: On 31 March, long-term loan interest payable is $5 000 and property taxes payable are $900.) Sunshine Electric Company is a small, rapidly growing wholesaler of consumer electrical products. The firm's main product lines are small kitchen appliances and power tools. The new marketing manager, Maria Brown, has recently completed a sales forecast. She believes that the company's sales during the first quarter of next year will increase by 10 per cent each month over the previous month's sales. Brown then expects sales to remain constant for several months. Sunshine's projected balance sheet as at 31 December this year is as follows: Cash $ 35 000 Accounts receivable Marketable securities 270 000 Inventory Buildings and equipment (net of acc. depr.) Total assets 15 000 154 000 626 000 $1 100 000 Accounts payable Long-term loan interest payable Property taxes payable Long-term loan payable (10% p.a.) Share capital Retained earnings Total liabilities and shareholders' equity $176 400 12 500 3 600 300 000 500 000 107 500 $1 100 000 Peter Jackman, the management accountant, is now preparing a monthly budget for the first quarter of next year. In the budgeting process, the following information has been accumulated: Projected sales for December this year are $400 000. Credit sales typically are 75 per cent of total sales. Sunshine's credit experience indicates that 10 per cent of the credit sales are collected during the month of sale, and the remainder are collected during the following month. Sunshine's cost of goods sold generally runs at 70 per cent of sales. Inventory is purchased on credit, and 40 per cent of each month's purchases is paid during the month of purchase. The remainder is paid during the following month. In order to have adequate inventory on hand, the firm aims to have inventory at the end of each month equal to half of the next month's projected cost of goods sold. Jackman has estimated that Sunshine's other monthly expenses will be as follows: Sales salaries Advertising and promotion Administrative salaries $18 000 19 000 21 000 Depreciation Interest on long-term loan Property taxes 25 000 2 500 900 In addition, sales commissions run at the rate of 1 per cent of sales. Sunshine's managing director, Beth Johnson, has indicated that the firm should, just after the new year begins, invest $125 000 in an automated inventory-handling system to control the movement of inventory in the firm's warehouse. To the extent possible, these equipment purchases would be financed from the firm's cash and marketable securities. Johnson believes that Sunshine needs to keep a minimum cash balance of $25 000. If necessary, the remainder of the equipment purchases would be financed using short-term credit from a local bank. The minimum period for such a loan is three months. Jackman believes short-term interest rates will be 5 per cent per year at the time of the equipment purchases. If a loan is necessary, Johnson has decided it should be paid off by the end of the first quarter if possible. Sunshine's board of directors has indicated an intention to declare and pay dividends amounting to $50 000 on the last day of each quarter. The interest on any short-term borrowing would be paid when the loan is repaid. Interest on Sunshine's long-term loan is paid semi-annually, on 31 January and 31 July, for the preceding six-month period. Property taxes are paid half-yearly on 28 February and 31 August for the preceding six-month period. Required: Prepare Sunshine's annual budget for the first quarter of next year commencing 1 January by completing the following schedules and statements: 1. Sales budget This year Next year December January February March 1st quarter Total sales Cash sales Credit sales Page 2 of 5 2. Cash receipts budget Cash receipts budget February January March 1st quarter Cash sales Cash receipts from credit sales made during current month Cash receipts from credit sales made during preceding month Total cash receipts 3. Purchases budget This year Next year December January February March 1st quarter Budgeted cost of goods sold Add Desired ending inventory Total goods needed Less Expected beginning inventory Purchases 4. Cash payments budget Cash payments budget January February March 1st quarter Inventory purchases Cash payments for purchases during the current month* Cash payments for purchases during the preceding month Total cash payments for inventory purchases Other expenses Sales salaries Advertising and promotion Administrative salaries Interest on long-term loan Property taxes Sales commissions Total cash payments for other Total cash payments * 40% of the current month's purchases (schedule 3). 60% of the preceding month's purchases (schedule 3). * Long-term loan interest is paid every six months, on 31 January and 31 July. Property taxes are also paid every six months, on 28 February and 31 August. 5. Complete the first three lines of the summary cash budget. Then do the analysis of short-term financing needs in requirement 6, and then finish requirement 5. Summary cash budget January February March 1st quarter Cash receipts (from schedule 2) Less Cash payments (from schedule 4) Change in cash balance during quarter due to operations Sale of marketable securities (2 Jan.) Proceeds from bank loan (2 Jan.) Purchase of equipment Repayment of bank loan (31 March) Interest on bank loan Payment of dividends Change in cash balance for 1st quarter Cash balance, 1 January Cash balance, 31 March 6. Analysis of short-term financial needs: Projected cash balance as at 31 December in current year Less Minimum cash balance Cash available for equipment purchases Projected proceeds from sale of marketable securities Cash available Less Cost of investment in equipment Required short-term borrowing 7. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted income statement for the first quarter. (Ignore income taxes.) 8. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted statement of retained earnings for the first quarter. 9. Prepare Sunshine's budgeted balance sheet as at 31 March. (Hint: On 31 March, long-term loan interest payable is $5 000 and property taxes payable are $900.)
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.49 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
ANALYSIS OF SHORTTERM NEEDS 35000 25000 Projected cash balance as at 31 December Less Minimum cash ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


