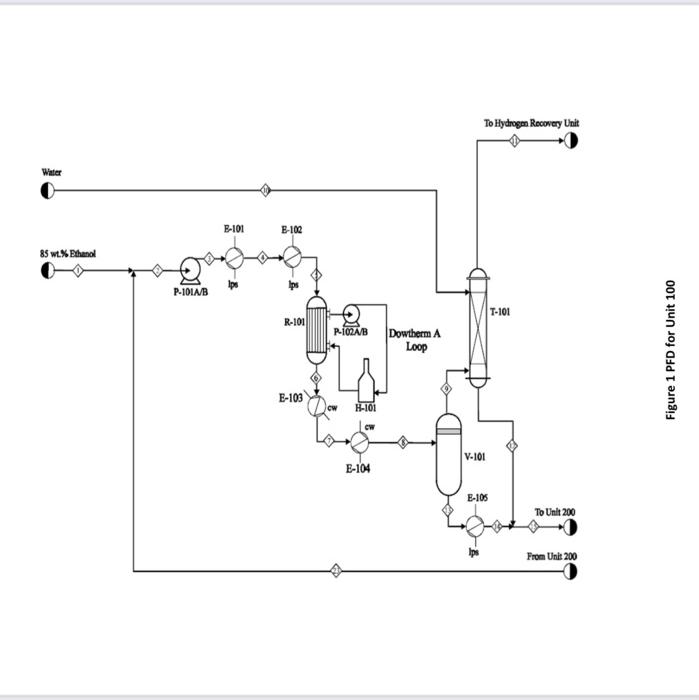
Acetaldehyde is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3CHO. It is primarily used as an intermediate in the manufacture of a range of chemicals, perfumes, aniline dyes, plastics and synthetic rubber and in some fuel compounds. Process flow diagram A PFD of the process is shown in Figures 1 and 2. Chemical reactions The following four reactions occur in the reactor: CH3CH2OHCH3CHO+H2EthanolAcetaldehyde+Hydrogen(mainreaction)(1)H=+82.5kJ/mol 2CH3CH2OHEthanol2CH3CH2OHEthanolCH3COOC2H5+2H2EthylAcetate+HydrogenCH3(CH2)3OH+H2OButanol+Water CH3CH2OH+H2OCH3COOH+2H2Ethanol+WaterAceticAcid+Hydrogen Generally, the ethanol dehydration into ethylene is an endothermic reaction (thermodynamically and kinetically controlled). The main side reaction of ethanol dehydration into diethyl ether is a slightly exothermic reaction. With the use of Figure 1 and 2 and stream summary Tables. 1. Draw a schematic BFD for the process (you need to display directions and the main inlet, outlet and recycle component). 2. Suggest two possible alternatives flowsheet for heat integration network (based on the schematic BFD). 3. Determine (i) The single -pass conversion and overall conversion of ethanol. (ii) The selectivity of ethanol for ethyl acete. (iii) The yield for butanol 4. Estimate the mass flow rate of the Ips for E-102. 5. Estimate the BHP of P101A/B. 6. Justify the use of V101 and T101. 7. Justify the operational conditions (top pressure at 650.18kPa and 84.7C ) for T203. 8. Plot a simple control loop to control: a. The temperature of the feed going into 101. b. The pressure of stream No.3. 9. Evaluate the profit margin for the process (use the stoichiometry of the reaction as your basis). *Year 2008 (Table 8.3 text book) Equipment Summary: E-101 Reactor Preheater, E-102 Reactor Preheater, E-103 Heat Exchanger, E-104 Heat Exchanger, E-105 Heat Exchanger, H-101 Fired Heater, P-101A/B Feed Pump, P-102A-B Dowtherm Figure 2 PFD for Unit 200 Equipment Summary: E-201 Condenser, E-202 Reboiler, E-203 Condenser, E-204 Reboiler, E-205 Condenser, E-206 Reboiler, E-207 Condenser, E-208 Reboiler, P-201A/B Reflux Pump, P-202A/B Reflux Pump, P-203A/B Reflux Pump, P-204A/B Reflux Pump, T-101 Absorber, T-201 Distillation Column, T202 Distillation Column, T-203 Distillation Column, T-204 Distillation Column, V-201 Reflux Vessel, V202 Reflux Vessel, V-203 Reflux Vessel, V-204 Reflux Vessel Table 1 Stream Summary Tables \begin{tabular}{|l|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline Stream & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 & 6 & 7 & 8 \\ \hline Temp. (C) & 42 & 74.5 & 74.5 & 195 & 330 & 330 & 197.5 & 69.5 \\ \hline Pressure (kPa) & 101.353 & 101.353 & 689.48 & 663.28 & 663.28 & 663.28 & 662.59 & 655.69 \\ \hline Vapor fraction & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 1.0 & 1.0 & 1.0 & 1.0 & 0.4 \\ \hline Totalflow(kmol/hr) & 471.2 & 680.4 & 680.4 & 680.4 & 680.4 & 942.5 & 942.5 & 942.5 \\ \hline Component flow rates (kmol/hr) & & & & & & & \\ \hline Acetaldehyde & 0.0 & 1.1 & 1.1 & 1.1 & 1.1 & 248.2 & 248.2 & 248.2 \\ \hline Acetic acid & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 5.36 & 5.36 & 5.36 \\ \hline Butanol & 0.0 & 1.0 & 1.0 & 1.0 & 1.0 & 7.17 & 7.17 & 7.17 \\ \hline Water & 152.9 & 211 & 211 & 211 & 211 & 211.7 & 211.7 & 211.7 \\ \hline Ethanol & 318.3 & 467.1 & 467.1 & 467.1 & 467.1 & 183.1 & 183.1 & 183.1 \\ \hline Ethyl acetate & 0.0 & 0.2 & 0.2 & 0.2 & 0.2 & 9.85 & 9.85 & 9.85 \\ \hline Hydrogen & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 277.12 & 277.12 & 277.12 \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|l|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline Stream & 9 & 10 & 11 & 12 & 13 & 14 & 15 & 16 \\ \hline Temp. (C) & 42 & 67 & 67 & 67 & 42 & 98.5 & 78.8 & 87.8 \\ \hline Pressure (kPa) & 650.18 & 650.18 & 650.18 & 650.18 & 650.18 & 650.18 & 650.18 & 650.18 \\ \hline Vapor fraction & 1.0 & 0.0 & 1.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 \\ \hline Totalflow(kmol/hr) & 310.35 & 1634.45 & 289.82 & 1655.06 & 632.13 & 632.13 & 2287.14 & 274.02 \\ \hline Component flow rates (kmol/hr) & & & & & & & \\ \hline Acetaldehyde & 28.78 & 0.0 & 0.41 & 28.38 & 219.4 & 219.4 & 247.75 & 246.6 \\ \hline Acetic acid & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 5.31 & 5.31 & 5.36 & 0 \\ \hline Butanol & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 7.17 & 7.17 & 7.17 & 0.045 \\ \hline Water & 2.59 & 1634.45 & 12.2 & 1624.82 & 209.11 & 209.11 & 1834 & 25.24 \\ \hline Ethanol & 1.45 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 1.45 & 181.7 & 181.7 & 183.1 & 1.135 \\ \hline Ethyl acetate & 0.41 & 0.0 & 0.09 & 0.32 & 9.44 & 9.44 & 9.76 & 1.0 \\ \hline Hydrogen & 277.12 & 0.0 & 277.12 & 0.09 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 \\ \hline \end{tabular}