
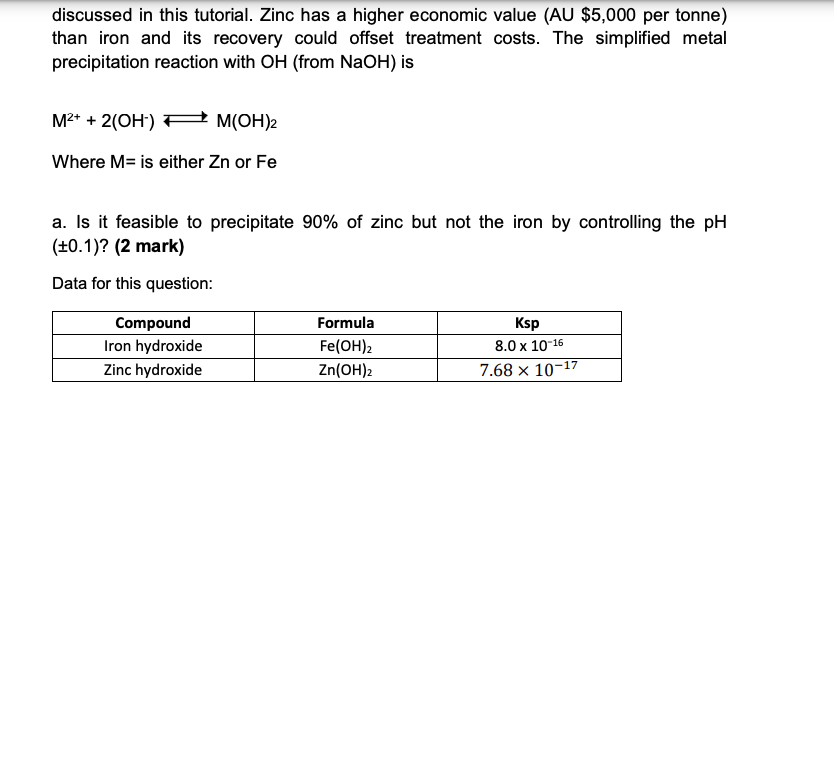
Acid mine drainage (AMD) is a worldwide problem, leading to ecological destruction in watersheds and the contamination of human water sources. AMD results from the oxidation of pyrite leading to mine drainage with acidic pH, high sulfate concentration. The stoichiometry of the pyrite oxidation reaction is FeS2+3.75O2+3.5H2O2SO4=+4H++Fe(OH)3 There are an estimated 15,000 legacy mine sites in Queensland and the following information is from one of these sites producing severe AMD. The AMD is produced at a flow rate of 40m3/h and has a sulfate concentration of 3360mg/L. 1. Determine the change in oxidation numbers of the elements in the pyrite oxidation reaction and the pH of the AMD. (1 mark) 2. The AMD has to be neutralised to meet discharge pH limits (effluent with a pH between 5 and 8.5 is generally acceptable for use in irrigation). For this, the addition of alkaline reagents such as caustic soda (NaOH) is a common practice (90% of treatment plants use this method). The neutralisation reaction is 2H++SO4=+2NaOHNa2SO4+2H2O a. Estimate the amount of caustic soda required in kg per year to neutralize the AMD (use the values that you need from question 1 to solve this problem). (1 mark) b. For the Australian mining industry, the additional cost of managing AMD sludge at operating mine sites is estimated to be about $60 million per year. Estimate the amount of sludge generated in kg per year as Na2SO4 and the overall treatment costs considering the disposal cost of sludge (AU $100/ tonne) and the cost of the caustic soda (AU $150/ tonne) needed for the treatment. Assume a water content in the sludge of 40%, which must be considered in both the sludge generated per year and in the treatment costs. (1 mark) 3. AMD usually contains dissolved metals that are toxic and must be removed but also some that have economic value. When AMD is treated through chemical precipitation as in this example, the metals in the ionic form are converted to an insoluble form by the chemical reaction between the soluble metal compounds and the precipitating reagent. Zinc and Iron both at a concentration of 0.10M are present in the AMD discussed in this tutorial. Zinc has a higher economic value (AU $5,000 per tonne) than iron and its recovery could offset treatment costs. The simplified metal precipitation reaction with OH (from NaOH ) is M2++2(OH)M(OH)2 Where M= is either Zn or Fe a. Is it feasible to precipitate 90% of zinc but not the iron by controlling the pH (0.1)?(2 mark) Data for this








