Question: Activity 1: Graph and interpret motion data of :1 moving object One way to analyze the motion of an object is to graph the position
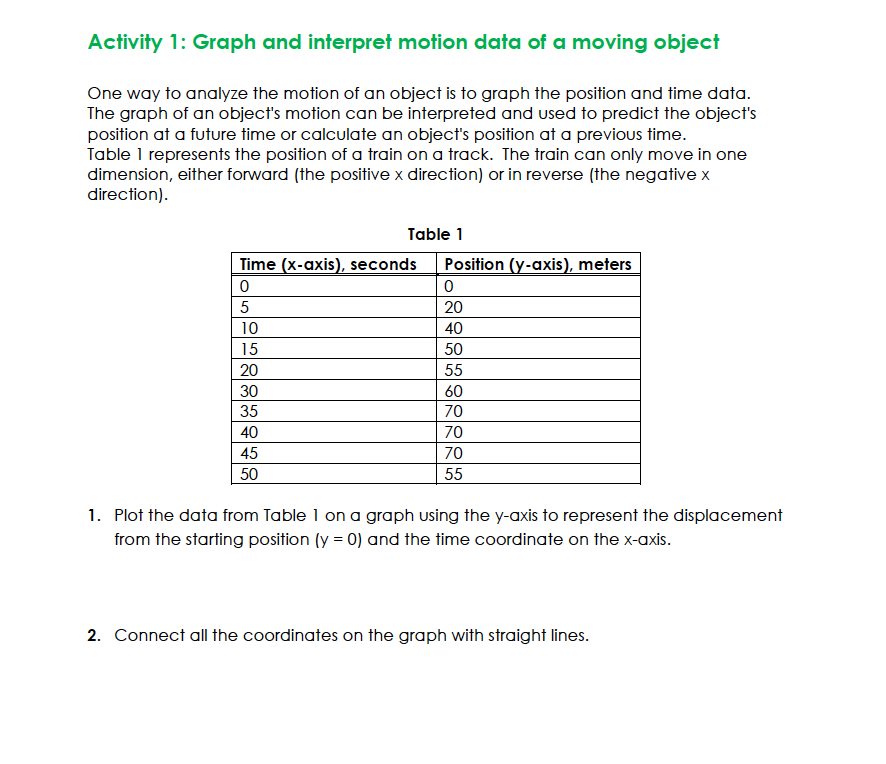

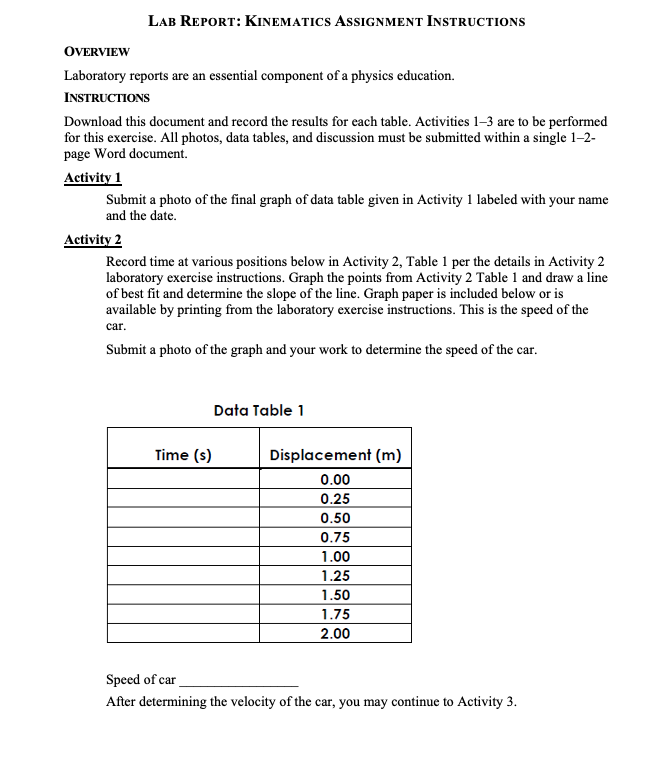
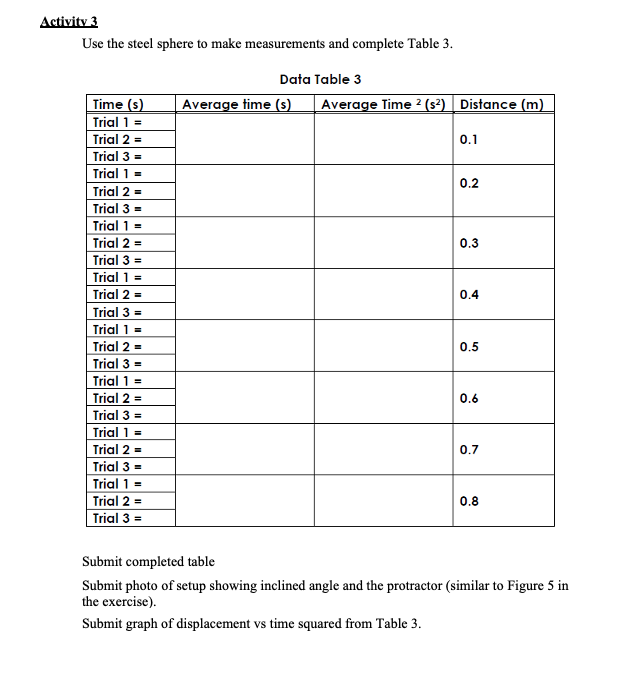
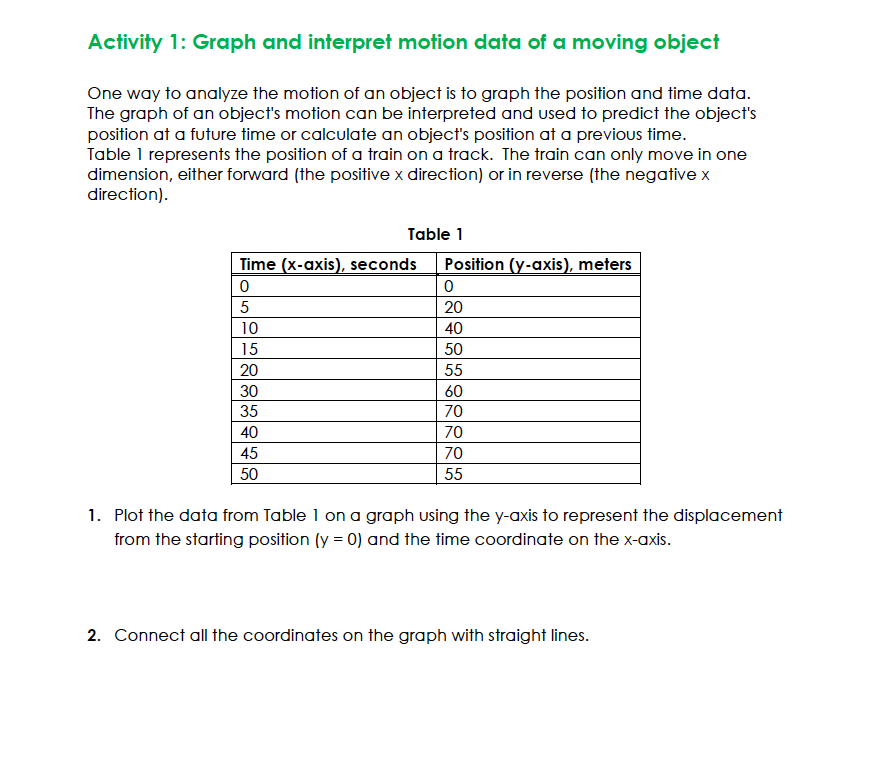

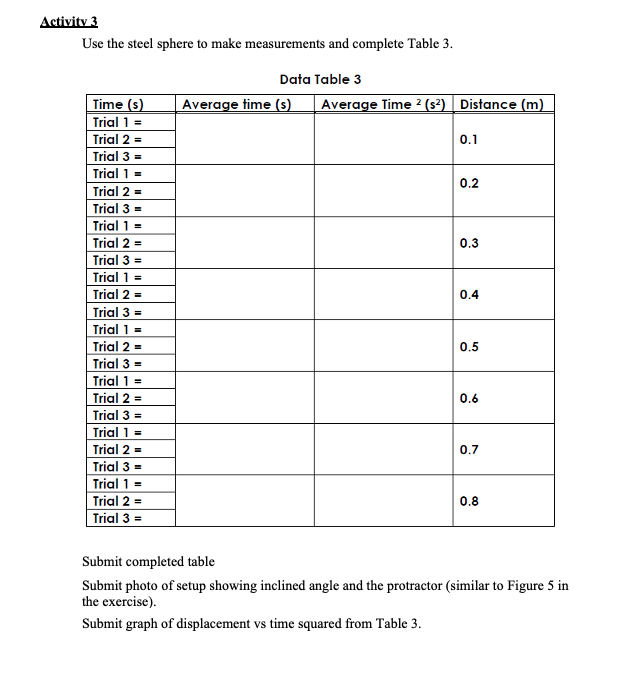
Activity 1: Graph and interpret motion data of :1 moving object One way to analyze the motion of an object is to graph the position and time data. The graph of an object's motion can be interpreted and used to predict the object's position at a future time or calculate an object's position at a previous time. Table l represents the position of a train on a track. The train can only move in one dimension, either forward {the positive x direction} or in reverse {the negative x direction}. Table 1 Time x-uxis , seconds Position -uxis , meters [2- 0 5 20 it) 40 l5 50 20 55 30 60 35 70 40 70 45 70 50 55 1. Plot the data from Table l on a graph using the yaxis to represent the displacement from the starting position [y = O} and the time coordinate on the xaxis. 2. Connect all the coordinates on the graph with straight lines. Activity 2: Calculate the velocity of o moving object In this activity you will graph the motion of an object moving with a constant velocity. The speed of the object can be calculated by allowing the Constant Velocity Vehicle to travel a given distance and measuring the time that it took to move this distance. As seen in Activity 1, this measurement will only provide the average speed. In this activity, you will collect time data at several travel distances, plot these data, and analyze the graph 1. Find and clear a straight path approximately two meters long. 2. Install the batteries and test the vehicle. Note: The vehicle should be able to travel two meters in a generally straight path. If the vehicle veers signicantly to one side, you may need to allow the vehicle to travel next to a wall. The friction will affect the vehicle's speed, but the effect will be uniform for each trial. 3. Use your tape measure or ruler to measure a track two meters long. The track should be level and smooth with no obstructions. Make sure the surface of the track provides enough traction for the wheels to turn without slipping. Place masking tape across the track at 25 cm intervals. 4. Set the car on the floor approximately 5 cm behind the start point of the track. Note: Starting the car a short distance before the start point allows the vehicle to reach its top speed before the time starts and prevents the short period of acceleration from affecting the data. Set the stopwatch to the timing mode and reset the time to zero. Start the car and allow the car to move along the track. Start the stopwatch when the front edge of the car crosses the start point. Stop the stopwatch when the front edge of the car crosses the first 25 cm point. 99F?!\" Recover the car, and switch the power off. Record the time and vehicle position on the data table. 10. Repeat steps #59 for each 25 cm interval marked. Each trial will have a distance that is 25 cm longer than the previous trial, and the stopwatch will record the time forthe car to travel the individual trial distance. 11. Record the data in Data Table I. LAB REPORT: KINEMATICS ASSIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS OVERVIEW Laboratory reports are an essential component of a physics education. INSTRUCTIONS Download this document and record the results for each table. Activities 1-3 are to be performed for this exercise. All photos, data tables, and discussion must be submitted within a single 1-2- page Word document. Activity 1 Submit a photo of the final graph of data table given in Activity 1 labeled with your name and the date. Activity 2 Record time at various positions below in Activity 2, Table 1 per the details in Activity 2 laboratory exercise instructions. Graph the points from Activity 2 Table 1 and draw a line of best fit and determine the slope of the line. Graph paper is included below or is available by printing from the laboratory exercise instructions. This is the speed of the car. Submit a photo of the graph and your work to determine the speed of the car. Data Table 1 Time (s) Displacement (m) 0.00 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 1.25 1.50 1.75 2.00 Speed of car After determining the velocity of the car, you may continue to Activity 3.MW Use the steel sphere to make measurements and complete Table 3. Data Table 3 Time is] Average time [3) Average Time 2 (s?) . Distance [m] 0.] 0.2 Submit completed table Submit photo of setup showing inclined angle and the protractor (similar to Figure 5 in the exercise}. Submit graph of displacement vs time squared from Table 3.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


