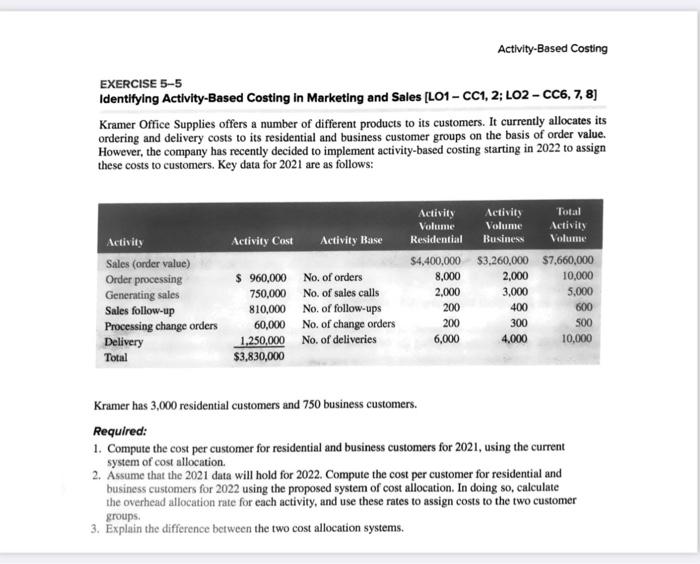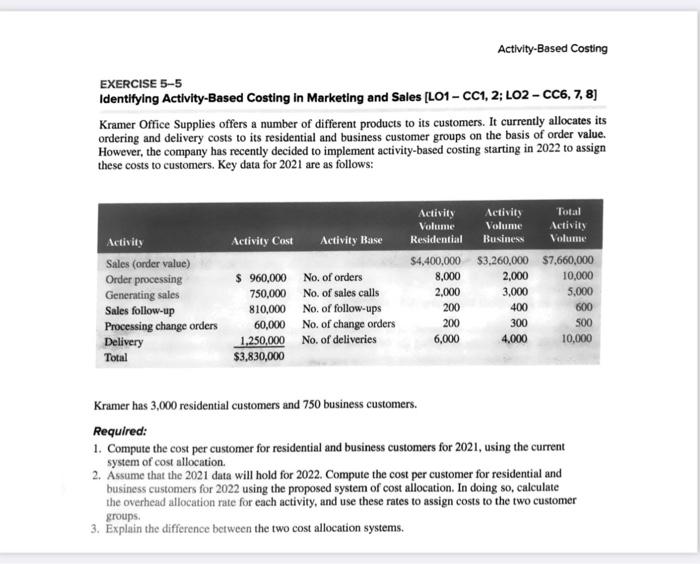
Activity-Based Costing EXERCISE 5-5 Identifying Activity-Based Costing in Marketing and Sales (L01 - CC1, 2; L02 - CC6, 7, 8) Kramer Office Supplies offers a number of different products to its customers. It currently allocates its ordering and delivery costs to its residential and business customer groups on the basis of order value. However, the company has recently decided to implement activity-based costing starting in 2022 to assign these costs to customers. Key data for 2021 are as follows: Activity Cost Activity Base Sales (order value) Order processing Generating sales Sales follow-up Processing change orders Delivery Total $ 960,000 750,000 810,000 60,000 1,250,000 $3,830,000 No. of orders No. of sales calls No. of follow-ups No. of change orders No. of deliveries Activity Activity Total Volume Volume Activity Residential Business Volume $4,400,000 $3,260,000 $7.660,000 8,000 2,000 10,000 2.000 3,000 5,000 200 400 600 200 300 6,000 4,000 10,000 500 Kramer has 3,000 residential customers and 750 business customers. Required: 1. Compute the cost per customer for residential and business customers for 2021, using the current system of cost allocation 2. Assume that the 2021 data will hold for 2022. Compute the cost per customer for residential and business customers for 2022 using the proposed system of cost allocation. In doing so, calculate the overhead allocation rate for each activity, and use these rates to assign costs to the two customer groups. 3. Explain the difference between the two cost allocation systems. Activity-Based Costing EXERCISE 5-5 Identifying Activity-Based Costing in Marketing and Sales (L01 - CC1, 2; L02 - CC6, 7, 8) Kramer Office Supplies offers a number of different products to its customers. It currently allocates its ordering and delivery costs to its residential and business customer groups on the basis of order value. However, the company has recently decided to implement activity-based costing starting in 2022 to assign these costs to customers. Key data for 2021 are as follows: Activity Cost Activity Base Sales (order value) Order processing Generating sales Sales follow-up Processing change orders Delivery Total $ 960,000 750,000 810,000 60,000 1,250,000 $3,830,000 No. of orders No. of sales calls No. of follow-ups No. of change orders No. of deliveries Activity Activity Total Volume Volume Activity Residential Business Volume $4,400,000 $3,260,000 $7.660,000 8,000 2,000 10,000 2.000 3,000 5,000 200 400 600 200 300 6,000 4,000 10,000 500 Kramer has 3,000 residential customers and 750 business customers. Required: 1. Compute the cost per customer for residential and business customers for 2021, using the current system of cost allocation 2. Assume that the 2021 data will hold for 2022. Compute the cost per customer for residential and business customers for 2022 using the proposed system of cost allocation. In doing so, calculate the overhead allocation rate for each activity, and use these rates to assign costs to the two customer groups. 3. Explain the difference between the two cost allocation systems