Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
AERM 1344 Aircraft Reciprocating Engines Lab Project 1 Objective: a. Reciprocating engines Name The student will inspect reciprocating engines: 1. Demonstrate an understanding of


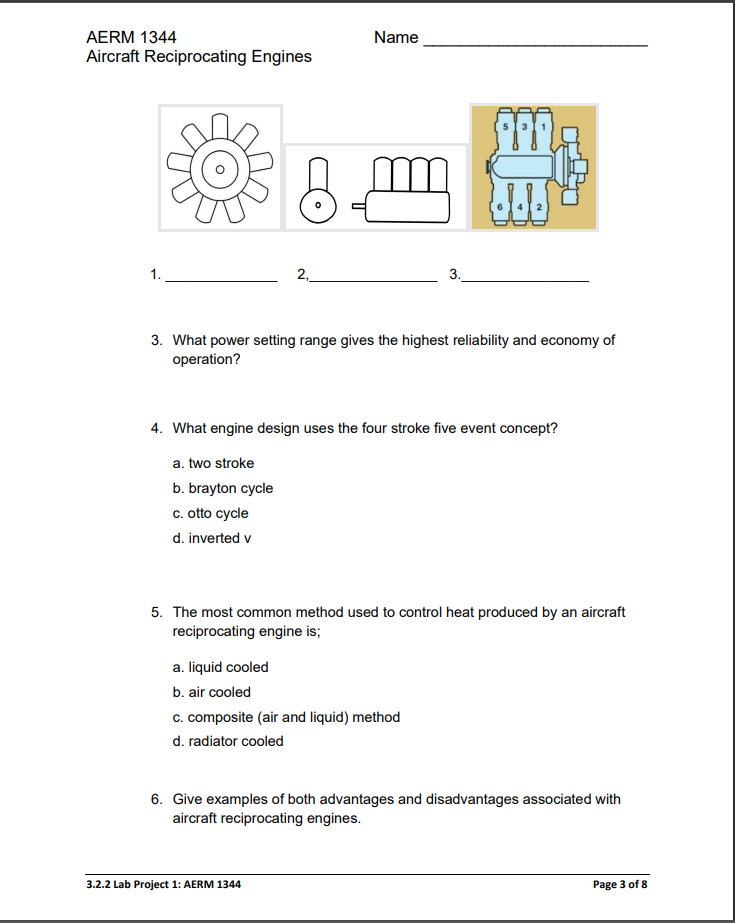





AERM 1344 Aircraft Reciprocating Engines Lab Project 1 Objective: a. Reciprocating engines Name The student will inspect reciprocating engines: 1. Demonstrate an understanding of reciprocating engine theory, engine types / classification, advantages and disadvantages and will be able to: a. Explain reciprocating engine (internal principles. b. Explain horsepower as it relates to aircraft reciprocating engines, including takeoff power, rated power, and maximum power. c. Explain mechanical and thermal efficiency. d. Explain weight to power ratio. e. Discuss reliability and economy of operation. f. List engines by types/classification using cylinder arrangement, cubic inch displacement, number of strokes per cycle and cooling. g. Give examples of both advantages and disadvantages associated with aircraft reciprocating engines. 2. Demonstrate knowledge of reciprocating engine component parts and reciprocating engine systems and will be able to: a. Identify and visually inspect aircraft reciprocating engine components as provided. b. Explain how each engine system supports engine operations. c. Identify component parts of engine systems. d. Identify nose and power cases of aircraft reciprocating engines. e. Describe loads placed on nose and power cases of aircraft reciprocating engines. f. Identify (from a group of assemblies provided) a crankshaft and rod assembly that incorporates a dynamic dampener. g. Explain the purpose of a dynamic dampener. h. Identify an articulating rod in a master rod assembly. i. Describe the functions of each principal part of a crankshaft assembly. 3. Demonstrate an understanding of volumetric efficiency and will be able to a. Describe factors affecting volumetric efficiency. b. Describe the purpose of valve overlap. c. Explain how valve overlap affects engine performance. d. Interpret a manufacturer's instructions for timing the valves of an engine. 4. Demonstrate the ability to locate and use engine firing order information located in engine maintenance manuals or on engine data plates and will be able to a. Explain the principles that determine the firing order for a given engine. b. Rotate the engine crankshaft; observing the valve rocker arm action and identify each cylinder in the order in which it will fire. ACS Element -S- Skills The student demonstrates the ability to: AM.III.A.S4 Identify the parts of a cylinder. AM.III.A.S5 Identify the parts of a crankshaft. 3.2.2 Lab Project 1: AERM 1344 Page 1 of 8 AERM 1344 Aircraft Reciprocating Engines Name AM.III.A.S8 Locate top dead-center position of number one cylinder Required: Appropriate FAA Advisory Circulars Assigned aircraft or training aid Aircraft or component Manufacturer's Service Information Hand tools prescribed by TCC Tool List Inspection aids as applicable Procedure: The student will inspect reciprocating engines: I Theory Explain reciprocating engine (internal combustion) principles; 1. Explain the terms: a. takeoff power: b. cruise power: c. maximum rated power; d. thermal efficiency e. specific fuel consumption f. write the formula used to calculate horsepower: Inst Intl: 2. Identify the following engine configurations. Which engine configuration has the highest power to weight ratio? 3.2.2 Lab Project 1: AERM 1344 Page 2 of 8 AERM 1344 Aircraft Reciprocating Engines 1. 2, Name 3. OPP 3. What power setting range gives the highest reliability and economy of operation? 4. What engine design uses the four stroke five event concept? a. two stroke b. brayton cycle c. otto cycle d. inverted v 5. The most common method used to control heat produced by an aircraft reciprocating engine is; a. liquid cooled b. air cooled c. composite (air and liquid) method d. radiator cooled 6. Give examples of both advantages and disadvantages associated with aircraft reciprocating engines. 3.2.2 Lab Project 1: AERM 1344 Page 3 of 8 AERM 1344 Aircraft Reciprocating Engines Engine Type Air Cooled Liquid Cooled Rotary Radial Static Radial In-Line Horizontally Opposed Name Advantage 7. Valve overlap occurs at the end of the beginning of the stroke. Disadvantage 8. How does valve overlap affect engine performance? stroke, and the 9. Describe the procedures for setting intake and exhaust valves and list the firing order for the following engines: a. Lycoming O-235 b. Lycoming O-320 10. Using the A65 cutaway: rotate the engine crankshaft; observing the valve rocker arm action, and identify each cylinder in the order in which it will fire. 3.2.2 Lab Project 1: AERM 1344 Page 4 of 8 AERM 1344 Aircraft Reciprocating Engines Name 11. Draw the cylinder configuration of an upright or inverted inline engine. 12. Draw the cylinder configuration of an upright or inverted "V" engine. 13. Draw the cylinder configuration of a radial Engine. 14. Draw the cylinder configuration of a horizontally opposed engine. 15. List the two common types of cylinder treatment or material. 16. List advantages and disadvantages of the common types of cylinder treatment or material. 17. Inspect a piston and draw 4 types of pistons and label the parts. 3.2.2 Lab Project 1: AERM 1344 Page 5 of 8 AERM 1344 Aircraft Reciprocating Engines Name 18. Draw 3 types of rings and identify by function. 19. Draw 3 ring shapes and identify by cross section. 20. List 3 ring end gap configurations. 21. List 2 possible ring materials. 22. Why are most aircraft compression rings wedge shaped? 23. List and describe factors affecting volumetric efficiency. III Task Inst Intl: 24. Inspect nose and power cases of aircraft reciprocating engines. How is the thrust load transmitted from the propeller to the airframe? 3.2.2 Lab Project 1: AERM 1344 Page 6 of 8 AERM 1344 Name Aircraft Reciprocating Engines 25. Inspect, draw, and label a crankshaft and rod assembly that incorporates a dynamic dampener. Explain the purpose of a dynamic dampener. 26. Inspect an articulating rod in a master rod assembly; draw and label components. 27. Inspect a cylinder assembly, draw and label the parts. II Technical Data Reference Inst Intl: 3.2.2 Lab Project 1: AERM 1344 Page 7 of 8 AERM 1344 Aircraft Reciprocating Engines Name 28. Identify by title, page, and paragraph the reference for setting intake and exhaust valves of a Lycoming O-235. IV. Maintenance Record Entry Inst Intl: 29. Make a maintenance record entry for setting the valves of a Lycoming O- 235. 3.2.2 Lab Project 1: AERM 1344 Page 8 of 8
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


