Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
AERO3630 Aerodynamics (Degree) HO Table 1: Atmospheric Data Potential Flow Experiment T 22 C T 295.15 K Patm 103200 Pa Patm 1.278 kg m-3
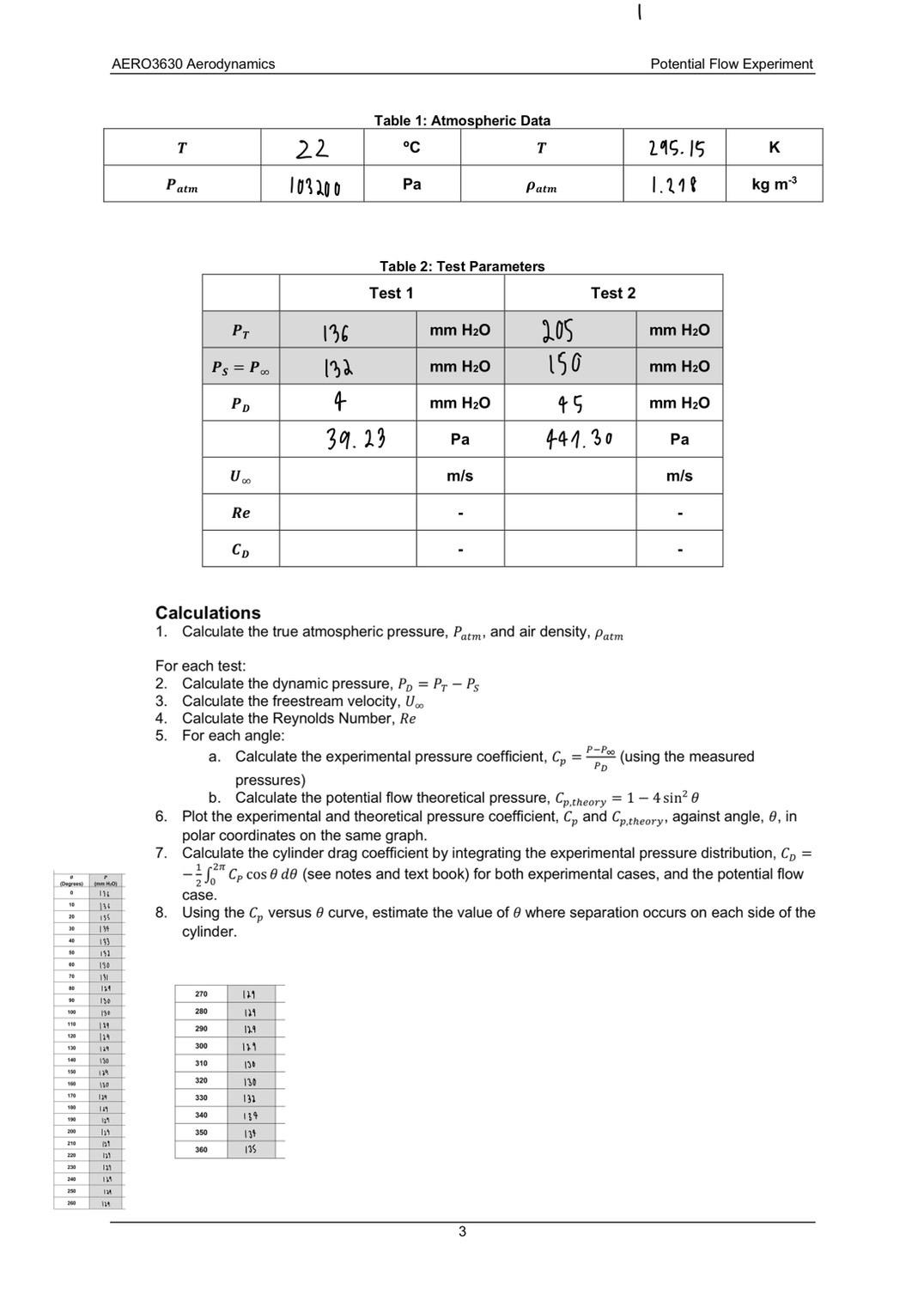
AERO3630 Aerodynamics (Degree) HO Table 1: Atmospheric Data Potential Flow Experiment T 22 C T 295.15 K Patm 103200 Pa Patm 1.278 kg m-3 Table 2: Test Parameters Test 1 Test 2 PT 136 mm HO 205 mm HO Ps = Poo 132 mm HO 150 mm HO Pp 4 mm H2O 45 mm HO 39.23 Pa 441.30 Pa U 00 m/s m/s Re Calculations 1. Calculate the true atmospheric pressure, Patm, and air density, Patm For each test: 2. Calculate the dynamic pressure, PD = PT - Ps 3. Calculate the freestream velocity, U.. 4. Calculate the Reynolds Number, Re 5. For each angle: 6. a. P-Poo PD Calculate the experimental pressure coefficient, C = (using the measured pressures) b. Calculate the potential flow theoretical pressure, Cp,theory = 1-4 sin 0 Plot the experimental and theoretical pressure coefficient, C, and Cp.theory, against angle, e, in polar coordinates on the same graph. 7. Calculate the cylinder drag coefficient by integrating the experimental pressure distribution, C = - Cp cos e do (see notes and text book) for both experimental cases, and the potential flow case. 8. Using the Cp versus & curve, estimate the value of 0 where separation occurs on each side of the cylinder. 10 136 20 155 134 40 193 so 152 00 130 20 131 80 134 270 129 90 130 100 130 280 129 110 139 290 12.9 120 129 130 300 129 129 140 130 310 130 150 320 100 110 130 170 129 330 132 100 19 340 190 134 200 350 134 210 et 360 135 220 121 230 121 240 135 250 124 200 13 3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


