After you have completed P6-2A, consider the following additional question.
Assume that a number of units sold changed to 10,000 units. How does this change impact ending inventory and cost of goods sold under FIFO, LIFO, and Average cost?
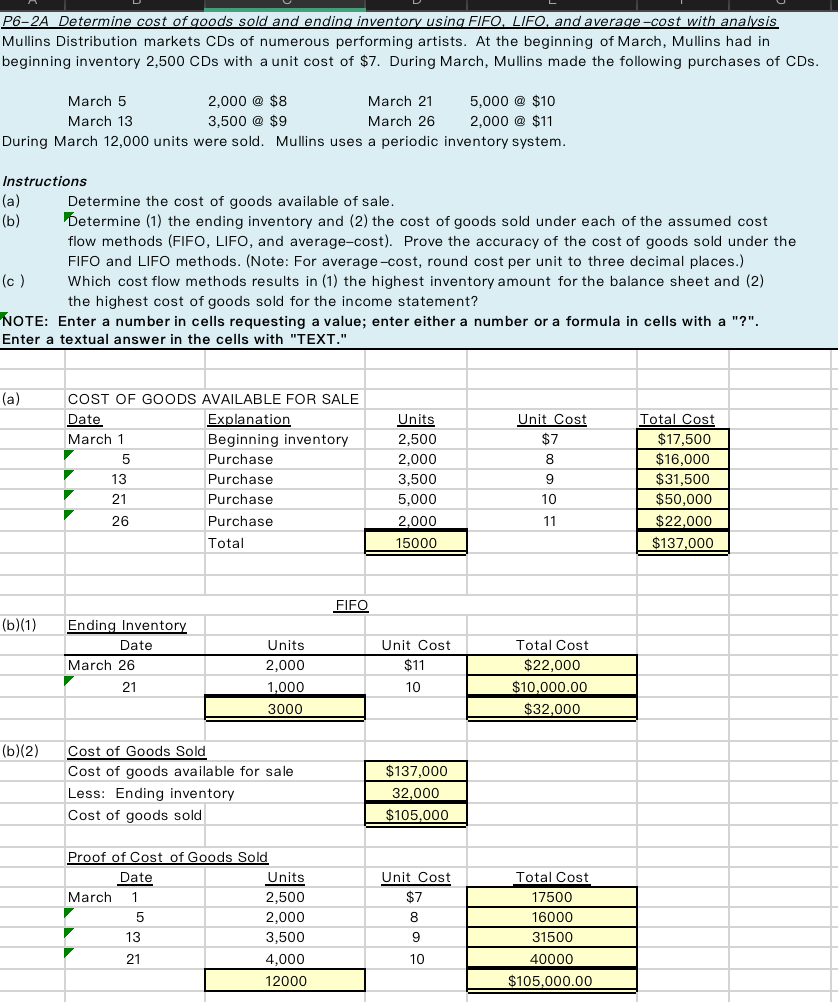
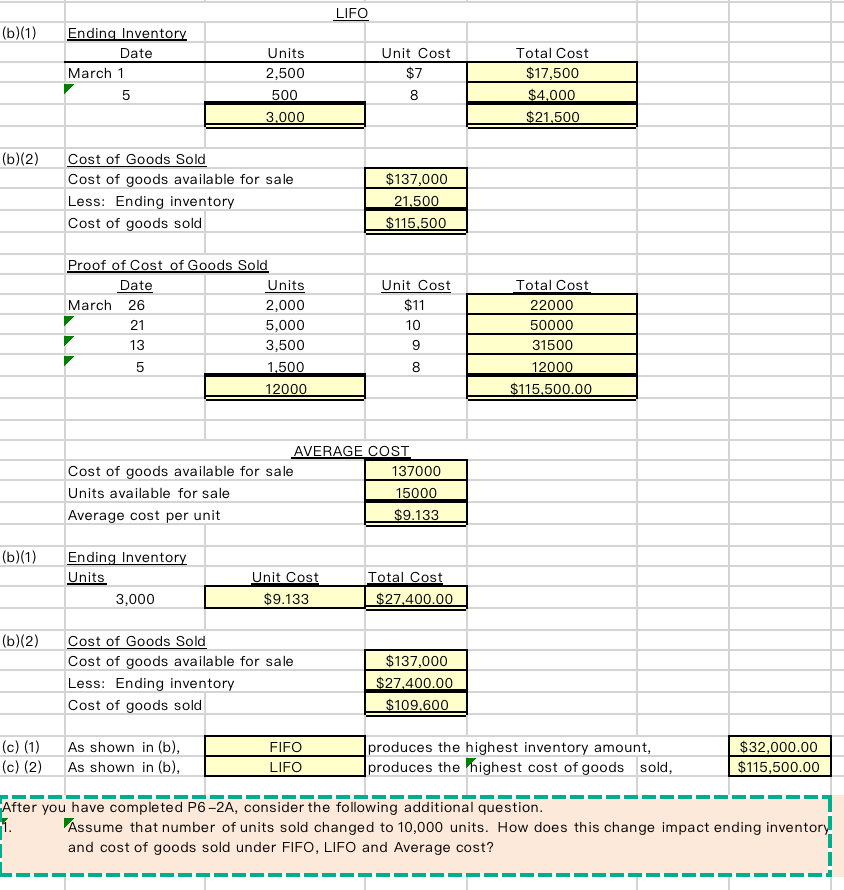
P6-2A Determine cost of goods sold and ending inventory using FIFO, LIFO, and average-cost with analysis Mullins Distribution markets CDs of numerous performing artists. At the beginning of March, Mullins had in beginning inventory 2,500 CDs with a unit cost of $7. During March, Mullins made the following purchases of CDs. March 5 2,000 @ $8 March 21 5,000 @ $10 March 13 3,500 @ $9 March 26 2,000 @ $11 During March 12,000 units were sold. Mullins uses a periodic inventory system. Instructions (a) Determine the cost of goods available of sale. (b) Determine (1) the ending inventory and (2) the cost of goods sold under each of the assumed cost flow methods (FIFO, LIFO, and average-cost). Prove the accuracy of the cost of goods sold under the FIFO and LIFO methods. (Note: For average-cost, round cost per unit to three decimal places.) (c) Which cost flow methods results in (1) the highest inventory amount for the balance sheet and (2) the highest cost of goods sold for the income statement? NOTE: Enter a number in cells requesting a value; enter either a number or a formula in cells with a "?". Enter a textual answer in the cells with "TEXT." (a) COST OF GOODS AVAILABLE FOR SALE Date Explanation March 1 Beginning inventory 5 Purchase 13 Purchase 21 Purchase 26 Purchase Total Units 2,500 2,000 3,500 5,000 2,000 15000 Unit Cost $7 8 9 -22 Total Cost $17,500 $16,000 $31,500 $50,000 $22,000 $137,000 10 11 FIFO (b)(1) Ending Inventory Date March 26 21 Units 2.000 Unit Cost $11 Total Cost $22.000 $10,000.00 $32,000 10 1,000 3000 (b)(2) Cost of Goods Sold Cost of goods available for sale Less: Ending inventory Cost of goods sold $137,000 32.000 $105,000 Proof of Cost of Goods Sold Date Units March 1 2,500 5 2,000 13 3,500 21 4.000 12000 Unit Cost $7 8 9 10 Total Cost 17500 16000 31500 40000 $105,000.00 LIFO (b)(1) Ending Inventory Date March 1 5 Units 2,500 Unit Cost $7 8 Total Cost $17,500 $4,000 $21.500 500 3.000 (b)(2) Cost of Goods Sold Cost of goods available for sale Less: Ending inventory Cost of goods sold $137,000 21.500 $115,500 Proof of Cost of Goods Sold Date Units March 26 2,000 21 5,000 13 3,500 5 1.500 12000 Unit Cost $11 10 9 8 Total Cost 22000 50000 31500 12000 $115,500.00 AVERAGE COST Cost of goods available for sale 137000 Units available for sale 15000 Average cost per unit $9.133 (b)(1) Ending Inventory Units 3,000 Unit Cost $9.133 Total Cost $27.400.00 (b)(2) Cost of Goods Sold Cost of goods available for sale Less: Ending inventory Cost of goods sold $137,000 $27.400.00 $109.600 (c) (1) (c) (2) As shown in (b), As shown in (b), FIFO LIFO produces the highest inventory amount, produces the highest cost of goods sold, $32,000.00 $115,500.00 After you have completed P6-2A, consider the following additional question. 1. Assume that number of units sold changed to 10,000 units. How does this change impact ending inventory and cost of goods sold under FIFO, LIFO and Average cost? 1 - 1








