Question
Allow X and Y to be two discrete arbitrary factors whose individual arrangements of conceivable results {x} and {y} are portrayed by likelihood conveyances p(x)
Allow X and Y to be two discrete arbitrary factors whose individual arrangements of conceivable
results {x} and {y} are portrayed by likelihood conveyances p(x) and p(y),
what's more, by a joint likelihood conveyance p(x, y).
(I) Give an articulation for the common data I(X; Y ) among X and Y ,
utilizing just the likelihood disseminations p(x), p(y), and p(x, y). [2 marks]
(ii) on the off chance that X and Y are autonomous arbitrary factors, what happens to
their shared data, and why? [1 mark]
(iii) Let the peripheral entropy of arbitrary variable X be H(X), and assume
that the two arbitrary factors X and Y are impeccably corresponded with each
other. All things considered, demonstrate that I(X; Y ) = H(X). [2 marks]
(iv) What is I(X; X), the common data of an arbitrary variable with itself,
concerning H(X)? [1 mark]
(b) Prove that the data measure is added substance: that the data acquired
from noticing the mix of N autonomous occasions, whose probabilities
are pi
for I = 1....N, is the amount of the data acquired from noticing each
one of these occasions independently and in any request. [3 marks]
(c) An invertible change creates projection coefficients by incorporating the
result of a sign onto every one of a group of capacities. In an opposite cycle,
development coefficients can be utilized on those equivalent capacities to replicate the
signal. On the off chance that the capacities being referred to end up framing an orthonormal set, what is
the ramification for the projection coefficients and the extension coefficients?
What punishment should be paid without a trace of symmetry? Name one such
punished change. [3 marks]
(d) In the Information Diagram (a plane whose tomahawks are time and recurrence),
for what reason does the Gabor-Heisenberg-Weyl Uncertainty Principle infer that
data is quantised even in ceaseless signs - i.e., that a sign's
data content comprises of a countable, predetermined number of autonomous
quanta? [3 marks]
(e) Define the Kolmogorov algorithmic intricacy K of a series of information. For
a line of length N bits, how huge could its Minimal Description Length
be, and why? Remark on how, or whether, you can realize that you have
genuinely resolved the Minimal Description Length for a bunch of information. Give a
sensible gauge of the Kolmogorov intricacy K of a fractal, and make sense of
why it is sensible. [5 marks]
10
CST.2010.7.11
12 Optimizing Compilers
Another programming language follows an "assess just on need" technique. The
outcome is, for instance, that in a program section
int x = SomeExpression;
on the off chance that (SomeBoolean) print x;
if (x == 0) x = SomeOtherExpression;
the given (possibly confounded) articulation isn't assessed on the line that
proclaims x, yet possibly gets assessed if and when x is utilized, as in the print articulation
on line 2. On line 3 the worth of x is unquestionably required, so on the off chance that the articulation had not
been assessed before it should be there.
Advancing aggregation regularly further develops execution of assembled code in view of
changes that are "protected" in a few sense. Propose types of examination and henceforth
advancement applicable for this situation in the conditions:
(a) It is protected however bothersome to assess an articulation regardless of whether its worth will not
in this manner be utilized, yet it should not be assessed a subsequent time. [8 marks]
(b) It is protected to assess an articulation over and over assuming is assessed by any means, however if the
program wouldn't utilize the worth it should not be figured by any means. [7 marks]
(c) Extra executable rationale must be placed in the program to guarantee that each
articulation is assessed precisely once in the event that its worth is required, yet not in the least
in any case. It is attractive to limit how much this additional rationale, safeguarding
semantics precisely. [5 marks]
You really want just think about the instance of streamlining of a solitary methodology at a time.
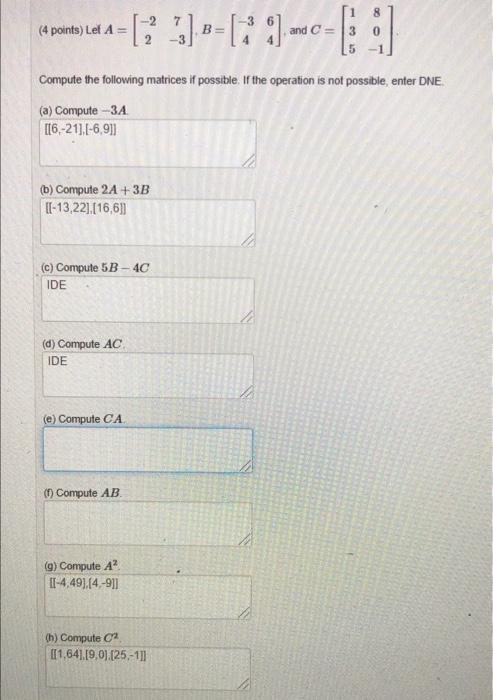

-[2])--[9) ---=[ ] B= and C= (4 points) Let A = Compute the following matrices if possible. If the operation is not possible, enter DNE. (a) Compute-3A [[6,-21],[-6,9]] (b) Compute 2A +3B [[-13,22],[16,6]] (c) Compute 5B-4C IDE (d) Compute AC IDE (e) Compute CA (f) Compute AB (9) Compute A2. [1-4,49),(4,-9]] (h) Compute C [1,64] [9,0).(25.-1]]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


