Question
Almost a Forest build many BST trees where each tree has a name. To store the names of all the trees, you will maintain a
Almost a Forest build many BST trees where each tree has a name. To store the names of all the trees, you will maintain a binary search tree for the tree names.
After building the trees, you will have to perform a set of operations and queries.
Here is an example. In this example fish, animal, bird, and fruit are part of the name BST. Each node of the name tree points to a BST of items. Here, the fish node points to a BST that contains name and count of fishes. Note that all the green colored nodes are of same type of node structure and all the black colored nodes are of same type of node structure.
Input Specification: You have to read the inputs from in.txt file. There will many strings in this file and you can assume that all the strings will be lower case letter and the maximum length of a string is 30 character. For simplicity, use static array of char to store a string.
The first line of the file contains three integers N, I, and Q, where N represents number of Tree Names, I represents the total number of items in the list to be inserted to all the trees, and Q represents the number of queries listed in the input file.
After the first line, next N lines will contain the list of Names of the trees and you need to insert them to a Name tree.
Next, I lines will contain the list of items to be inserted in different trees. Each line of the list contains two strings and one integer. The first string contains the name of that tree, second string contains the item name, and then the last integer contains the count of that item. You have to insert the item in the tree with that tree name. You need to use the item name as the key of the BST. Also note that the item count need to be added to the node as well. [Assumption: You can assume that a tree name as well as an item name will not be repeated in the input]
After the I lines, the next Q lines will contain a set of queries and you need to process them. Here is the list of queries: ? search: search for a particular item in a given tree and display the count of the item if it is found. Otherwise, prints item not found. However, if the tree does not exist, then it prints tree does not exist o [Example: search fruit avocado should search for avocado in the fruit tree and then prints the count of avocado. If the fruit tree exists, but the avocado does not exist, it should print "not found". However, if fruit tree does not exist, then it should print tree does not exist. ? item_before: this command counts the items in a given tree coming before a given item name (alphabetically). o [For example, if your query is like this item_before animal deer, it should print 4 as cat, bear, alligator, and cow come before deer alphabetically.] ? height_balance: It finds whether a given tree is height balanced or not. In order to do that, you need to know the height of left sub tree and then height of right sub tree. If their height difference's absolute value is more than 1, then we say the tree is imbalanced. In this assignment, a tree with 1 node, will be consider as height 0, and a tree with no node will be considered as height -1. o [Example: height_balance animal, will print, left height 1, right height 3, difference 2, not balanced] ? count: this command prints the total number of items in a given tree. o [Example: count animal, should print 142 (as 30 + 20+ 10 +50 +3 + 3 +5 +15 = 142)] ? reduce: this command reduces the count of an item in a given tree. The min value of the count needs to be >0. So, if it becomes <=0, you need to delete the
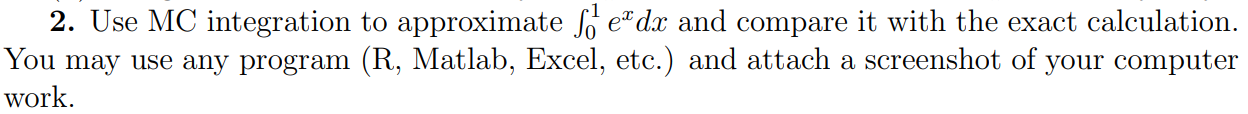
2. Use MC integration to approximate fedx and compare it with the exact calculation. You may use any program (R, Matlab, Excel, etc.) and attach a screenshot of your computer work.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The detailed answer for the above question is provided below The correct options are 1 I...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


