Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
An accelerator produces an He+ ion current of 50 nA at 1.0 MeV. Using a 1 cm2 detector 5 cm from the target at a
An accelerator produces an He+ ion current of 50 nA at 1.0 MeV. Using a 1 cm2 detector 5 cm from the target at a scattering angle of 170, determine the smallest amount of Au (atoms/cm2) that can be detected. Detectability is arbitrarily defined as 100 counts in 1 hr. Under similar conditions, what is the detection limit for oxygen? Compare these limits with the number of atoms/cm2 in a monolayer (=1015 atoms/cm2)
Please use the following equation for the first part:
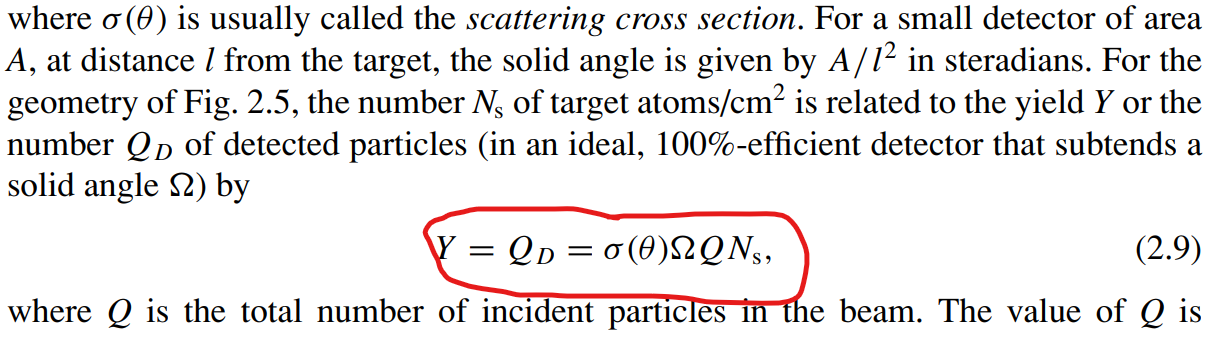
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


