Question
An air hockey table is a good approximation of a flat surface with no friction. The puck is a flat disc that can slide on
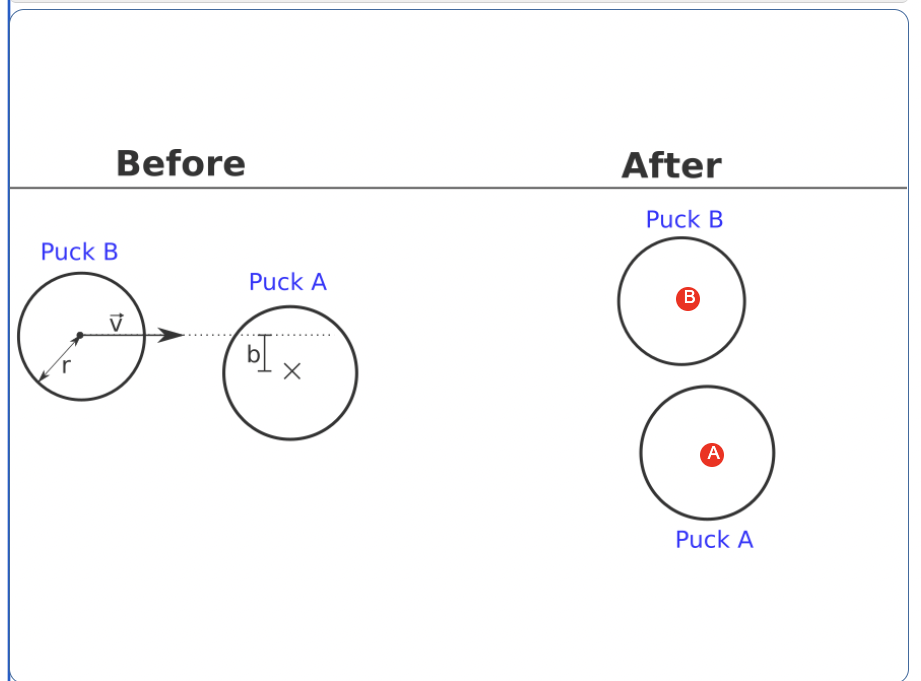
An air hockey table is a good approximation of a flat surface with no friction. The puck is a flat disc that can slide on the table. The aim of this exercise is to predict the trajectory of a puck hit by a second puck moving with a known speed. Assume that the mass of the pucks is m=9 (kg) and their radius is r=10 (m) (the thickness of the pucks is irrelevant for this exercise). The initial setup of the puck is described in the figure, where the puck A is standing still while the puck B is moving with constant velocity v=10 (m/s) toward the puck A with an impact parameter of b=2 (m) (the impact parameter is the distance between the centers of the two pucks in the direction orthogonal to the motion).
a) Given below is a schematic of the two pucks before and after impact. The velocity of the puck B is indicated with an arrow. Fill in possible velocities for puck A and puck B after the collision:
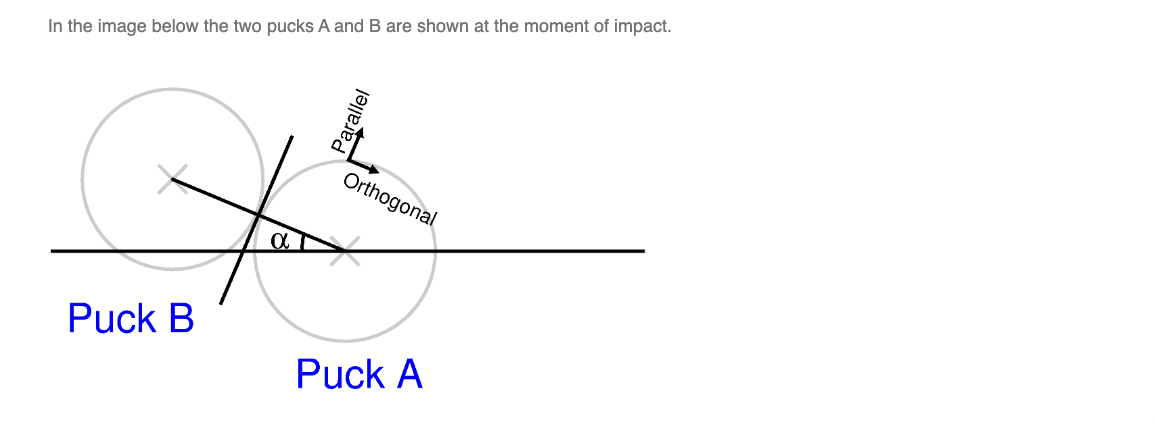
Note: I did provided the reference as a screenshot for both parts A and C which should be down below.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


