Question
In this exercise, we will examine space/time optimizations for page tables. The following list provides parameters of a virtual memory system. 1. For a single-level
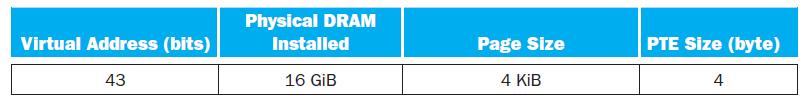
1. For a single-level page table, how many page table entries (PTEs) are needed? How much physical memory is needed for storing the page table?
2. Using a multilevel page table can reduce the physical memory consumption of page tables, by only keeping active PTEs in physical memory. How many levels of page tables will be needed in this case? And how many memory
references are needed for address translation if missing in TLB?
3. An inverted page table can be used to further optimize space and time. How many PTEs are needed to store the page table? Assuming a hash table implementation, what are the common case and worst case numbers of memory references needed for servicing a TLB miss?
The following table shows the contents of a 4-entry TLB.
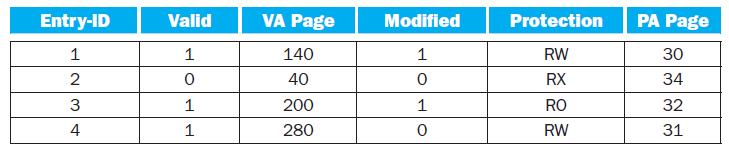
4. Under what scenarios would entry 2€™s valid bit be set to zero?
5. What happens when an instruction writes to VA page 30? When would a soft ware managed TLB be faster than a hardware managed TLB?
6. What happens when an instruction writes to VA page 200?
Physical DRAM Virtual Address (bits) Installed Page Size PTE Size (byte) 43 16 GB 4 KIB 4
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


