Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
00
1 Approved Answer
An investor is interested in modelling the daily log returns for Toyota, denoted by rTM,t, over the period 4 January 2005 to 22 April 2022.


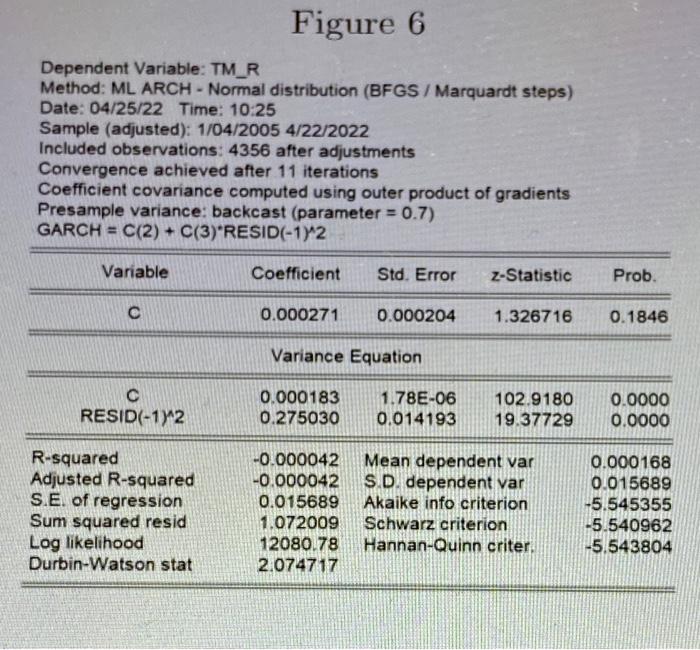 An investor is interested in modelling the daily log returns for Toyota, denoted by rTM,t, over the period 4 January 2005 to 22 April 2022. 1. She uses a constant mean equation and conducts an ARCH (5) test on the residuals of this. model, it. The results are shown in Figure 5. (a) What is the purpose of using an ARCH(5) test? Provide all steps in the testing procedure. (2 marks) (b) What conclusion do you draw from the results of Figure 5? What advice would you give to this investor in terms of her modelling strategy? (1 mark) 2. The investor revises the specification of her model for Toyota returns, TTMt, to that implied by the results of Figure 6. (a) Neatly write the theoretical model that is implied by the results of Figure 6 and verify that the parameter estimates provided in Figure 6 comply with the conditions of this model. Why are these conditions necessary? (2 marks) (b) Derive the unconditional kurtosis of the errors from the mean equation of this theoretical model. Compute its numerical value using the results from Figure 6. How does this estimate compare to that implied by a theoretical normal distribution? (4 marks) [Hint: the fourth moment of a conditionally normal random variable is equal to 3]. Figure 5 113.9280 Prob. F(5,4345) 504.3102 Heteroskedasticity Test: ARCH F-statistic Obs R-squared Prob. Chi-Square (5) 0.0000 0.0000 Figure 6 Dependent Variable: TM_R Method: ML ARCH - Normal distribution (BFGS/ Marquardt steps) Date: 04/25/22 Time: 10:25 Sample (adjusted): 1/04/2005 4/22/2022 Included observations: 4356 after adjustments Convergence achieved after 11 iterations Coefficient covariance computed using outer product of gradients Presample variance: backcast (parameter = 0.7) GARCH = C(2) + C(3) RESID(-1)^2 Variable Coefficient Std. Error z-Statistic C 0.000271 0.000204 1.326716 Variance Equation 0.000183 1.78E-06 RESID(-1)^2 0.275030 0.014193 R-squared -0.000042 Mean dependent var Adjusted R-squared -0.000042 S.D. dependent var 0.015689 Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion 1.072009 S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat 12080.78 Hannan-Quinn criter. 2.074717 Prob. 0.1846 102.9180 0.0000 19.37729 0.0000 0.000168 0.015689 -5.545355 -5.540962 -5.543804 An investor is interested in modelling the daily log returns for Toyota, denoted by rTM,t, over the period 4 January 2005 to 22 April 2022. 1. She uses a constant mean equation and conducts an ARCH (5) test on the residuals of this. model, it. The results are shown in Figure 5. (a) What is the purpose of using an ARCH(5) test? Provide all steps in the testing procedure. (2 marks) (b) What conclusion do you draw from the results of Figure 5? What advice would you give to this investor in terms of her modelling strategy? (1 mark) 2. The investor revises the specification of her model for Toyota returns, TTMt, to that implied by the results of Figure 6. (a) Neatly write the theoretical model that is implied by the results of Figure 6 and verify that the parameter estimates provided in Figure 6 comply with the conditions of this model. Why are these conditions necessary? (2 marks) (b) Derive the unconditional kurtosis of the errors from the mean equation of this theoretical model. Compute its numerical value using the results from Figure 6. How does this estimate compare to that implied by a theoretical normal distribution? (4 marks) [Hint: the fourth moment of a conditionally normal random variable is equal to 3]. Figure 5 113.9280 Prob. F(5,4345) 504.3102 Heteroskedasticity Test: ARCH F-statistic Obs R-squared Prob. Chi-Square (5) 0.0000 0.0000 Figure 6 Dependent Variable: TM_R Method: ML ARCH - Normal distribution (BFGS/ Marquardt steps) Date: 04/25/22 Time: 10:25 Sample (adjusted): 1/04/2005 4/22/2022 Included observations: 4356 after adjustments Convergence achieved after 11 iterations Coefficient covariance computed using outer product of gradients Presample variance: backcast (parameter = 0.7) GARCH = C(2) + C(3) RESID(-1)^2 Variable Coefficient Std. Error z-Statistic C 0.000271 0.000204 1.326716 Variance Equation 0.000183 1.78E-06 RESID(-1)^2 0.275030 0.014193 R-squared -0.000042 Mean dependent var Adjusted R-squared -0.000042 S.D. dependent var 0.015689 Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion 1.072009 S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat 12080.78 Hannan-Quinn criter. 2.074717 Prob. 0.1846 102.9180 0.0000 19.37729 0.0000 0.000168 0.015689 -5.545355 -5.540962 -5.543804
An investor is interested in modelling the daily log returns for Toyota, denoted by rTM,t, over the period 4 January 2005 to 22 April 2022. 1. She uses a constant mean equation and conducts an ARCH (5) test on the residuals of this. model, it. The results are shown in Figure 5. (a) What is the purpose of using an ARCH(5) test? Provide all steps in the testing procedure. (2 marks) (b) What conclusion do you draw from the results of Figure 5? What advice would you give to this investor in terms of her modelling strategy? (1 mark) 2. The investor revises the specification of her model for Toyota returns, TTMt, to that implied by the results of Figure 6. (a) Neatly write the theoretical model that is implied by the results of Figure 6 and verify that the parameter estimates provided in Figure 6 comply with the conditions of this model. Why are these conditions necessary? (2 marks) (b) Derive the unconditional kurtosis of the errors from the mean equation of this theoretical model. Compute its numerical value using the results from Figure 6. How does this estimate compare to that implied by a theoretical normal distribution? (4 marks) [Hint: the fourth moment of a conditionally normal random variable is equal to 3]. Figure 5 113.9280 Prob. F(5,4345) 504.3102 Heteroskedasticity Test: ARCH F-statistic Obs R-squared Prob. Chi-Square (5) 0.0000 0.0000 Figure 6 Dependent Variable: TM_R Method: ML ARCH - Normal distribution (BFGS/ Marquardt steps) Date: 04/25/22 Time: 10:25 Sample (adjusted): 1/04/2005 4/22/2022 Included observations: 4356 after adjustments Convergence achieved after 11 iterations Coefficient covariance computed using outer product of gradients Presample variance: backcast (parameter = 0.7) GARCH = C(2) + C(3) RESID(-1)^2 Variable Coefficient Std. Error z-Statistic C 0.000271 0.000204 1.326716 Variance Equation 0.000183 1.78E-06 RESID(-1)^2 0.275030 0.014193 R-squared -0.000042 Mean dependent var Adjusted R-squared -0.000042 S.D. dependent var 0.015689 Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion 1.072009 S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat 12080.78 Hannan-Quinn criter. 2.074717 Prob. 0.1846 102.9180 0.0000 19.37729 0.0000 0.000168 0.015689 -5.545355 -5.540962 -5.543804 An investor is interested in modelling the daily log returns for Toyota, denoted by rTM,t, over the period 4 January 2005 to 22 April 2022. 1. She uses a constant mean equation and conducts an ARCH (5) test on the residuals of this. model, it. The results are shown in Figure 5. (a) What is the purpose of using an ARCH(5) test? Provide all steps in the testing procedure. (2 marks) (b) What conclusion do you draw from the results of Figure 5? What advice would you give to this investor in terms of her modelling strategy? (1 mark) 2. The investor revises the specification of her model for Toyota returns, TTMt, to that implied by the results of Figure 6. (a) Neatly write the theoretical model that is implied by the results of Figure 6 and verify that the parameter estimates provided in Figure 6 comply with the conditions of this model. Why are these conditions necessary? (2 marks) (b) Derive the unconditional kurtosis of the errors from the mean equation of this theoretical model. Compute its numerical value using the results from Figure 6. How does this estimate compare to that implied by a theoretical normal distribution? (4 marks) [Hint: the fourth moment of a conditionally normal random variable is equal to 3]. Figure 5 113.9280 Prob. F(5,4345) 504.3102 Heteroskedasticity Test: ARCH F-statistic Obs R-squared Prob. Chi-Square (5) 0.0000 0.0000 Figure 6 Dependent Variable: TM_R Method: ML ARCH - Normal distribution (BFGS/ Marquardt steps) Date: 04/25/22 Time: 10:25 Sample (adjusted): 1/04/2005 4/22/2022 Included observations: 4356 after adjustments Convergence achieved after 11 iterations Coefficient covariance computed using outer product of gradients Presample variance: backcast (parameter = 0.7) GARCH = C(2) + C(3) RESID(-1)^2 Variable Coefficient Std. Error z-Statistic C 0.000271 0.000204 1.326716 Variance Equation 0.000183 1.78E-06 RESID(-1)^2 0.275030 0.014193 R-squared -0.000042 Mean dependent var Adjusted R-squared -0.000042 S.D. dependent var 0.015689 Akaike info criterion Schwarz criterion 1.072009 S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood Durbin-Watson stat 12080.78 Hannan-Quinn criter. 2.074717 Prob. 0.1846 102.9180 0.0000 19.37729 0.0000 0.000168 0.015689 -5.545355 -5.540962 -5.543804



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access with AI-Powered Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started

