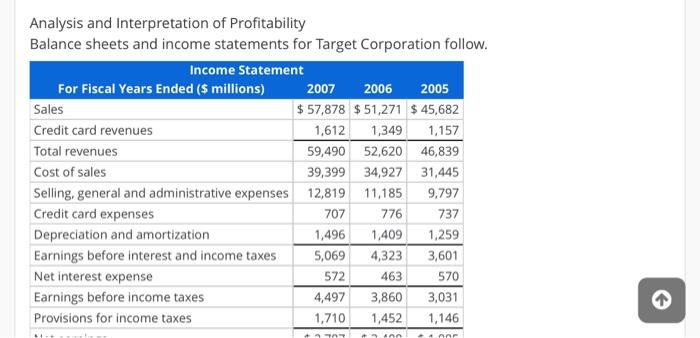
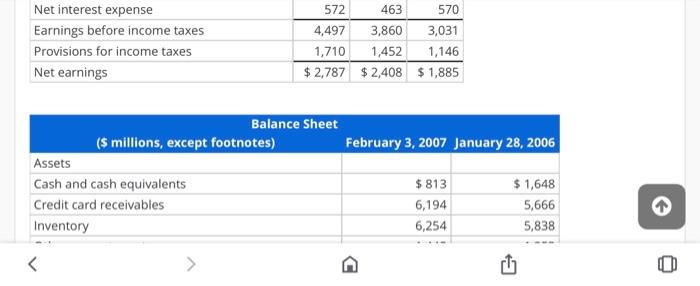
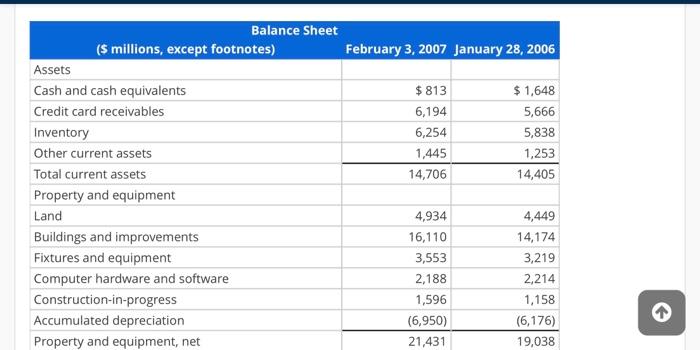
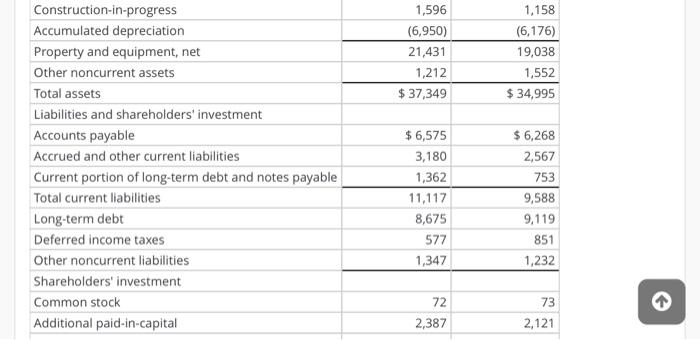
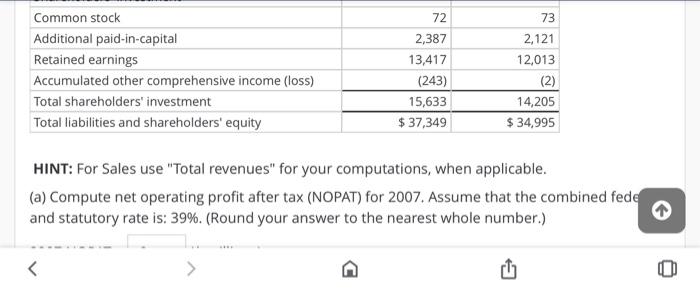
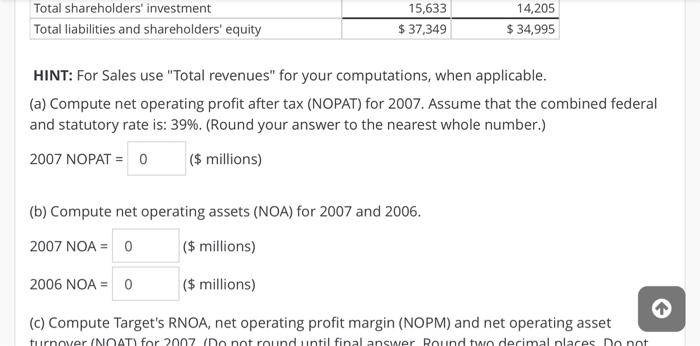
Analysis and Interpretation of Profitability Balance sheets and income statements for Target Corporation follow. Income Statement For Fiscal Years Ended (5 millions) 2007 2006 2005 Sales $ 57,878 $ 51,271 $ 45,682 Credit card revenues 1,612 1,349 1,157 Total revenues 59,490 52,620 46,839 Cost of sales 39,399 34,927 31,445 Selling, general and administrative expenses 12,819 11,185 9,797 Credit card expenses 707 776 737 Depreciation and amortization 1,496 1,409 1,259 Earnings before interest and income taxes 5,069 4,323 3,601 Net interest expense 570 Earnings before income taxes 4,497 3,860 3,031 Provisions for income taxes 1,710 1,452 1,146 572 463 +1 A AAF Net interest expense Earnings before income taxes Provisions for income taxes Net earnings 572 463 570 4,497 3,860 3,031 1,710 1,452 1,146 $ 2,787 $2,408 $ 1,885 February 3, 2007 January 28, 2006 Balance Sheet (s millions, except footnotes) Assets Cash and cash equivalents Credit card receivables Inventory $813 6,194 6,254 $ 1,648 5,666 5,838 February 3, 2007 January 28, 2006 $ 813 6,194 6,254 1,445 14,706 $1,648 5,666 5,838 1,253 14,405 Balance Sheet ($ millions, except footnotes) Assets Cash and cash equivalents Credit card receivables Inventory Other current assets Total current assets Property and equipment Land Buildings and improvements Fixtures and equipment Computer hardware and software Construction-in-progress Accumulated depreciation Property and equipment, net 4,934 16,110 3,553 2,188 1,596 (6,950) 21,431 4,449 14,174 3,219 2,214 1,158 (6,176) 19,038 1,596 (6,950) 21,431 1,212 $ 37,349 1,158 (6,176) 19,038 1,552 $34,995 Construction-in-progress Accumulated depreciation Property and equipment, net Other noncurrent assets Total assets Liabilities and shareholders' investment Accounts payable Accrued and other current liabilities Current portion of long-term debt and notes payable Total current liabilities Long-term debt Deferred income taxes Other noncurrent liabilities Shareholders' investment Common stock Additional paid-in-capital $6,575 3,180 1,362 11,117 8,675 577 1,347 $ 6,268 2,567 753 9,588 9,119 851 1,232 72 73 2,121 2,387 Total shareholders' investment Total liabilities and shareholders' equity 15,633 $ 37,349 14,205 $ 34,995 HINT: For Sales use "Total revenues" for your computations, when applicable. (a) Compute net operating profit after tax (NOPAT) for 2007. Assume that the combined federal and statutory rate is: 39%. (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) 2007 NOPAT = 0 ($ millions) (b) Compute net operating assets (NOA) for 2007 and 2006. 2007 NOA = 0 ($ millions) 2006 NOA = 0 ($ millions) (c) Compute Target's RNOA, net operating profit margin (NOPM) and net operating asset turnover (NOAT for 2007 (Do not round until final answer Round two decimal places do not 2006 NOA = 0 ($ millions) (c) Compute Target's RNOA, net operating profit margin (NOPM) and net operating asset turnover (NOAT) for 2007. (Do not round until final answer. Round two decimal places. Do not use NOPM x NOAT to calculate RNOA.) 2007 RNOA = 0 % 2007 NOPM = 0 % 2007 NOAT = 0 (d) Compute net nonoperating obligations (NNO) for 2007 and 2006. 2007 NNO = 0 ($ millions) 2006 NNO = 0 ($ millions) (e) Compute return on equity (ROE) for 2007. (Round your answers to two decimal places. Do not round until your final answer.) 2007 ROE = 0 % () Infer the nonoperating return component of ROE for 2007. (Use answers from above to calculate. Round your answer to two decimal places.) 2007 nonoperating return = 0 % (g) Which of the following statements reflects the best inference we can draw from the difference between Target's ROE and RNOA? OROE > RNOA implies that Target's equity has grown faster than its NOA. OROE > RNOA implies that Target has taken on too much financial leverage. nor nini (g) Which of the following statements reflects the best inference we can draw from the difference between Target's ROE and RNOA? ORDE > RNOA implies that Target's equity has grown faster than its NOA. OROE > RNOA implies that Target has taken on too much financial leverage. OROE > RNOA implies that Target is able to borrow money to fund operating assets that yield a return greater than its cost of debt; the excess accrues to the benefit of Target's stockholders. OROE > RNOA implies that Target has increased its financial leverage during the period, Analysis and Interpretation of Profitability Balance sheets and income statements for Target Corporation follow. Income Statement For Fiscal Years Ended (5 millions) 2007 2006 2005 Sales $ 57,878 $ 51,271 $ 45,682 Credit card revenues 1,612 1,349 1,157 Total revenues 59,490 52,620 46,839 Cost of sales 39,399 34,927 31,445 Selling, general and administrative expenses 12,819 11,185 9,797 Credit card expenses 707 776 737 Depreciation and amortization 1,496 1,409 1,259 Earnings before interest and income taxes 5,069 4,323 3,601 Net interest expense 570 Earnings before income taxes 4,497 3,860 3,031 Provisions for income taxes 1,710 1,452 1,146 572 463 +1 A AAF Net interest expense Earnings before income taxes Provisions for income taxes Net earnings 572 463 570 4,497 3,860 3,031 1,710 1,452 1,146 $ 2,787 $2,408 $ 1,885 February 3, 2007 January 28, 2006 Balance Sheet (s millions, except footnotes) Assets Cash and cash equivalents Credit card receivables Inventory $813 6,194 6,254 $ 1,648 5,666 5,838 February 3, 2007 January 28, 2006 $ 813 6,194 6,254 1,445 14,706 $1,648 5,666 5,838 1,253 14,405 Balance Sheet ($ millions, except footnotes) Assets Cash and cash equivalents Credit card receivables Inventory Other current assets Total current assets Property and equipment Land Buildings and improvements Fixtures and equipment Computer hardware and software Construction-in-progress Accumulated depreciation Property and equipment, net 4,934 16,110 3,553 2,188 1,596 (6,950) 21,431 4,449 14,174 3,219 2,214 1,158 (6,176) 19,038 1,596 (6,950) 21,431 1,212 $ 37,349 1,158 (6,176) 19,038 1,552 $34,995 Construction-in-progress Accumulated depreciation Property and equipment, net Other noncurrent assets Total assets Liabilities and shareholders' investment Accounts payable Accrued and other current liabilities Current portion of long-term debt and notes payable Total current liabilities Long-term debt Deferred income taxes Other noncurrent liabilities Shareholders' investment Common stock Additional paid-in-capital $6,575 3,180 1,362 11,117 8,675 577 1,347 $ 6,268 2,567 753 9,588 9,119 851 1,232 72 73 2,121 2,387 Total shareholders' investment Total liabilities and shareholders' equity 15,633 $ 37,349 14,205 $ 34,995 HINT: For Sales use "Total revenues" for your computations, when applicable. (a) Compute net operating profit after tax (NOPAT) for 2007. Assume that the combined federal and statutory rate is: 39%. (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) 2007 NOPAT = 0 ($ millions) (b) Compute net operating assets (NOA) for 2007 and 2006. 2007 NOA = 0 ($ millions) 2006 NOA = 0 ($ millions) (c) Compute Target's RNOA, net operating profit margin (NOPM) and net operating asset turnover (NOAT for 2007 (Do not round until final answer Round two decimal places do not 2006 NOA = 0 ($ millions) (c) Compute Target's RNOA, net operating profit margin (NOPM) and net operating asset turnover (NOAT) for 2007. (Do not round until final answer. Round two decimal places. Do not use NOPM x NOAT to calculate RNOA.) 2007 RNOA = 0 % 2007 NOPM = 0 % 2007 NOAT = 0 (d) Compute net nonoperating obligations (NNO) for 2007 and 2006. 2007 NNO = 0 ($ millions) 2006 NNO = 0 ($ millions) (e) Compute return on equity (ROE) for 2007. (Round your answers to two decimal places. Do not round until your final answer.) 2007 ROE = 0 % () Infer the nonoperating return component of ROE for 2007. (Use answers from above to calculate. Round your answer to two decimal places.) 2007 nonoperating return = 0 % (g) Which of the following statements reflects the best inference we can draw from the difference between Target's ROE and RNOA? OROE > RNOA implies that Target's equity has grown faster than its NOA. OROE > RNOA implies that Target has taken on too much financial leverage. nor nini (g) Which of the following statements reflects the best inference we can draw from the difference between Target's ROE and RNOA? ORDE > RNOA implies that Target's equity has grown faster than its NOA. OROE > RNOA implies that Target has taken on too much financial leverage. OROE > RNOA implies that Target is able to borrow money to fund operating assets that yield a return greater than its cost of debt; the excess accrues to the benefit of Target's stockholders. OROE > RNOA implies that Target has increased its financial leverage during the period