Question
Analyze case 1 with in accordance with the notes provided Case 1.Income and Risk Two types of temporary job contract for one year are offered
Analyze case 1 with in accordance with the notes provided
Case 1.Income and Risk
Two types of temporary job contract for one year are offered to you. Type 1 job
depends on the achievement of your performance, where you can earn a 200,000 Yen
monthly wage if you achieve a pre-specified goal, or you can earn 100,000 Yen if
you fail to achieve the goal. Achievement of the goal depends on good luck or bad
luck with 50-50 percent possibility of achieving it each month. The other type of job
contract offers you a fixed wage of 151,000 Yen, but has a slim chance of 1 percent
of removal into reserve with only 51,000 Yen compensation. Which of the two job
contracts do you choose and why? Do you maximize the average wage or minimize
risk associated with job contracts? Calculate your expected income and the degree of
uncertainty of your wage. Discuss your decision making.
Hint: Ch.5 of Pindyck and Rubinfeld, Microeconomcs 8-th ed., 2013.
Reading Notes: Expected Utility Theory
People often face decision making under uncertainty. Popular method to understand
this behavior is the utility function and the expected utility theory. Suppose you face the
following three gambles with a combination of income and uncertainty. Assume you are
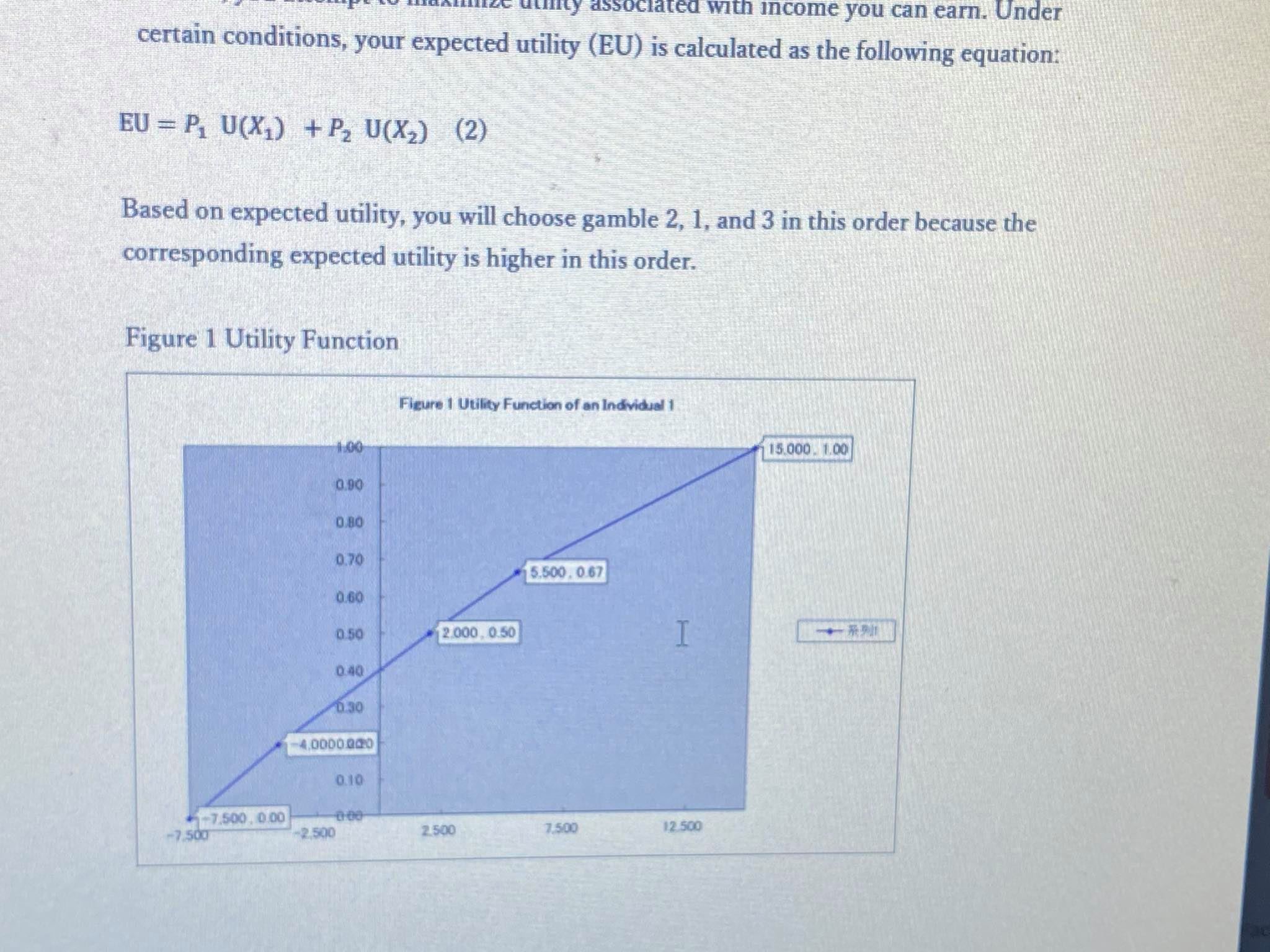
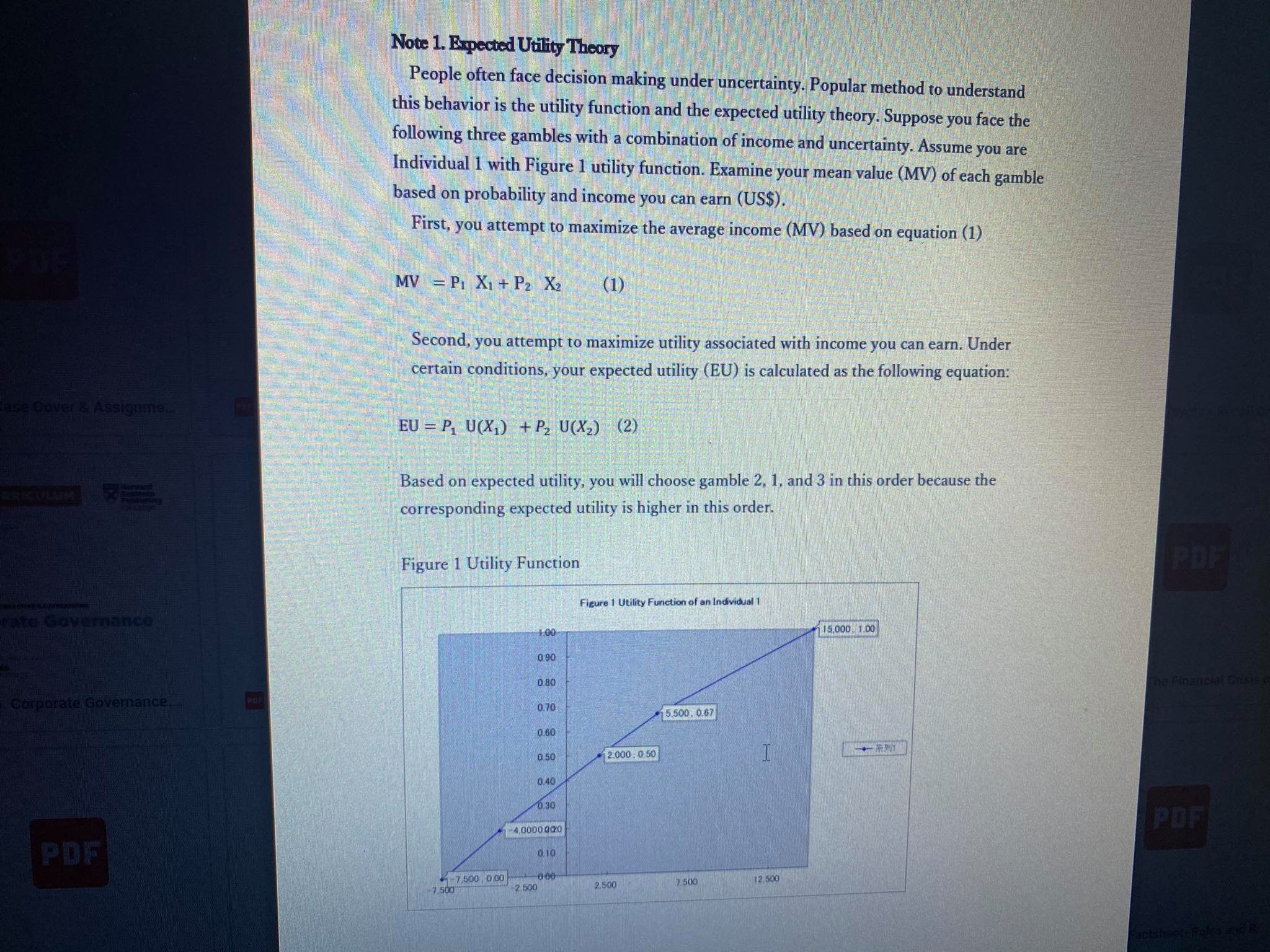
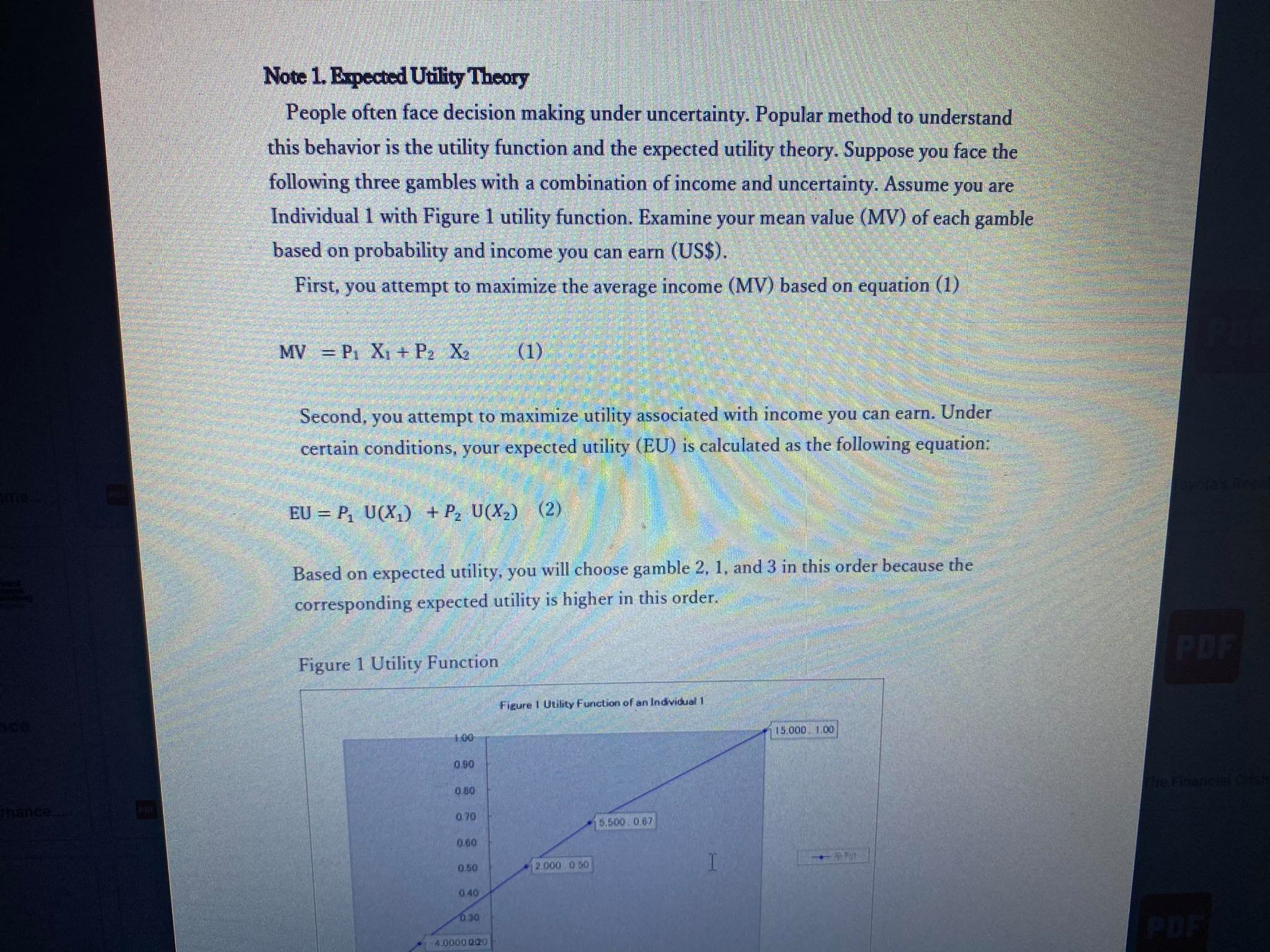
Individual 1 with Figure 1 utility function. Examine your mean value (MV) of each gamble
based on probability and income you can earn (US$).
First, you attempt to maximize the average income (MV) based on equation (1)
MV = P1 X1 + P2 X2 (1)
Second, you attempt to maximize utility associated with income you can earn. Under
certain conditions, your expected utility (EU) is calculated as the following equation:
EU = P1 U(X1
) + P2 U(X2
) (2)
Based on expected utility, you will choose gamble 2, 1, and 3 in this order because the
corresponding expected utility is higher in this order.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


