Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. Suppose Russia's inflation rate is 100 percent over one year but the inflation rate in Switzerland is only 5 percent. According to relative


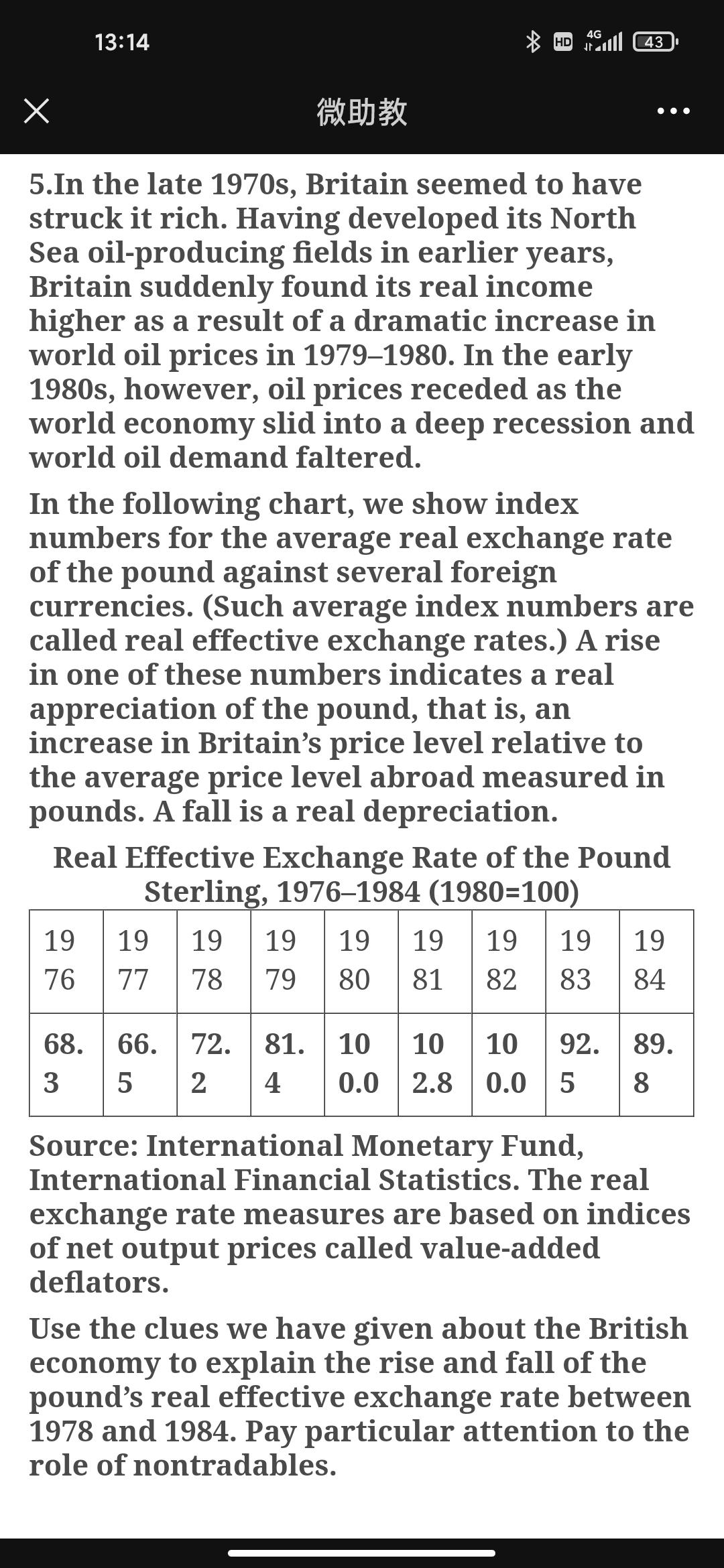
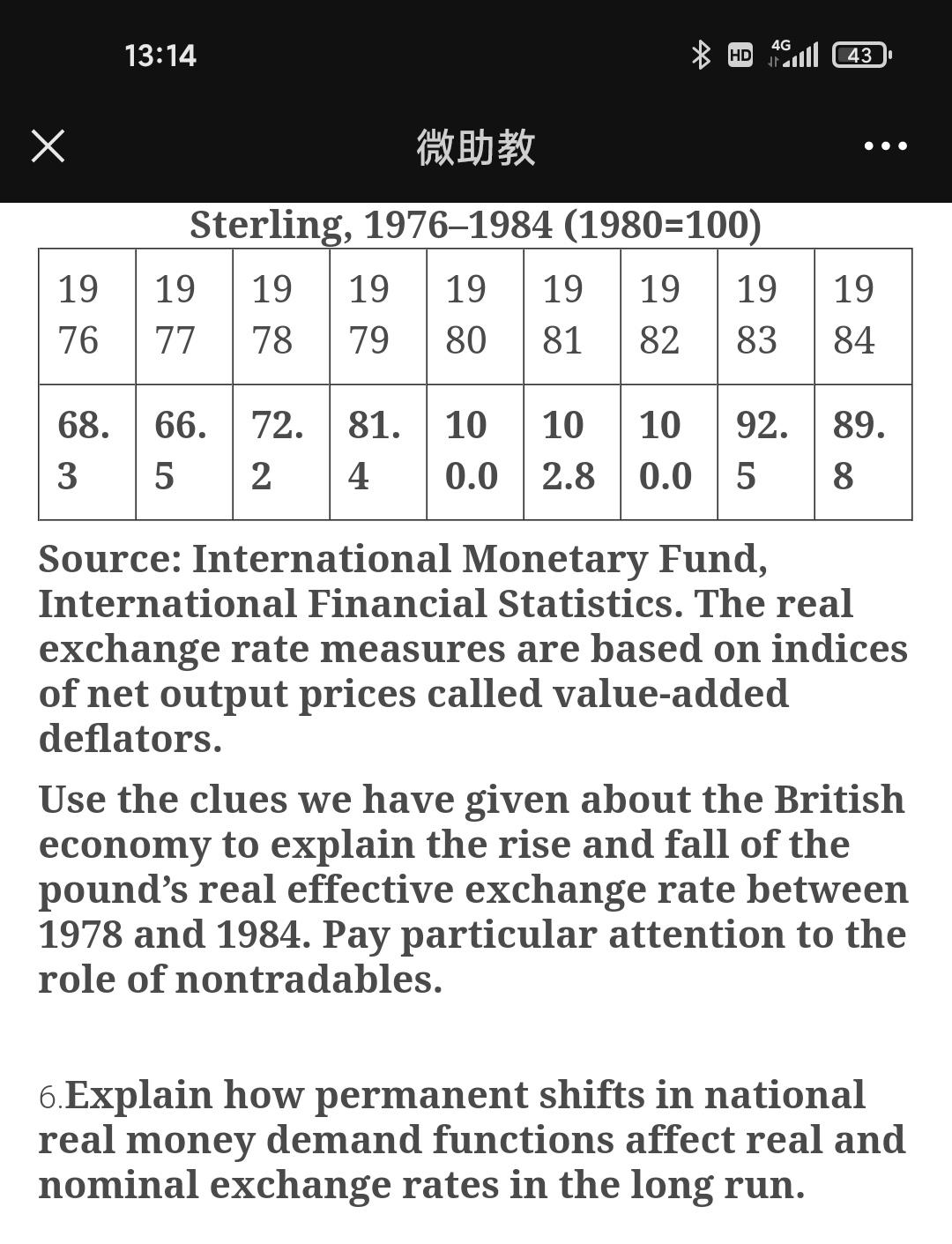
1. Suppose Russia's inflation rate is 100 percent over one year but the inflation rate in Switzerland is only 5 percent. According to relative PPP, what should happen over the year to the Swiss franc's exchange rate against the Russian ruble? 2. Discuss why it is often asserted that exporters suffer when their home currencies appreciate in real terms against foreign currencies and prosper when their home currencies depreciate in real terms. 3. Other things equal, how would you expect the following shifts to affect a currency's real exchange rate against foreign currencies? a. The overall level of spending doesn't change, but domestic residents decide to spend more of their income on nontraded products and less on tradables. b. Foreign residents shift their demand away from their own goods and toward the home country's exports. 4G 13:14 HD ll 43 4. Large-scale wars typically bring a suspension of international trading and financial activities. Exchange rates lose much of their relevance under these conditions, but once the war is over, governments wishing to fix exchange rates face the problem of deciding what the new rates should be. The PPP theory has often been applied to this problem of postwar exchange rate realignment. Imagine that you are a British Chancellor of the Exchequer and that World War I has just ended. Explain how you would figure out the dollar/pound exchange rate implied by PPP. When might it be a bad idea to use the PPP theory in this way? 5.In the late 1970s, Britain seemed to have struck it rich. Having developed its North Sea oil-producing fields in earlier years, Britain suddenly found its real income higher as a result of a dramatic increase in world oil prices in 19791980. In the early 1980s, however, oil prices receded as the world economy slid into a deep recession and world oil demand faltered. In the following chart, we show index numbers for the average real exchange rate of the pound against several foreign currencies. (Such average index numbers are called real effective exchange rates.) A rise in one of these numbers indicates a real appreciation of the pound, that is, an increase in Britain's price level relative to the average price level abroad measured in pounds. A fall is a real depreciation. Real Effective Exchange Rate of the Pound Sterling, 19761984 (1980=100) 4G 13:14 HD ll 43 5.In the late 1970s, Britain seemed to have struck it rich. Having developed its North Sea oil-producing fields in earlier years, Britain suddenly found its real income higher as a result of a dramatic increase in world oil prices in 19791980. In the early 1980s, however, oil prices receded as the world economy slid into a deep recession and world oil demand faltered. In the following chart, we show index numbers for the average real exchange rate of the pound against several foreign currencies. (Such average index numbers are called real effective exchange rates.) A rise in one of these numbers indicates a real appreciation of the pound, that is, an increase in Britain's price level relative to the average price level abroad measured in pounds. A fall is a real depreciation. Real Effective Exchange Rate of the Pound Sterling, 19761984 (1980=100) 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 68. 66. 72. 81. 10 10 10 92. 89. 3 5 2 4 0.0 2.8 0.0 5 8. Source: International Monetary Fund, International Financial Statistics. The real exchange rate measures are based on indices of net output prices called value-added deflators. Use the clues we have given about the British economy to explain the rise and fall of the pound's real effective exchange rate between 1978 and 1984. Pay particular attention to the role of nontradables. 4G 13:14 HD ll 43 .. Sterling, 19761984 (1980=100) 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 68. 66. 72. 81. 10 10 10 92. 89. 3 5 2 4 0.0 2.8 0.0 5 8 Source: International Monetary Fund, International Financial Statistics. The real exchange rate measures are based on indices of net output prices called value-added deflators. Use the clues we have given about the British economy to explain the rise and fall of the pound's real effective exchange rate between 1978 and 1984. Pay particular attention to the role of nontradables. 6.Explain how permanent shifts in national real money demand functions affect real and nominal exchange rates in the long run.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.60 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 ANSWER 2...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


