

Answer all.
1) Which country has a an absolute advantage in wine? In cheese? Which country has a comparative advantage in wine? In cheese?
2) Draw the Production Possibilities Frontier for each country and label graphs
Remember that the production possibilities frontier is the combination of wine and cheese that can be produced in each country, given the amount of labor)
3) Describe the autarky equilibrium in each country. (can show graphically)
Remember that for equilibrium we want to know how much each country is producing and consumingof each good, and at what (relative) price. (no precise numerica answer needed for production and consumption)
a) Suppose now that preferences are such that consumers in both countries (tastes are the same across both countries) always want to consume twice as much cheese as wine. What would the autarky equilibrium be? (precise number needed)
4) Suppose the two countries are allowed to trade. What will be the range of relative prices of wine for which there will be trade? What will be the range of relative price of cheese for which there will be trade?
5)Suppose the world relative price of wine is 1.5
a. Will the countries trade? If so, describe the pattern of trade
b. At this price, exactly how much wine and cheese will Portugal produce? In particular, what can you tell about specialization?
c. Explain the gains from trade.
6) Suppose the world relative price of wine is 1.7. What changes with respect to question 5?
More specifically, does the pattern of trade change? Does the level of production change? Do the gains from
trade change? If so, specify how (numerically if possible, qualitatively - increases or decreases if not).
For the gains from trade, look carefully at how the Consumption Possibilities changes with the new price.
7) Suppose the amount of labor in Portugal grew to 120. How would the PPF in Portugal change? Would Portugal's comparative advantage change? Would the range of prices for which trade occurs change?
8) Suppose now the world relative price of wine is 2. Will there still be trade? Why or why not? l(ook at the gains from trade)
9) Suppose now the world relative price of wine is 3. Will there still be trade? Why or why not? (look at the gains from trade)
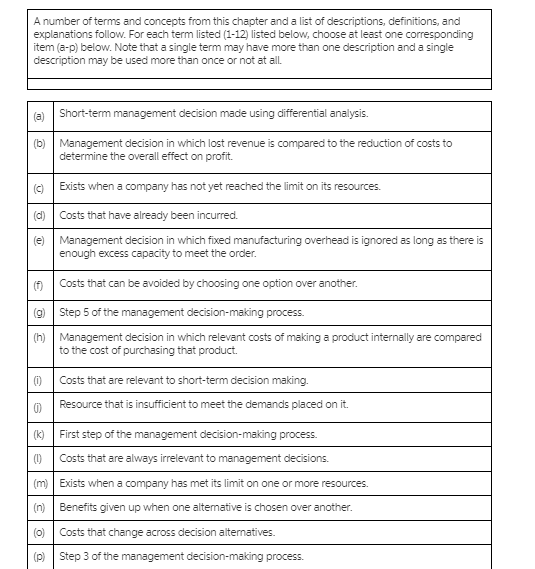
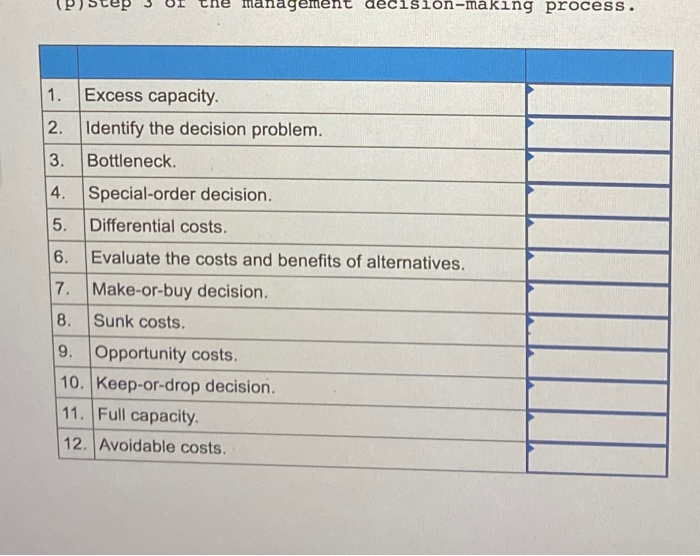
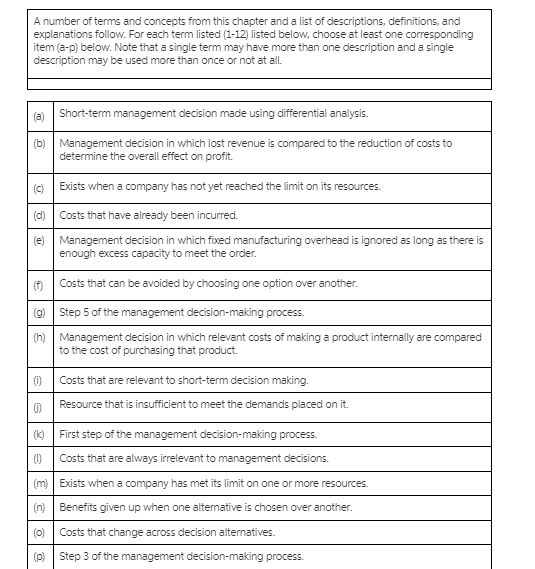
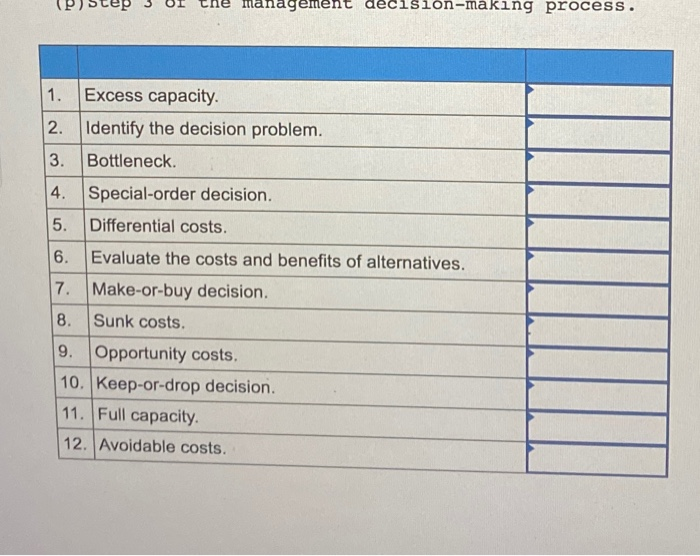
A number of terms and concepts from this chapter and a list of descriptions, definitions, and explanations follow. For each term listed (1-12) listed below, choose at least one corresponding item (a-p) below. Note that a single term may have more than one description and a single description may be used more than once or not at all. Short-term management decision made using differential analysis. Management decision in which lost revenue is compared to the reduction of costs to determine the overall effect on profit. (C) Exists when a company has not yet reached the limit on its resources. Costs that have already been incurred. Management decision in which fixed manufacturing overhead is ignored as long as there is enough excess capacity to meet the order. (f) Costs that can be avoided by choosing one option over another. Step 5 of the management decision-making process (h) Management decision in which relevant costs of making a product internally are compared to the cost of purchasing that product. Costs that are relevant to short-term decision making. Resource that is insufficient to meet the demands placed on it. First step of the management decision-making process. Costs that are always irrelevant to management decisions. m Exists when a company has met its limit on one or more resources (n Benefits given up when one alternative is chosen over another. (0) Costs that change across decision alternatives. (p) Step 3 of the management decision-making process(p) Step the management decision-making process. 1. Excess capacity. 2. Identify the decision problem. 3. Bottleneck. 4. Special-order decision. 5. Differential costs. 6. Evaluate the costs and benefits of alternatives. 7 Make-or-buy decision. 8. Sunk costs. 9. Opportunity costs. 10. Keep-or-drop decision. 11. Full capacity. 12. Avoidable costs.Course Learning Outcomes-Covered Identify and analyze different perspectives on understanding problems for different situations. (3.1) Utilize different decision making tools to enhance problem solving and decision making approaches. (4.3) . Identify organized alternatives and select among possible alternative to evaluate business options. (210) . Create a Decision Making and Problem Solving worksheet document. (4.5) Critical Thinking Questions: (Marks 5) Question 1: (1 Mark) Suppose you are a member of a group asked to find ways to cut costs throughout your organization for the upcoming year. Sales have fallen sharply, and the company is in danger of going out of business. After gathering information, your group concludes that the company will save the most money by freezing pay for a year, despite a tradition of annual salary increases. How can you make sure this is a fair decision? How can you make sure that others in the organization will see it as a fair decision? Question 2: Case Analysis (2 Marks) Care, a health consultancy company in Saudi Arabia, is studying the economic benefits of a program of preventative COVID-19 flu vaccinations. Care has to give advice to government for COVID-19 vaccination. If vaccinations are not introduced then the estimated cost to the government if flu strikes in the next year is SR.70m with probability 0.1, SR.100m with probability 0.3 and SR.150m with probability 0.6. It is estimated that such a program will cost SR.70m and that the probability of flu striking in the next year is 0.75. One alternative open to the committee is to institute an "early-warning" monitoring scheme (costing SR.30m) which will enable it to detect an outbreak of flu early and hence institute a rush vaccination program (costing SR.100m because of the need to vaccinate quickly before the outbreak spreads). Question As a consultant of Care, Develop a decision tree for alternatives and make recommendation to Indian government that which alternative can maximize expected economic benefits? Question 3: (1 Mark) Decision support tools rely on objective, mathematical data. What part does ethics play in using decision support software? Question 4: (1 Mark) If you collect too much information for analyzing a decision, you can suffer from analysis paralysis, where you spend too much time thinking about a decision rather than making one. Recall a major financial decision you made recently, such as of a car or housing purchase or rental. Describe your process for making the decision. How could analysis paralysis have affected this process?Marginal analysis and decision-making: Concept: The Fundamental Assumption of Economics All social phenomena emerge from the actions and interactions of individuals who are gathering in response to expected marginal benefits and expected marginal costs to themselves. Definition: Marginal is additional or incremental (amount of increase) or decremental (amount of decrease). Should I do (choose) activity x? MC (() = the additional costs of doing x MB (x) = the additional benefits of doing x Rule: If Expected MB (x)> Expected MC (), do x; otherwise don't. Application: Would an employer ever hire anyone if the additional cost of his or her employment were greater than the marginal / additional benefit? Of course not, to do so would be irrational. Assumptions: - Are you married? When will you get married? You will make that decision using marginal analysis, right? Explain