:Answer all.
A firm is considering three mutually exclusive alternatives as part of a production improvement program. The alternatives are as follows:
A
B
C
Installed cost
$10,000
$15,000
$20,000
Uniform annual benefit
1,625
1,625
1,890
Useful life, in years
10
20
20
For each alternative, the salvage value at the end of useful life is zero. At the end of 10 years, Alt. A could be replaced by another A with identical cost and benefits.
A) Construct a choice table for interest rates from 0% to 100%.
B) The MARR is 6%. If the analysis period is 20 years, which alternative should be selected?
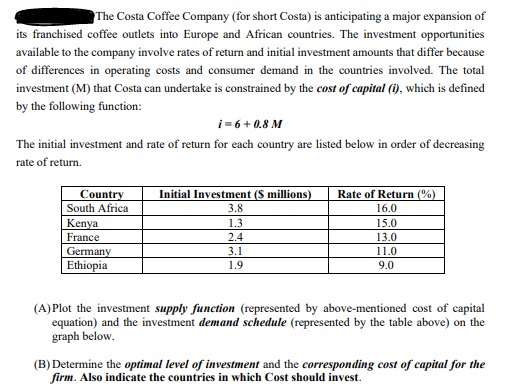
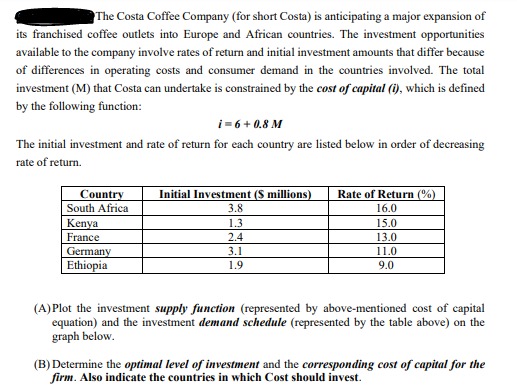
1. An entrepreneur is thinking of starting a rm. The rm will pay Tk. 320,000 in wages/salary, Tk. 150,000 on raw materials, Tk. 100,000 for rent per month. If the entrepreneur worked as a manager for somebody else, he would earn 'I'k. 50,000 per month. The rm's total revenue per month is Tk. 600,000. a) Calculate the accounting prot of this rm. 13) Do you think the entrepreneur should start this rm, explain your answer. 2. List the characteristics of the four different types of market structures discussed in class and give an example of each. 3. Suppose you start a business of manufacturing computer software. Assume that this computer software company is a perfectly competitive rm. Your xed cost per month is Tk. 60,000 and total cost is Tk. 140,000. If you sell 1000 software per month and the average revenue is TR. 90, what should be your short-run decision regarding shut down and long run decision regarding exit? 4. On it and y axes, draw ATC, AVC and MC curves and four alternative demand curves that the Perfectly Competitive Firm might face. a) Draw D] such that the rm makes a prot. b) Draw D2 such that the firm breaks even (prot=0). c) Draw D3 such that the rm is at its shut down point. (:1) Draw D4 such that the rm would shut down rather than produce. Question 2 (20 points) This question studies the co-existence of different currencies. Time is discrete with an infinite horizon. Each period consists of two subperiods. In the day, trade is bilateral and anonymous as in Kiyotaki and Wright (1989) (call this the KW market). At night trade takes place in a Walrasian or centralized market (call this the CM). There are two types of agents, buyers and sellers, and the measure of both is normalized to 1. The per period utility for buyers is u(q) + U(X) - H, and for sellers it is -q + U(X) - H, where q is the quantity of the day good produced by the seller and consumed by the buyer, X is consumption of the night good (the numeraire), and H is hours worked in the CM. In the CM, all agents have access to a technology that turns one unit of work into a unit of good. The functions u, U satisfy the usual assumptions; I will only spell out the most crucial ones: There exists X"* 6 (0, co) such that U'(X*) = 1, and we define the first-best quantity traded in the KW market as q' = {q : u'(q") = 1}. We will assume that there are two types of money, m, and my. There are also two types of sellers. For reasons that we will leave out of the model, Type-1 sellers, with measure o E [0, 1], do not recognize m2, thus, they accept only the local currency my. Type-2 sellers, with measure 1 6, recognize and, hence, accept my, as well as my. Hence, local currency has a liquidity advantage over the foreign one, since it is recognized by all sellers. All buyers meet a seller in the KW market, so that o is the probability with which a buyer meets a type-1 seller, and 1 - o is the probability with which she meets a type-2 seller. In any type of meeting, buyers have all the bargaining power. The rest is standard. Goods are non storable. The supply of each money is con- trolled by an individual authority, and evolves according to Mitti = (1 + (;) Mis. New money (of both types) is introduced, or withdrawn if /4; 0) in every equilibrium? If not, can you provide a condition on policy parameters that would guarantee zz > 0?1. Some equipment will be installed in a warehouse that a firm has leased for 7 years. There are two alternatives: A B Initial cost $1000 $1500 Uniform annual benefit $550 $610 Useful life, in years 3 4 At any time after equipment is installed, it has no salvage value. Assume that alternative A and B will be replaced at the end of their useful lives by identical equipment with the same costs and benefits. For a 7-year analysis period and a 10% interest rate, use an annual cash flow analysis to determine which alternative should be selected.The Costa Coffee Company (for short Costa) is anticipating a major expansion of its franchised coffee outlets into Europe and African countries. The investment opportunities available to the company involve rates of return and initial investment amounts that differ because of differences in operating costs and consumer demand in the countries involved. The total investment (M) that Costa can undertake is constrained by the cost of capital (1), which is defined by the following function: 1-6+0.8 M The initial investment and rate of return for each country are listed below in order of decreasing rate of return. Country Initial Investment ($ millions) Rate of Return (%) South Africa 3.8 16.0 Kenya 1.3 15.0 France 2.4 13.0 Germany 3.1 11.0 Ethiopia 1.9 9.0 (A) Plot the investment supply function (represented by above-mentioned cost of capital equation) and the investment demand schedule (represented by the table above) on the graph below. (B) Determine the optimal level of investment and the corresponding cost of capital for the firm. Also indicate the countries in which Cost should invest