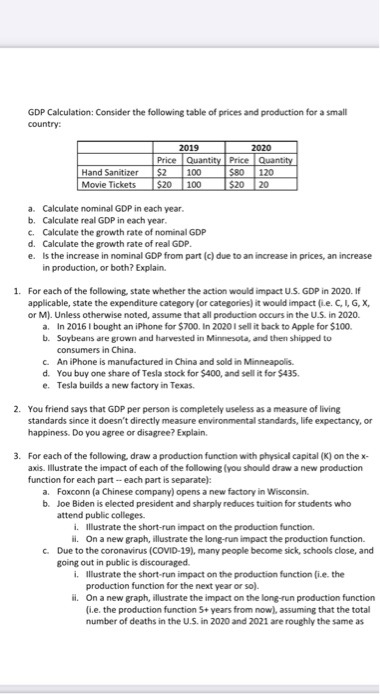
Question
:Answer all questions. After nearly five years with Coca-Cola, engineer Xiaorong Shannon You was getting downsized. Prosecutors allege that two days before her final shift


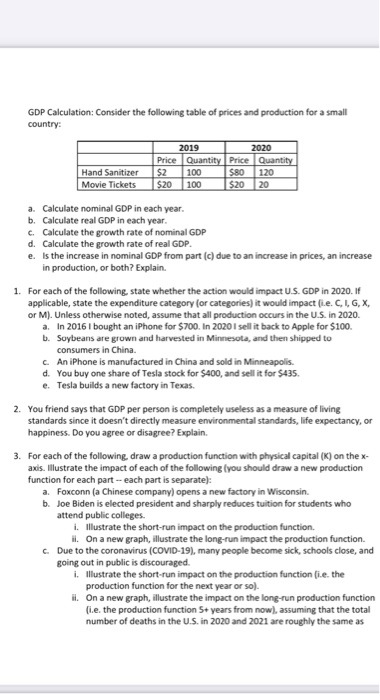

:Answer all questions.
After nearly five years with Coca-Cola, engineer Xiaorong "Shannon" You was getting downsized. Prosecutors allege that two days before her final shift in Atlanta, You gave herself a lucrative parting gift.
You uploaded to her Google Drive account confidential documents detailing trade secrets from six Coke vendors worth more than $100 million, according to a federal indictment and an FBI agent's testimony. It wasn't Coke's secret formula, but prosecutors say the records helped You win Chinese government funding to start a company making next-generation can coatings in a beverage industry segment that's worth $3 billion a year.
The case of You, who has pleaded not guilty, is just a pebble in an increasingly troubled terrain portrayed by U.S. trade players. Chinese companies, individuals and agents steal between $225 billion and $600 billion a year in U.S. intellectual property ranging from copying designs to make knock-off handbags to pirated music and movies to corporate America's most sensitive technologies, according to one outside estimate U.S. officials cite.
The first phase of a new U.S.-China trade pact ? signed Wednesday ? addresses issues such as protecting trade secrets and battling pirated and counterfeit goods, as well as providing U.S. companies and farmers with more access to Chinese markets. China also agreed to no longer force U.S. companies to transfer their technology to Chinese companies to enter that country's market.
Yet some longtime observers question if the deal changes much because they doubt the willingness of China's government to fix the issue.
"Meaningful mechanisms are not going to be accepted" by political leaders in China, predicted Fei-Ling Wang, a Georgia Tech professor of international affairs. "There will be great promises but the promises are likely to be, at best, partially implemented."
U.S. presidents and corporations have wrestled with the issue for decades, contending it eliminates American jobs, reduces business wealth and threatens innovation. The economic espionage is portrayed as so great, President Obama branded it an issue of national security. President Trump and lawmakers consider it a top priority in trade talks with China.
Federal officials launched an initiative two years ago specifically aimed at fighting Chinese theft of trade secrets. U.S. reports say the designs and formulas for technologies as diverse as proprietary corn seeds, pigments, turbines and semiconductors have been stolen, with tactics ranging from employees stealing documents to intercontinental hacking.
China's embassy in the U.S. did not respond to requests for comment from The Atlanta Journal-Constitution, but authorities have said they don't organize or encourage heists of corporate secrets. "China's technological achievements did not come from theft," a foreign ministry spokesman said late last year, according to Reuters.
You, a naturalized U.S. citizen born in China, is scheduled to stand trial in April in Tennessee. Her attorneys did not respond to requests for comment, but one, Thomas Jessee, said in an April court hearing that the government's case is overblown and that the documents You took weren't trade secrets.
Coke said in a written statement it has a "multi-layered security system" to protect against intellectual theft. It declined to comment on You's case.
You was arrested at her apartment in Lansing, Mich., last February. The apartment had no furniture, save for a folding chair and table and a mattress on the floor. FBI Special Agent Bill Leckrone told a judge in April that agents also found a bag with You's passport and thousands of dollars worth of cash in several currencies, including Chinese and Australian.
Thousand Talents
China is hardly the sole source of intellectual property theft. Last fall, a North Carolina man pleaded guilty in U.S. District Court in Savannah to conspiracy to steal anti-icing technology from aircraft companies.
In 2007, a former Coke secretary from Norcross was convicted of plotting to sell confidential documents to rival Pepsi for $1.5 million. Pepsi instead tipped off Coke. The FBI swooped in after collecting documents stuffed in an Armani bag.
Yet some experts in the U.S. familiar with corporate espionage say China stands out.
"Their economy is so ingrained with counterfeiting and thefts of trade secrets that even if they wanted to stop, it would be a devastating blow to their economy," said Vic Hartman, a former FBI agent who has investigated intellectual property theft and is the author of a book on fraud.
The FBI contends You left a trail.
Coke and many other companies have faced consumer angst over potential health threats from bisphenol A , a chemical used in a variety of consumer goods, including the coatings inside beverage cans. Before she was laid off, You worked on a Coke team assigned to select BPA-free coatings for future beverage containers.
You earned a Ph.D. in polymer science and engineering at Lehigh University in Pennsylvania. She was one of a few Coke researchers who interacted with companies competing to develop BPA-free coatings and had access to the vendors' confidential information, prosecutors allege.
In March 2017, prosecutors said You, an engineer at a Chinese firm and an unnamed person conspired for You to steal records and eventually put up a new company in China to develop BPA-free coatings.
But in June 2017, amid a broader corporate restructuring, You was told her job was being eliminated. Two months later, Special Agent Leckrone said You learned of a gap in Coke's systems that would allow her to bypass security and download files.
The Chinese company agreed that summer to sponsor You in a Chinese government-backed grant program known as Thousand Talents, according to court records. The program recruited foreign-trained Chinese scientists, engineers and others to return to their homeland to develop new technologies. You's associates also sponsored her for a second grant program run by a Chinese province, prosecutors allege.
U.S. Assistant Attorney General John Demers said in announcing You's indictment last year that China uses programs like Thousand Talents "to solicit and reward the theft of our nation's trade secrets."
Representatives of China's U.S. embassy as well as the Thousand Talents program did not respond to AJC emails requesting comment about allegations surrounding the program.
After You was let go from Coke, she got a job with Eastman Chemical in Kingsport, Tenn., where she also worked on BPA-free coatings.
Prosecutors allege she won the two grant programs and made multiple China trips to arrange the launch of a new company and forge joint ventures with her Chinese sponsors and Metlac, an Italian company. The government alleges You earned thousands of dollars in salary from the Chinese company while working for Eastman.
Text messages show You expressed interest in using her grant funds to acquire a beachfront apartment in the city of Weihai, the FBI's Leckrone testified.
You suspected she would be fired when Eastman became disenchanted with her work, and prosecutors said she again downloaded confidential records. Eastman detected the breach, fired You and seized her hard drive, prosecutors said.
Eastman officials later contacted the FBI after finding corporate documents belonging to six Coca-Cola vendors You previously worked with in her role at Coke, including Dow Chemical, Leckrone testified in the April hearing.
Jessee, You's attorney, argued the records weren't trade secrets. Some were older products, and others were publicly available records involving patented materials or products requiring public vetting through FDA approvals, he said.
Coca-Cola's global headquarters in Atlanta. (LEVETTE BAGWELL/AJC STAFF)
Concern 'verging on paranoia'?
Federal officials have traveled the nation urging companies to report international theft of secrets. But Elizabeth Rowe, a University of Florida law professor and expert in trade secret issues, said businesses often see little benefit from doing so.
Publicity could put the U.S. companies in an uncomfortable light, and they risk angering Chinese officials who could block access to a massive market and important suppliers.
China is one of the top markets for Coke. The company is banking on more business there, with Asia Pacific its fastest-growing region by drink volume.
"We recognize that there are trade issues between the United States and China that should be addressed," a Coke spokeswoman wrote to the AJC. "Our hope is that the two governments find creative solutions to effectively address those concerns. A trade war is not in either side's interest."
Meanwhile, U.S. law enforcement also is scrutinizing university-based researchers in the U.S. who are involved in Chinese-funded activities. The crackdown has raised broader questions about distinctions between important global collaboration among researchers and intellectual property theft.
Last year, Emory University dismissed two Chinese-born researchers involved in the search for a Huntington's disease treatment. Emory said they hadn't fully disclosed foreign research funding or the extent of work for research institutions in China. Like You, the researchers, a husband and wife team, were naturalized U.S. citizens.
Attorney Peter Zeidenberg, who represented the husband, declined to comment on the Emory case. But Zeidenberg, speaking generally, said federal authorities have been overly aggressive charging some researchers and others with Chinese ties.
"This concern, which is now verging on paranoia, has led them to prosecute people on the most trivial infractions while they are having the perverse effect of driving some of the most talented scientists in America back to China," he said.
Questions to be answered:
Do feel the United States is overreaching on the pursuit of this matter, why or why not?
2. How might have Coke protected themselves or improve their security? What impact may this have on the hiring process in the future?



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


