Answer all questions.,,,
Question 1 - a:
It's TRUE, because in an overheating economy, the aggregate demand becomes greater than the production capacity of the economy and this situation results in to inflation. In order to control the inflation the federal reserves would like to decrease the supply of money, so that the rising demand could be contained.
Question 1 - a-i:
Monetary policy measures:
Increase interest rates
Increase reserve requirements upon commercial banks
Increase statutory liquidity requirements upon commercial banks
Sell the government securities in open market operations
Increase the margin requirements
Question 1 - a-ii:
In light of the monetary policy measures taken above, the federal fund rate and short term interest rates, both will go up .
Question 1 - a-iii:
A measure of 'Selling' in open market operations:
will reduce commercial banks' reserves because depositors would like to withdraw their bank deposits and buy government securities
will reduce the federal funds rate because when commercial banks will have reduced reserves due to open market selling, those will be under pressure and Federal bank will help them by reducing the federal funds rate
will increase the bank loans because people would like to take cheap loans from bank and invest the money in government securities at higher interest rates.
Will decrease the money supply because 'selling' in open market will cause decrease in 'required reserves' with commercial banks.
Will cause the over-heating aggregate demand cool off.
Question 2:
In current economic recession caused by COVID-19 pandemic, the Fed is conducting expansionary monetary policy so that the demand could be revived.
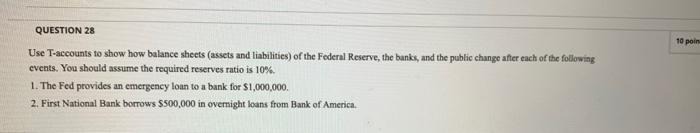
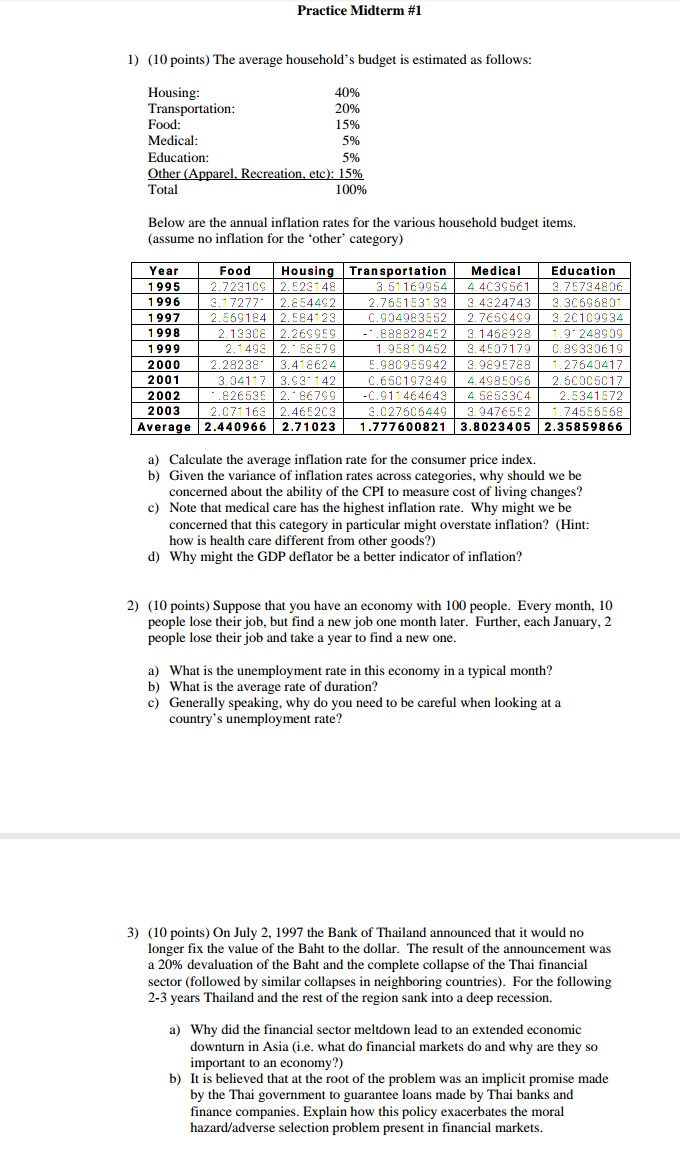
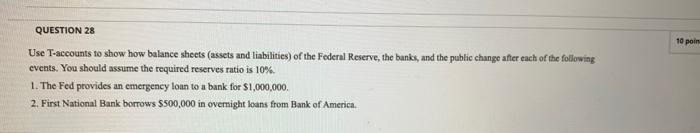
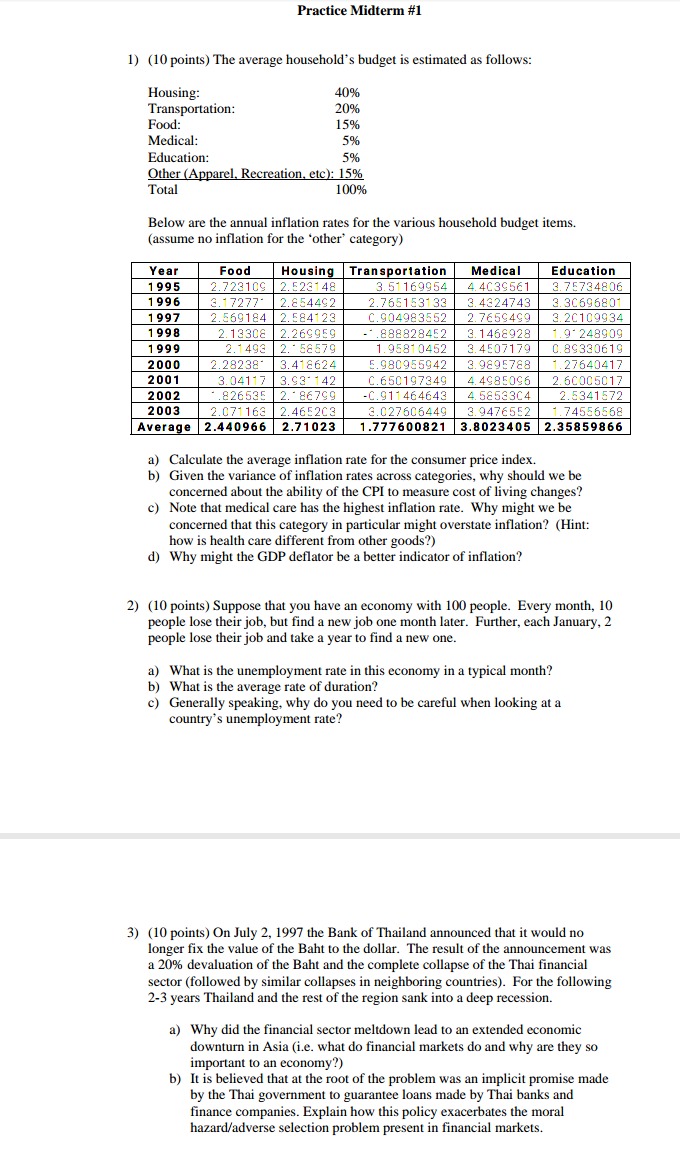
QUESTION 28 10 pain Use T-accounts to show how balance sheets (assets and liabilities) of the Federal Reserve, the banks, and the public change after each of the following events. You should assume the required reserves ratio is 10%. 1. The Fed provides an emergency loan to a bank for $1,000,000, 2. First National Bank borrows $500,000 in overnight loans from Bank of America.Practice Midterm #1 1) (10 points) The average household's budget is estimated as follows: Housing: 40% Transportation: 20% Food: 15% Medical: 5% Education: 5% Other (Apparel. Recreation, etc): 15% Total 100% Below are the annual inflation rates for the various household budget items. (assume no inflation for the 'other' category) Year Food Housing Transportation Medical Education 1995 2.723109 . E23148 3.51169954 4. 4039561 . 75734806 1996 2.17277. 2.854492 2.765153133 3. 4324743 B. 30696801 1997 2.569184 2. 584123 C. 904983552 7659499 3. 20109934 1998 2. 13 308 2.269959 882828452 3.1468928 9 248909 1999 2.1493 2. - 58579 1. 9581 0452 3. 4507179 0. 89330619 2000 2.28238. 3. 418624 . 980955942 2.9895788 1. 27640417 2001 3.04117 3. 93- 142 C. 650197349 4. 4985096 2. 50005017 2002 826535 86799 C. 911464643 4. 5852304 2.5341572 2003 2.071163 2.465203 3. 027606449 3.9476552 1. 74556568 Average 2.440966 2.71023 1.777600821 3.8023405 2.35859866 a) Calculate the average inflation rate for the consumer price index. b) Given the variance of inflation rates across categories, why should we be concerned about the ability of the CPI to measure cost of living changes? c) Note that medical care has the highest inflation rate. Why might we be concerned that this category in particular might overstate inflation? (Hint: how is health care different from other goods?) d) Why might the GDP deflator be a better indicator of inflation? 2) (10 points) Suppose that you have an economy with 100 people. Every month, 10 people lose their job, but find a new job one month later. Further, each January, 2 people lose their job and take a year to find a new one. a) What is the unemployment rate in this economy in a typical month? b) What is the average rate of duration? c) Generally speaking, why do you need to be careful when looking at a country's unemployment rate? 3) (10 points) On July 2, 1997 the Bank of Thailand announced that it would no longer fix the value of the Baht to the dollar. The result of the announcement was a 20% devaluation of the Baht and the complete collapse of the Thai financial sector (followed by similar collapses in neighboring countries). For the following 2-3 years Thailand and the rest of the region sank into a deep recession. a) Why did the financial sector meltdown lead to an extended economic downturn in Asia (i.e. what do financial markets do and why are they so important to an economy?) b) It is believed that at the root of the problem was an implicit promise made by the Thai government to guarantee loans made by Thai banks and finance companies. Explain how this policy exacerbates the moral hazard/adverse selection problem present in financial markets