Question
Answer all the following questions: Q1. Many physical topologies are used to build networks. Compare between the Star topology and the Ring topology (in terms
Answer all the following questions:
Q1. Many physical topologies are used to build networks. Compare between the Star topology and the Ring topology (in terms of cost, reliability, performance, ) [1.5 Marks]
Q2. Explain how layered network architectures are working by implementing encapsulation and de-encapsulation mechanisms. Use a layered architecture of 4 layers as example. [1.5 Marks]
Q3. Compare between TCP/IP and OSI layered models. [1.5 Marks]
Q4. In a TCP/IP communication 4 different types of addresses are needed to establish a communication between two devices. Explain and justify why each of these types of addresses is needed. [1.5 Marks]
Q5. Assume the following signal in the frequency domain plot: [2 Marks]
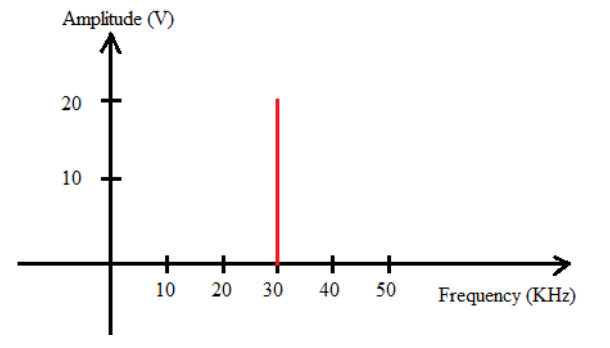
Q5.a. What is the amplitude of this signal?
Q5.b. What is the frequency of this signal?
Q5.c. Calculate the period of this signal.
Q5.d. Is this signal periodic or non periodic? Justify your answer.
Q5.e. Is this signal digital or analog? Justify your answer.
Q6. A periodic signal is composed of five sine waves with frequencies of 100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 MHz. [1.5 Marks]
Q6.a. Draw the frequency domain plot of this signal, assuming the first three components (lowest frequencies) have a maximum amplitude of 10 V and that the last two components have a maximum amplitude of 5 V.
Q6.b. Calculate the Bandwidth of the signal.
Q7. We have a low-pass channel with a bandwidth of 100 MHz. [1 Marks]
Q7.a. Calculate the maximum bit rate of this channel if baseband transmission is used?
Q7.b. Explain how the bit rate will decrease if we opt for more accuracy by increasing the number of harmonics.
Q8. Suppose a signal travels through a transmission medium and its power is reduced to one-quarter. [1 Mark]
Q8.a Calculate the attenuation of the signal.
Q8.b What is the solution to increase the power of the signal?
Q9. The SNRdB of a signal is equal to 60. [1 Mark]
Q9.a Calculate the value of SNR
Q9.b Calculate the power of the signal if the power of the noise is equal to 20W.
Q10. We have a channel with a 10-GHz bandwidth. The SNR for this channel is 1027. [1 Mark]
Q10.a Calculate the appropriate bit rate for this channel.
Q10.b Calculate the number of signal levels?
Q11. We need to send a message of size 100 Kbytes through a network of a bandwidth of 1 Mbps. We assume that the distance between the sender and the receiver is 2,000 km and that the propagation speed is 1.2 108 m/s. [1 Mark]
Q11.a Calculate the propagation time.
Q11.b Calculate the transmission time.
Q11.c Deduce the latency if the processing time and queuing time are equal to zero
Q12. We use 2B1Q multilevel line encoding scheme. [1.5 Marks]
Q12.a. Using the transition table below, draw the transmitted signal if the bit sequence to send is 1011110100100101. Assume the original level is positive. Your sketch should be carefully labelled.
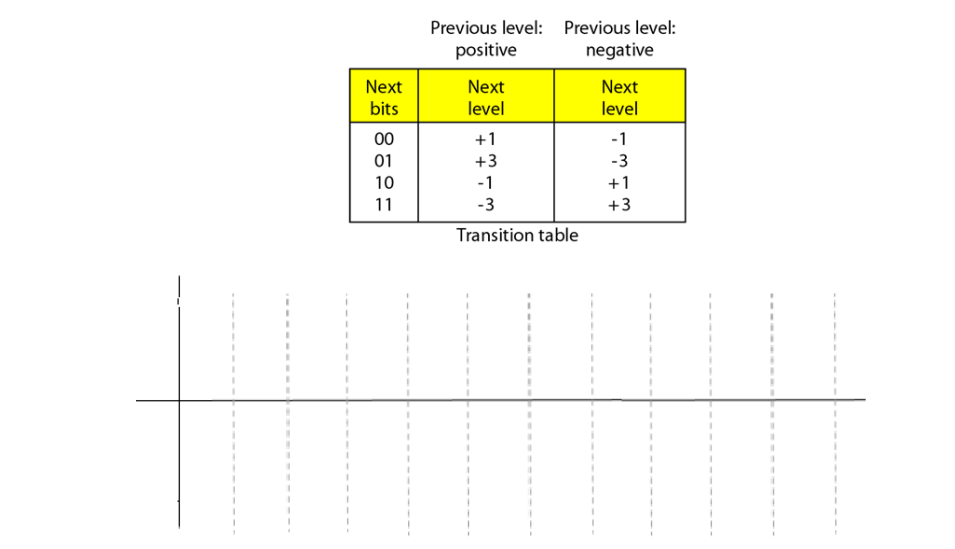 Q12.b. What is the value of r in this case (ratio between data elements and signal elements)?
Q12.b. What is the value of r in this case (ratio between data elements and signal elements)?
Q12.c. Calculate the average Baud rate if the bit rate is equal to 120 Kbps.
Q12.d. Is this line encoding scheme able to ensure self-synchronization? Justify your answer.
Q13. Assume we use PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) for an analog to digital signal conversion. [1.5 Marks]
Q13.a. Calculate the value of the sampling rate if the maximum frequency of the signal is 10 MHz.
Q13.b. Assume we have a voltage signal with amplitudes Vmin=-10V and Vmax=+10V. We want to use 16 quantization levels. - What are the quantization zones and their midpoints in this case? - What is the number of bits required to encode the zones?
Q13.c. Discuss the impact of the number of zones on the quantization error and the required medium capacity.
Q14. We need to send data 4 bits at a time at a bit rate of 8 Mbps using Multilevel Frequency Shift Keying. The carrier frequency is 100 MHz. [1 Mark]
Q14.a. Calculate the number of levels needed (different frequencies)
Q14.b. Calculate the baud rate and the bandwidth in this case
Q15. The following figure present the performance of an Unshielded Twisted Pair cable. [1.5 Marks]
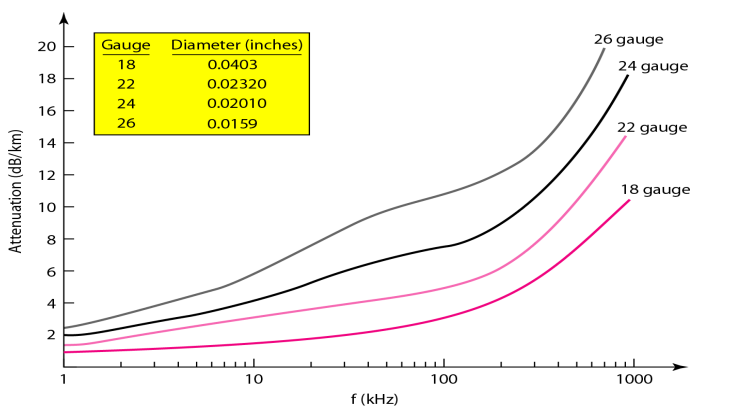
Q15.a Using the figure above, deduce the value of the attenuation (in dB/Km) if the frequency of the transmitted signal is 10 KHz using 26 Gauge cable?
Q15.b Assuming the value of the attenuation calculated in question a, and using a 6 Km long cable, if the signal at the end of the cable has a power of 10 mW, what is the power of the signal at the beginning of the cable?
IIdIsItivil LavieStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


