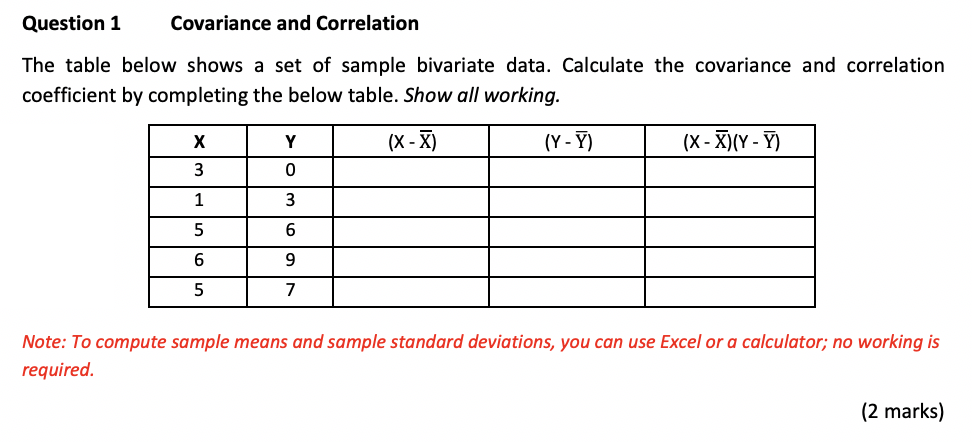
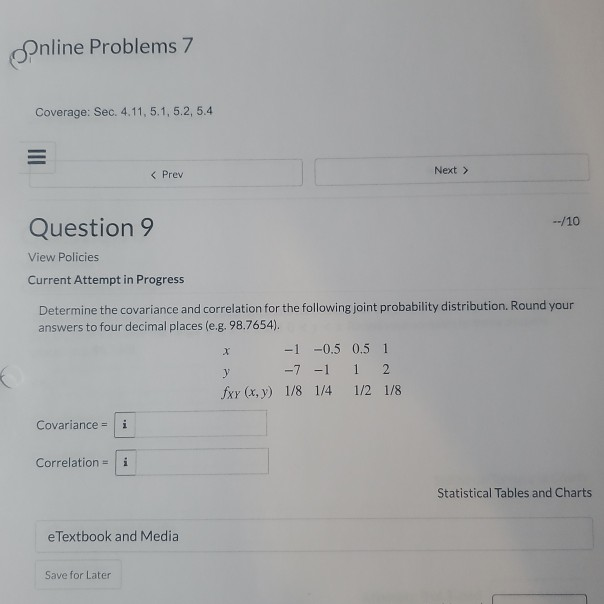
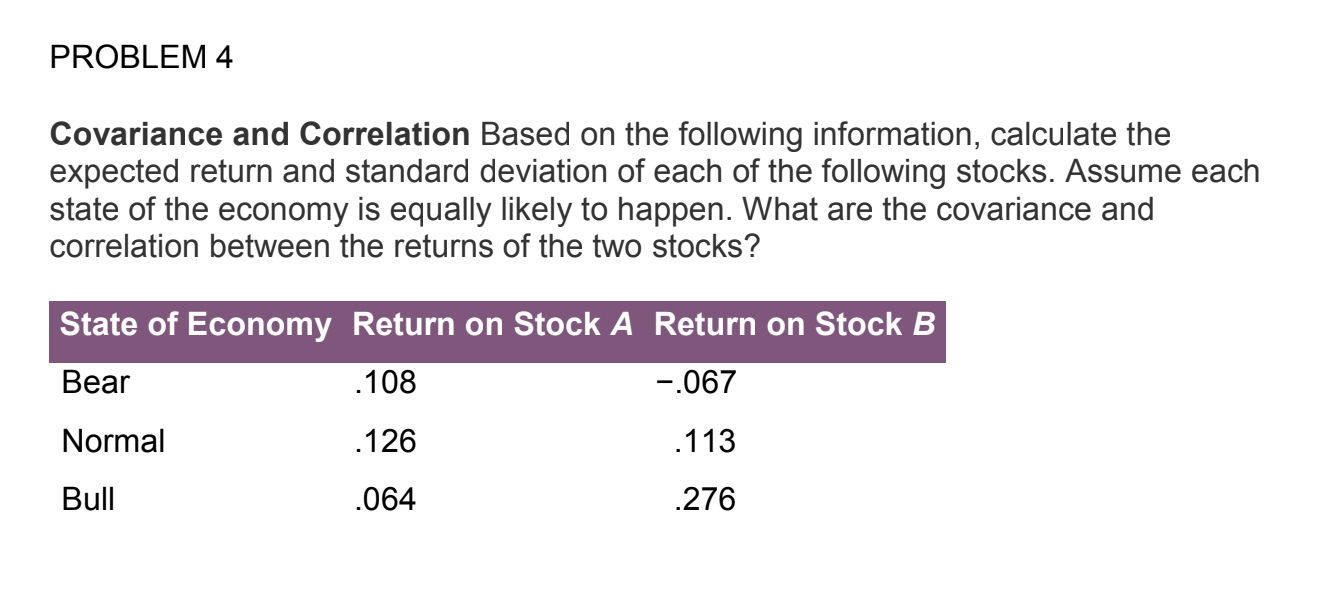
Question
Answer all You are at a table at a casino with a gambling game. In the game you spin two spinners. Spinner #1 has 4
Answer all
You are at a table at a casino with a gambling game. In the game you spin two spinners. Spinner #1 has 4 equal spaces numbered 1,2,3,4. Spinner #2, has only two equal spaces with the numbers 1 and 3. To play the game, you have to pay $4 dollars. Regardless of whether you win or lose you have to pay the $4. There are two different bets you can make that are related to the sum of the two spins (number from Spinner #1 + number from Spinner #2). Shown below are the two different bets and amounts associated with winning each.
?
Bet 1: You win $8 if the sum of Spinner #1 and Spinner #2 is less than 5?
Bet 2: You win $12 if the sum of Spinner #1 and Spinner #2 is greater than 5?
What is the sample space? Hint: this is the number of different outcomes where order does matter. So getting a 1 on Spinner #1 and 3 on Spinner #2 is a distinct outcome from the reverse.?
What is the probability of winning Bet 1? What is the probability of winning Bet 2??
What is the expected value of Bet 1? What is the expected value of Bet 2? Which is the better bet? Would you break even (i.e. not lose any money) with either bet??
For Bet 2, how much would you have to earn to exactly break even (neither lose nor win money in expectation)??
Now imagine for Bet 1 you only have to pay the $4 to play if you lose. What is the expected value of Bet 1 now? Would you break even??



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


