
Answer appropriately
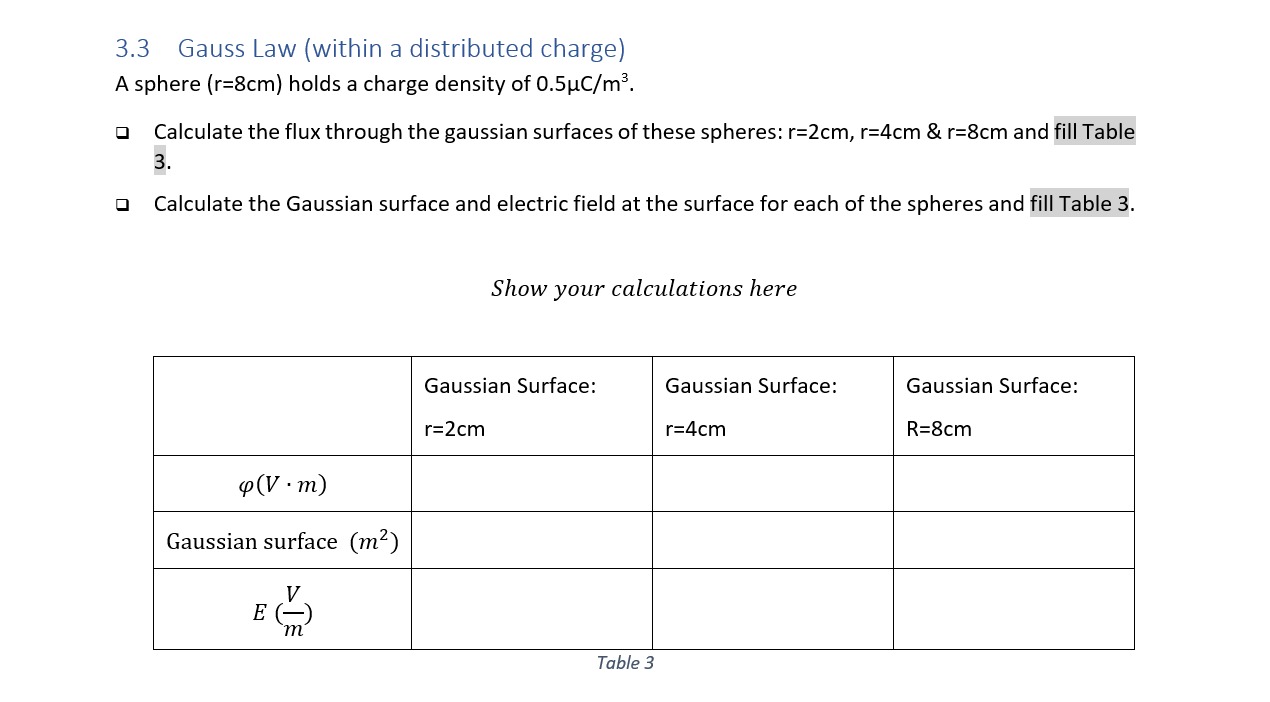
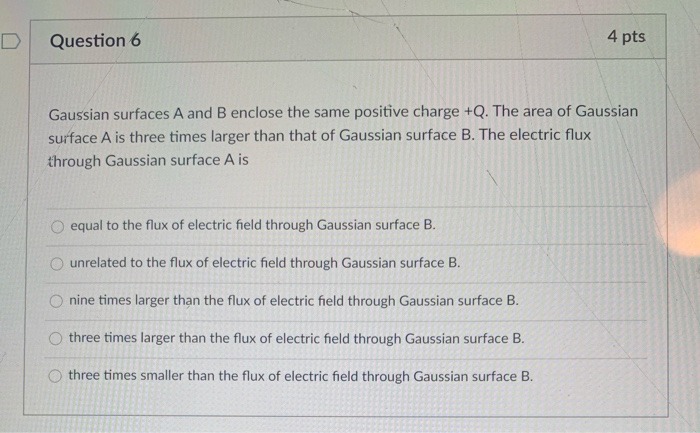
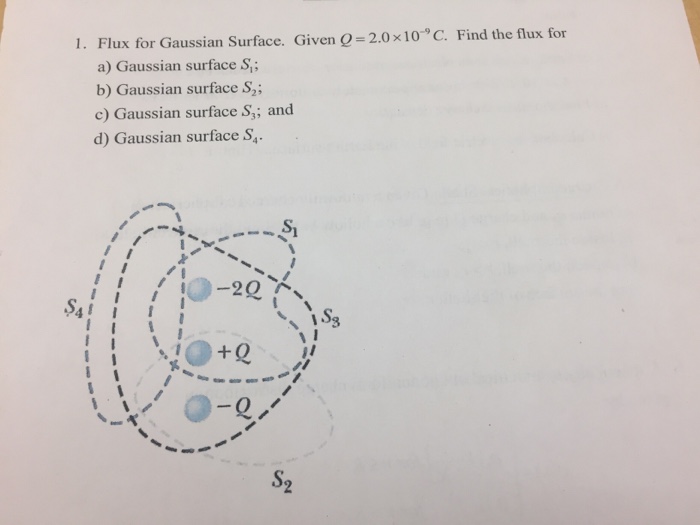
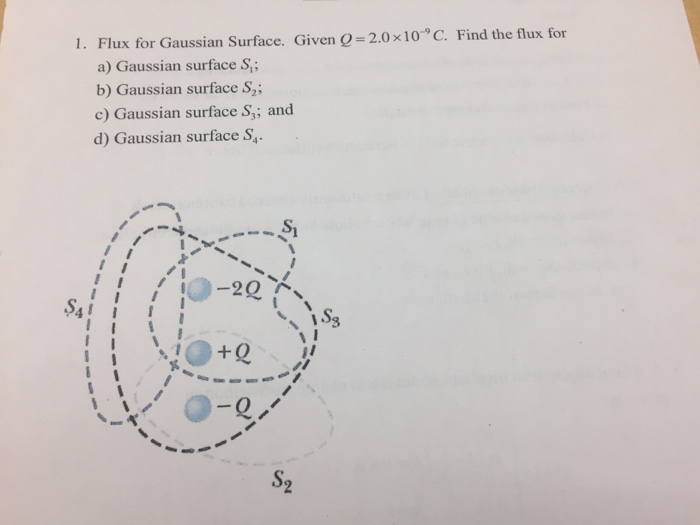
3.3 Gauss Law (within a distributed charge) A sphere (r=8cm) holds a charge density of 0.5uC/m3. 0 Calculate the flux through the gaussian surfaces of these spheres: r=2cm, r=4cm & r=8cm and fill Table 3. 0 Calculate the Gaussian surface and electric field at the surface for each of the spheres and fill Table 3. Show your calculations here Gaussian Surface: Gaussian Surface: Gaussian Surface: r=2cm r=4cm R=8cm 4(V . m) Gaussian surface (m2) m Table 3Question 6 4 pts Gaussian surfaces A and B enclose the same positive charge +Q. The area of Gaussian surface A is three times larger than that of Gaussian surface B. The electric flux through Gaussian surface A is O equal to the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. O unrelated to the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. O nine times larger than the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. O three times larger than the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. O three times smaller than the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B.1. Flux for Gaussian Surface. Given O =2.0 x10 *C. Find the flux for a) Gaussian surface S,; b) Gaussian surface S,; c) Gaussian surface S,; and d) Gaussian surface S, -20 SA + Q5) The figure shows electric field lines arising from two small charged particles P and Q. Consider the following two statements: (i) The charge on P is smaller than the charge on Q. (ii) The electrostatic force on P is smaller than the force on Q. Which of the above statements are true? A) Only (i) is true. B) Only (ii) is true. C) Both (i) and (ii) are true. D) Neither (i) nor (ii) is true. 6) Gaussian surfaces A and B enclose the same positive charge +Q. The area of Gaussian surface A is three times larger than that of Gaussian surface B. The electric flux through Gaussian surface A is A) three times smaller than the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. B) unrelated to the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. C) nine times larger than the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. D) three times larger than the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. E) equal to the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B. 7) A solid aluminum cube rests on a wooden table in a region where a uniform external electric field is directed straight upward. What can we say concerning the charge on the top surface of the cube? A) The top surface is neutral. B) The top surface is charged positively. C) The top surface is charged negatively. D) The top surface's charge cannot be determined without further information