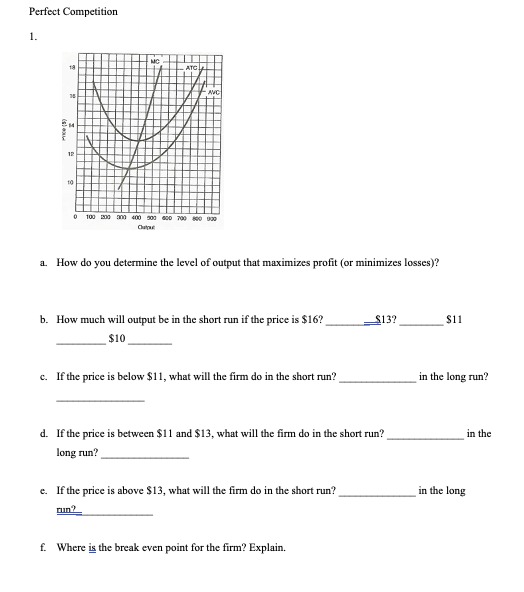
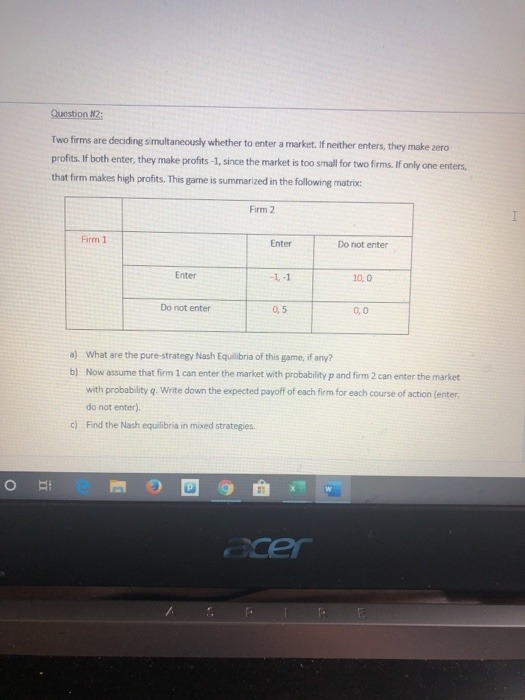
Answer by providing step by step explanations to the following.
1. The demand curve for hotel rooms is Qd = 1000-5Pp and the supply curve is Qs = 200+3Ps, where Qd is the quantity demanded and Qs is the quantity supplied, Pp is the price paid by buyers and Ps is the price received by sellers. Using the information above, find equilibrium Price and Quantity for Hotel Rooms 2. In Heartland, the minimum wage is currently $4.00 per hour and the fast-food industry is the only industry that pays the minimum wage. 50% of the workers in the industry are between 16 and 21 years old. The president of Heartland, concerned about decreasing the proportion of families with incomes below the poverty line, proposes increasing the minimum wage by 20%. a. Assume the labor market for low skilled workers is perfectly competitive. Explain why an increase in the minimum wage might reduce employment in the fast-food industry. b. Use supply and demand analysis to describe the likely effect of this increase in the minimum wage on the price and quantity sold of meals at fast-food restaurants? c. If an increase in the Minimum Wage will cause the Equilibrium Quantity of Minimum Wage Labor to decrease, would you then suggest that the Minimum Wage should not be increased? Why or Why not?Perfect Competition 1. ATG! a. How do you determine the level of output that maximizes profit (or minimizes losses)? b. How much will output be in the short run if the price is $16? $13? $11 $10 c. If the price is below $11, what will the firm do in the short run? in the long run? d. If the price is between $11 and $13, what will the firm do in the short run? in the long run? c. If the price is above $13, what will the firm do in the short run? in the long f. Where is the break even point for the firm? Explain.Question #2; Two firms are deciding simultaneously whether to enter a market. If neither enters, they make zero profits. If both enter, they make profits -1, since the market is too small for two firms. If only one enters, that firm makes high profits. This game is summarized in the following matrix: Firm 2 H Firm 1 Enter Do not enter Enter -1, -1 10, 0 Do not enter 0. 5 al. What are the pure-strategy Nash Equilibria of this game, if any? by Now assume that firm 1 can enter the market with probability p and firm 2 can enter the market with probability q. Write down the expected payoff of each firm for each course of action (enter, do not enter). cl Find the Nash equilibria in mixed strategies. O e P W acerwill have to sell the property at a loss. Prots (in thousands of dollars) are shown in the following payoff table: State of Nature Rezoning Approved Rezoning Not Approved Decision Alternative .31 3'2 Purchase, ch 600 - 200 Do not purchase, d2 0 0 a. If the probability that the rezoning will be approved is 0.5, what decision is recom- mended? What is the expected prot? b. The investor can purchase an option to buy the land. Under the Option, the investor maintains the rights to purchase the land anytime during the next three months while learning more about possible resistance to the rezoning prOposal from area residents. Probabilities are as follows: Let H = High resistance to rezoning L = Low resistance to rezoning P(H) = 0.55 P(sl l H) = 0.18 P(sZIH) = 0.82 P(L) = 0.45 Pm l L) = 0.39 13(52 | r.) = 0.11 What is the optimal decision strategy if the investor uses the option period to learn more about the resistance from area residents before making the purchase decision? c. If the option will cost the investor an additional $10,000, should the investor purchase the option? Why or why not? What is the maximum that the investor should he will- ing to pay for the option