Answer odd questions only
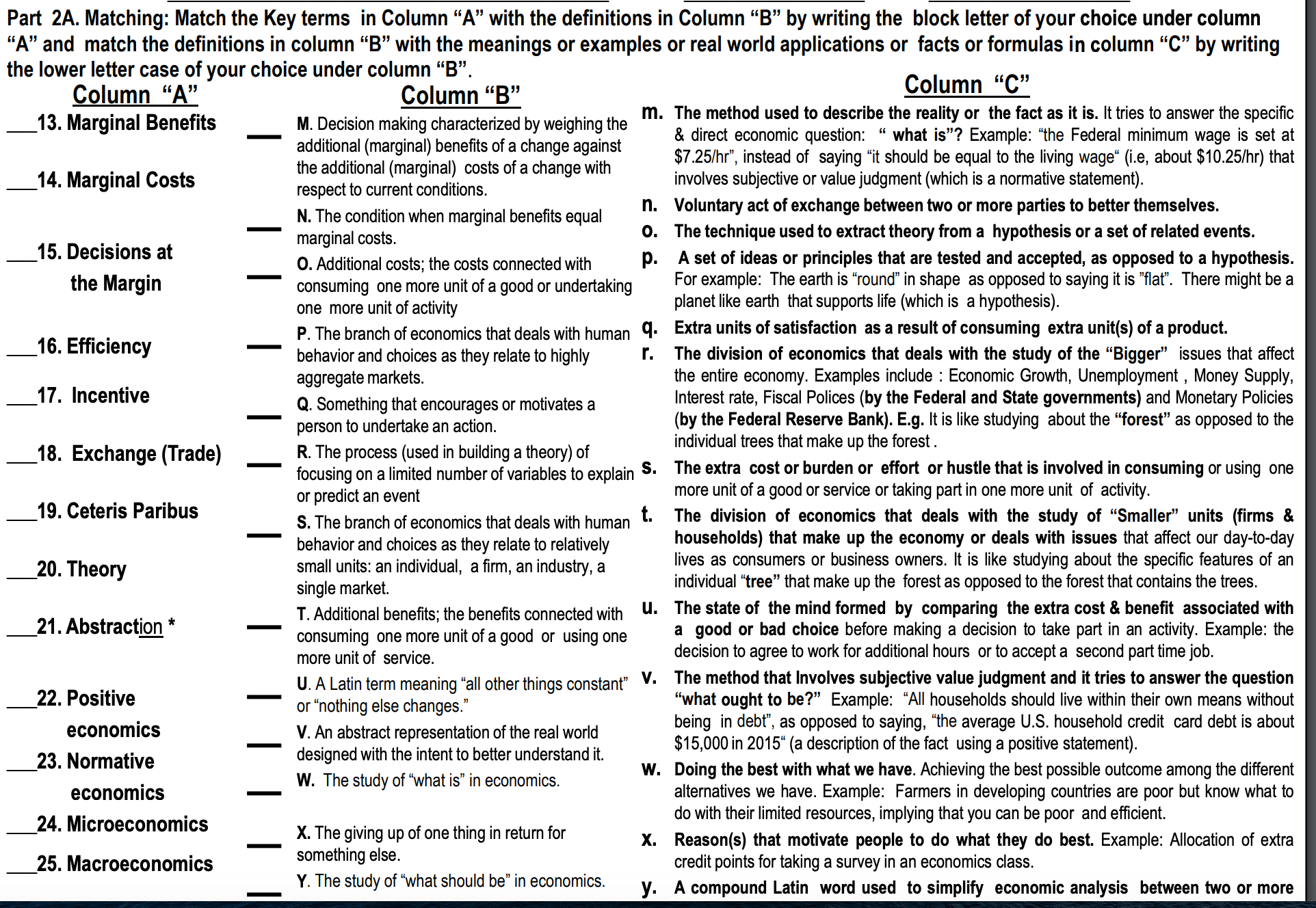
Part 2A. Matching: Match the Key terms in Column "A" with the definitions in Column "B" by writing the block letter of your choice under column "A" and match the definitions in column "B" with the meanings or examples or real world applications or facts or formulas in column "C" by writing the lower letter case of your choice under column "B". Column "A" Column "B" Column "C" 13. Marginal Benefits M. Decision making characterized by weighing the . The method used to describe the reality or the fact as it is. It tries to answer the specific additional (marginal) benefits of a change against & direct economic question: " what is"? Example: "the Federal minimum wage is set at 14. Marginal Costs the additional (marginal) costs of a change with $7.25/hr", instead of saying "it should be equal to the living wage" (i.e, about $10.25/hr) that respect to current conditions involves subjective or value judgment (which is a normative statement). N. The condition when marginal benefits equal n. Voluntary act of exchange between two or more parties to better themselves. 15. Decisions at marginal costs. O. The technique used to extract theory from a hypothesis or a set of related events. O. Additional costs; the costs connected with . A set of ideas or principles that are tested and accepted, as opposed to a hypothesis. the Margin consuming one more unit of a good or undertaking For example: The earth is "round" in shape as opposed to saying it is "flat". There might be a one more unit of activity planet like earth that supports life (which is a hypothesis). 16. Efficiency P. The branch of economics that deals with human q. Extra units of satisfaction as a result of consuming extra unit(s) of a product. behavior and choices as they relate to highly r. The division of economics that deals with the study of the "Bigger" issues that affect 17. Incentive aggregate markets. the entire economy. Examples include : Economic Growth, Unemployment , Money Supply, Q. Something that encourages or motivates a Interest rate, Fiscal Polices (by the Federal and State governments) and Monetary Policies person to undertake an action. (by the Federal Reserve Bank). E.g. It is like studying about the "forest" as opposed to the 18. Exchange (Trade) R. The process (used in building a theory) of individual trees that make up the forest . focusing on a limited number of variables to explain S. The extra cost or burden or effort or hustle that is involved in consuming or using one 19. Ceteris Paribus or predict an event more unit of a good or service or taking part in one more unit of activity. S. The branch of economics that deals with human t. The division of economics that deals with the study of "Smaller" units (firms & behavior and choices as they relate to relatively households) that make up the economy or deals with issues that affect our day-to-day 20. Theory small units: an individual, a firm, an industry, a lives as consumers or business owners. It is like studying about the specific features of an single market. Individual "tree" that make up the forest as opposed to the forest that contains the trees. 21. Abstraction * T. Additional benefits; the benefits connected with U. The state of the mind formed by comparing the extra cost & benefit associated with consuming one more unit of a good or using one a good or bad choice before making a decision to take part in an activity. Example: the more unit of service. decision to agree to work for additional hours or to accept a second part time job. 22. Positive U. A Latin term meaning "all other things constant" V. The method that Involves subjective value judgment and it tries to answer the question or "nothing else changes." 'what ought to be?" Example: "All households should live within their own means without economics V. An abstract representation of the real world being in debt , as opposed to saying, "the average U.S. household credit card debt is about 23. Normative designed with the intent to better understand it. $15,000 in 2015" (a description of the fact using a positive statement) W. Doing the best with what we have. Achieving the best possible outcome among the different economics W. The study of "what is" in economics. alternatives we have. Example: Farmers in developing countries are poor but know what to 24. Microeconomics X. The giving up of one thing in return for do with their limited resources, implying that you can be poor and efficient. X. Reason(s) that motivate people to do what they do best. Example: Allocation of extra 25. Macroeconomics something else. Y. The study of "what should be" in economics. credit points for taking a survey in an economics class. y. A compound Latin word used to simplify economic analysis between two or more