
Answer Questions 1 - 7
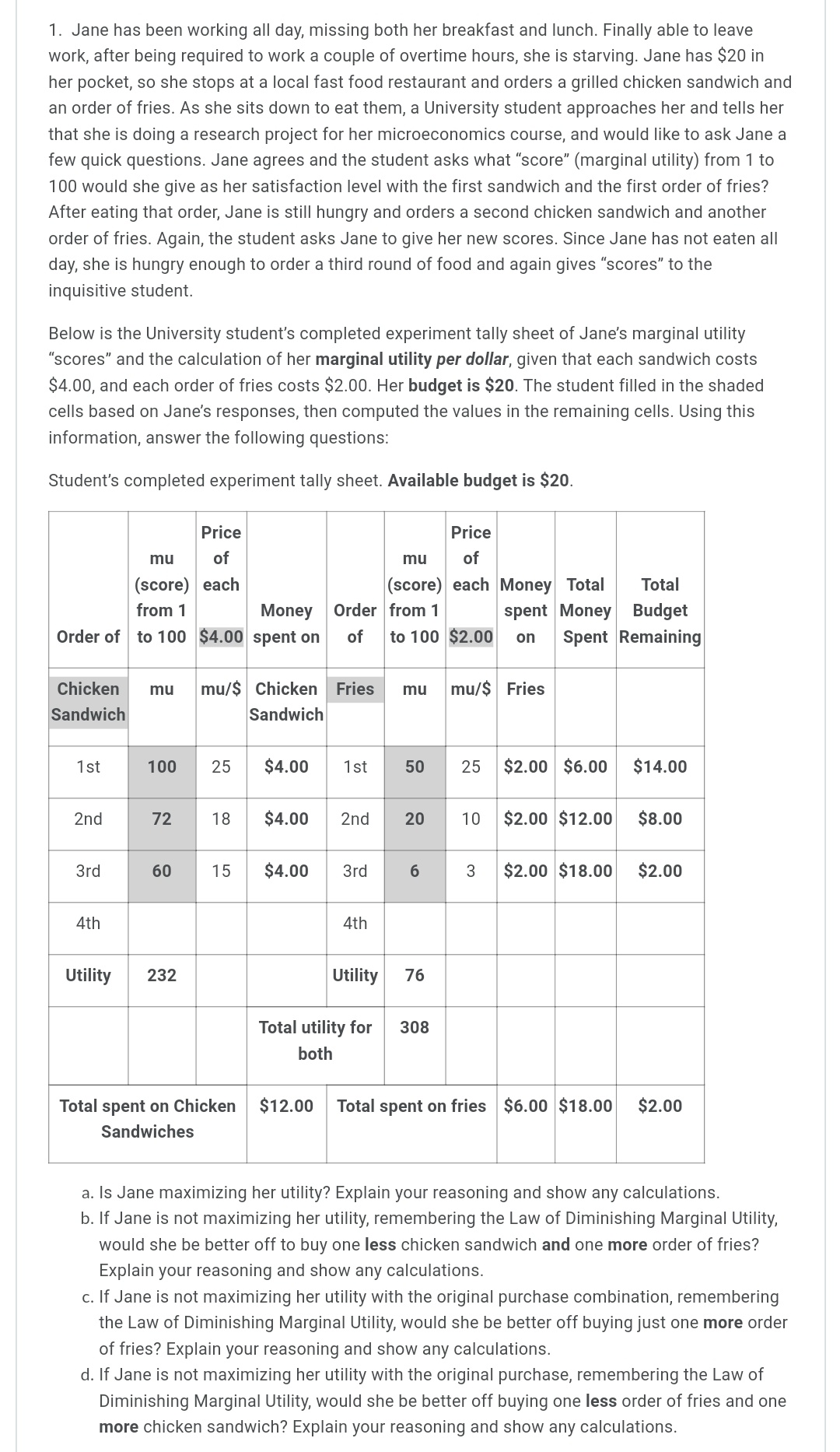
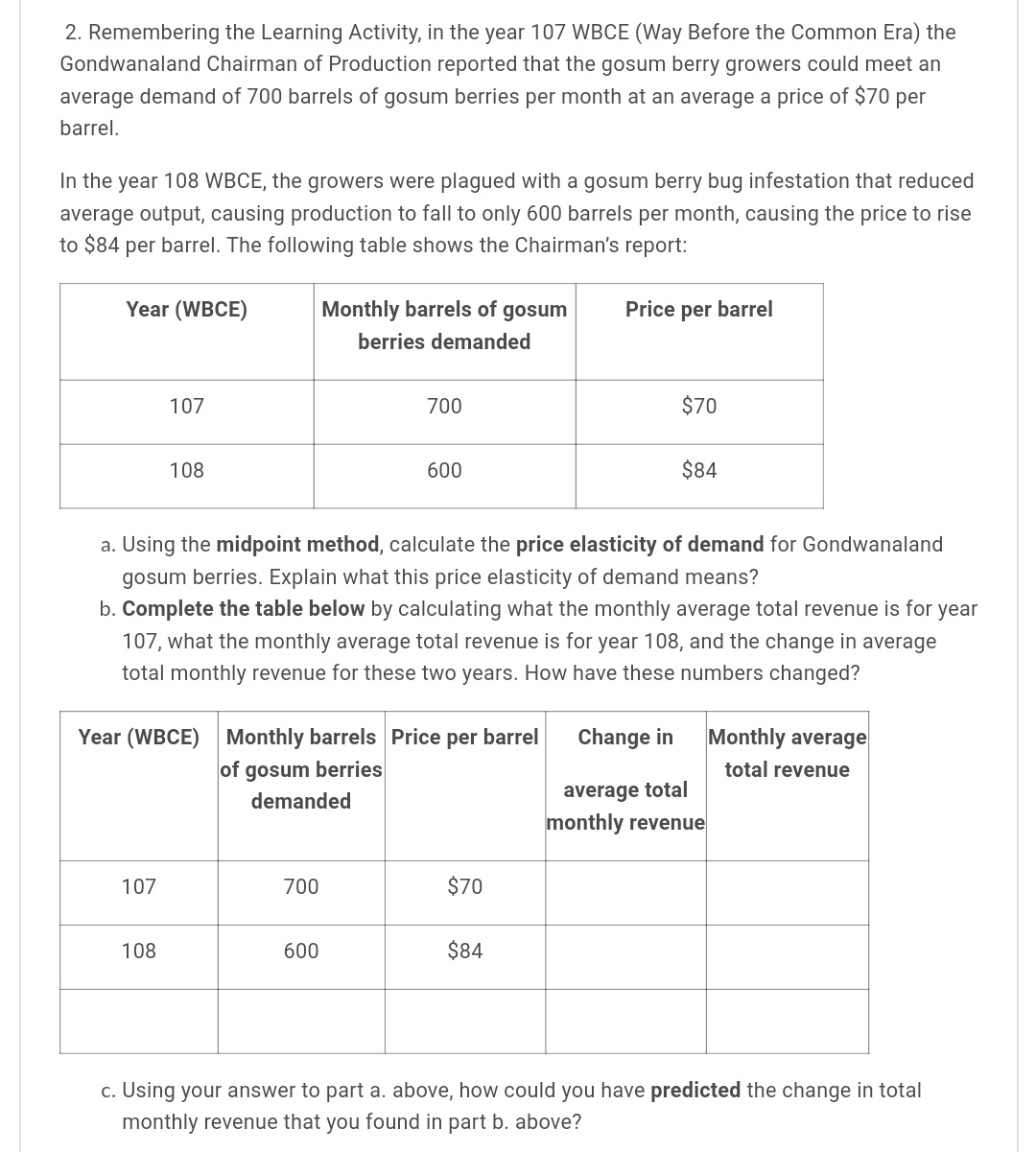
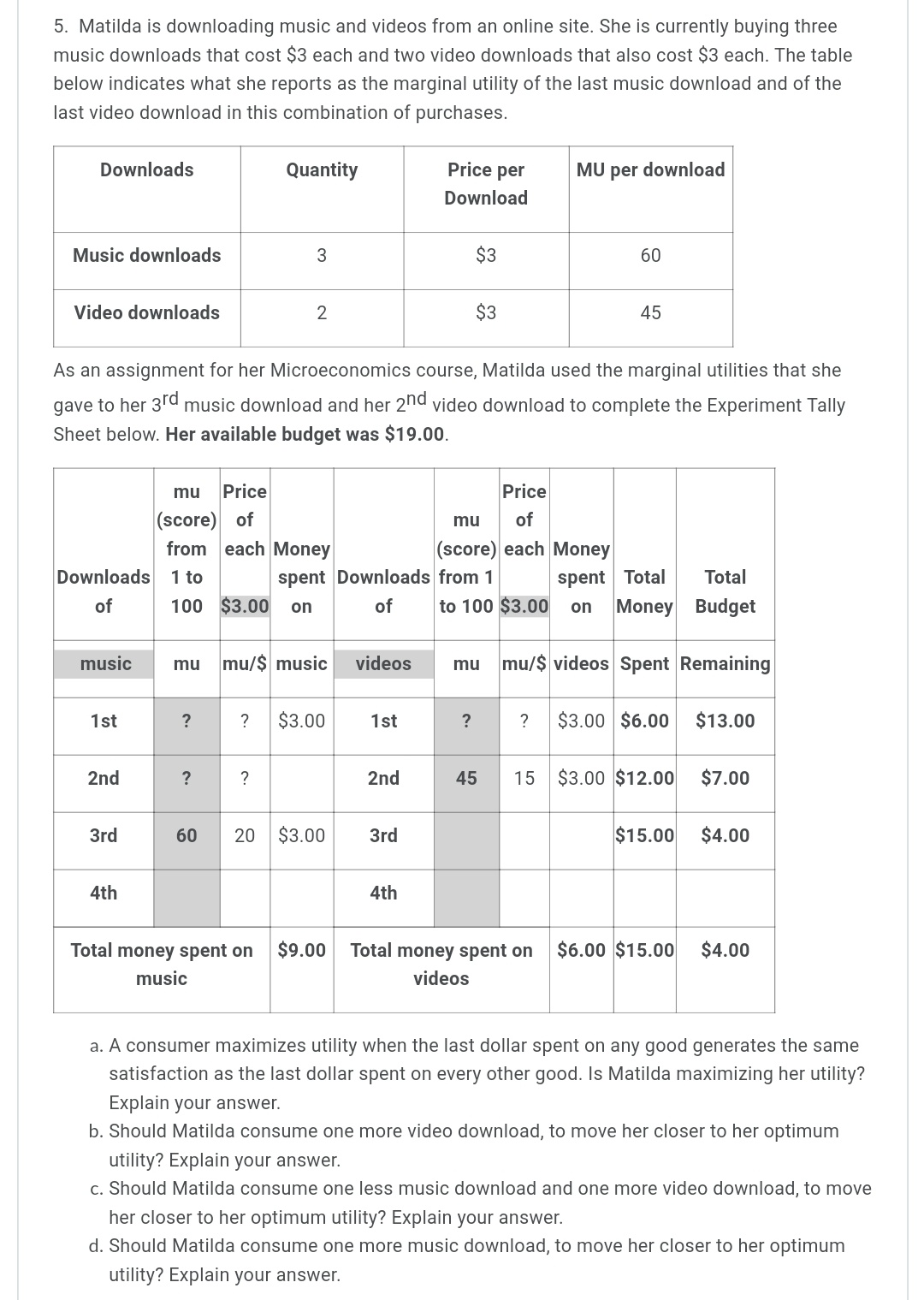
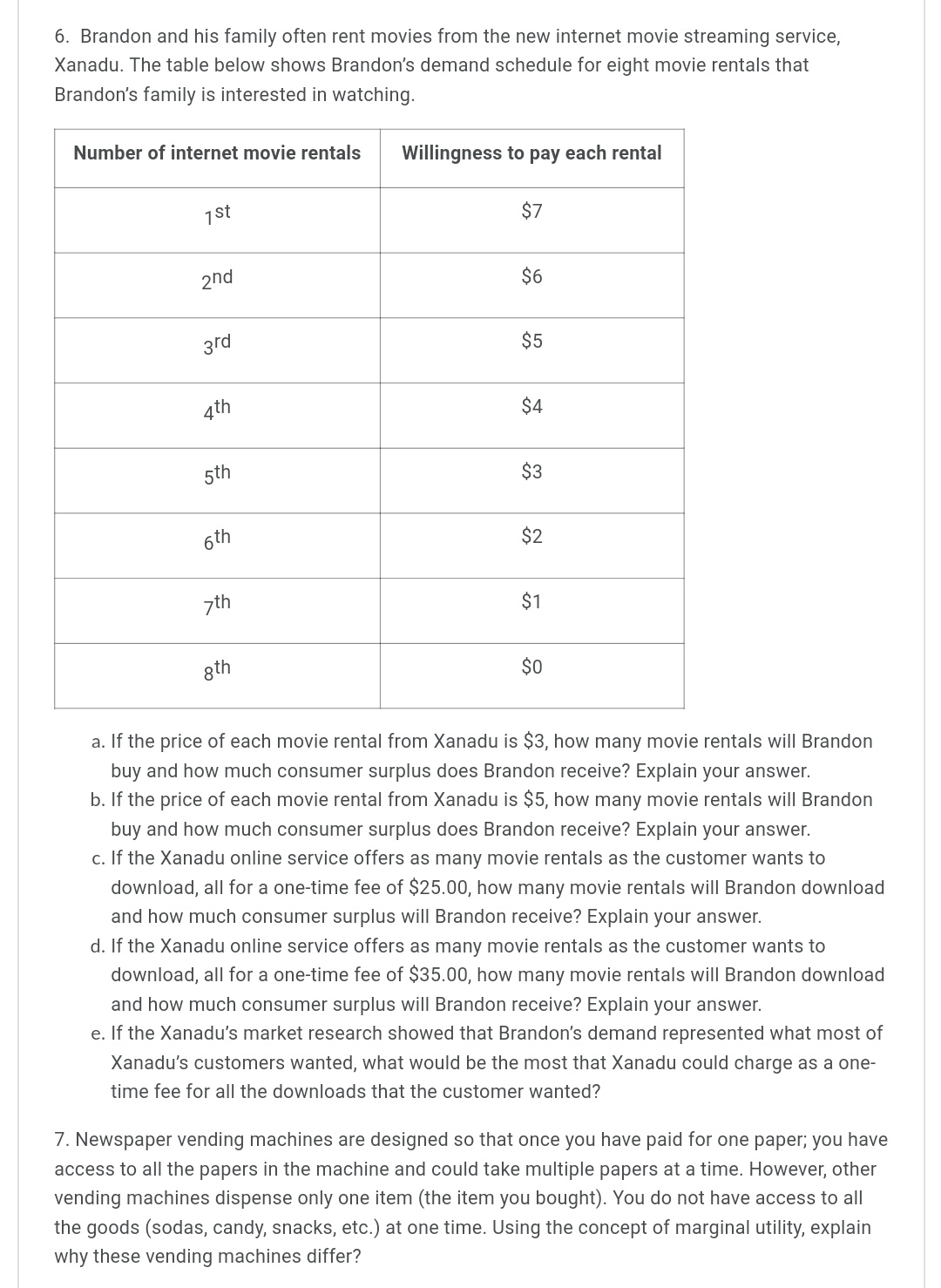
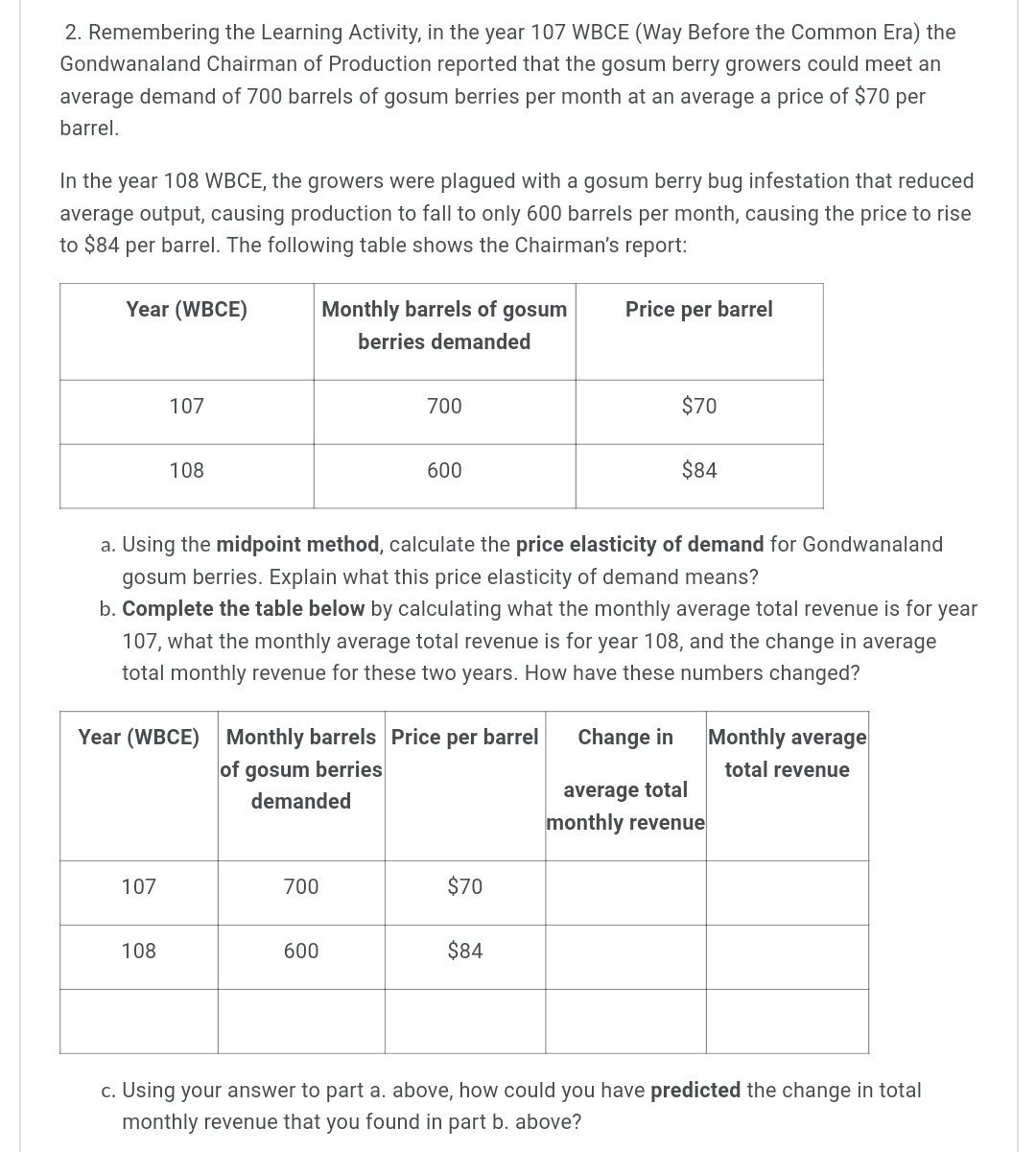
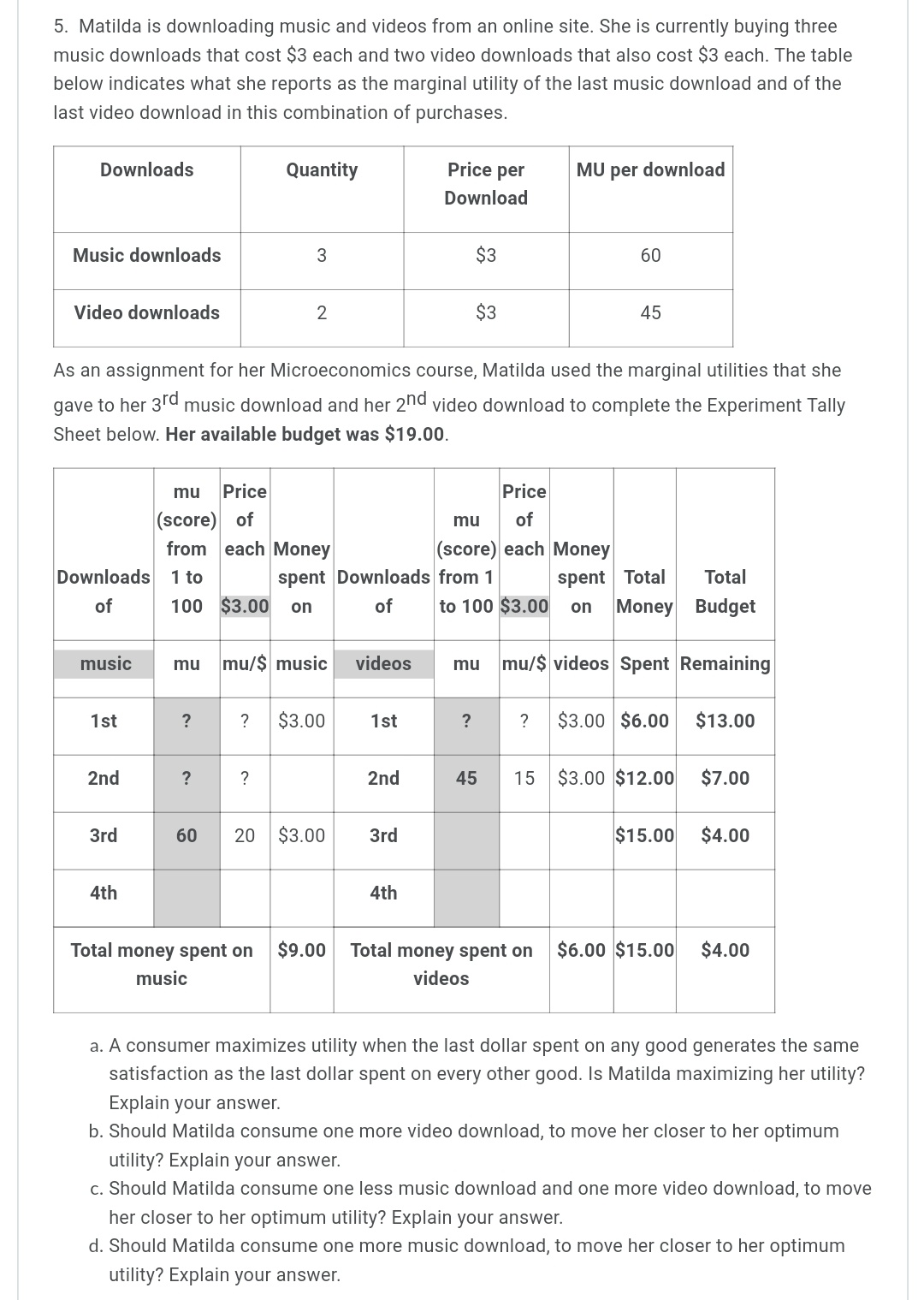
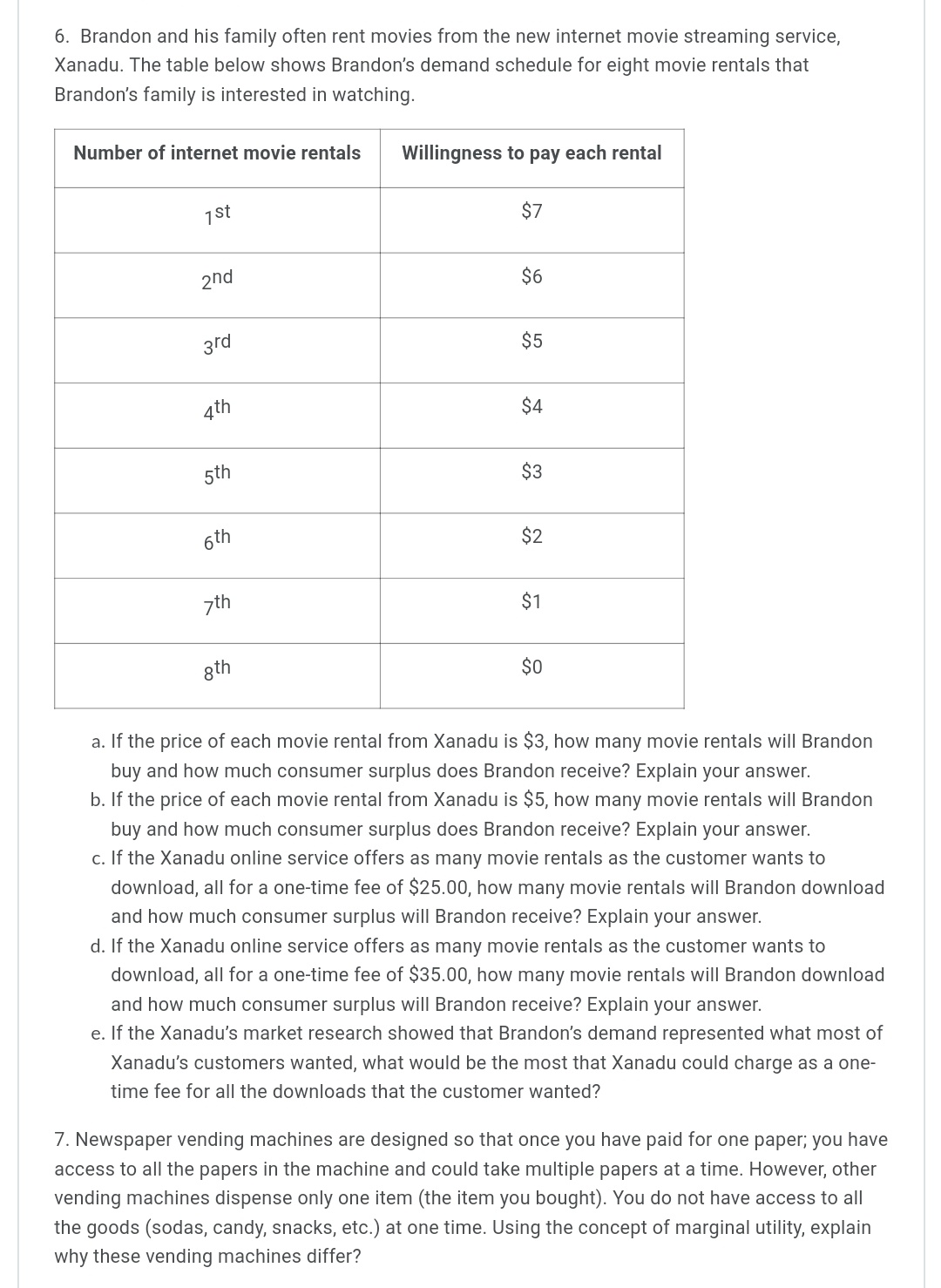
1. Jane has been working all day, missing both her breakfast and lunch. Finally able to leave work, after being required to work a couple of overtime hours, she is starving. Jane has $20 in her pocket, so she stops at a local fast food restaurant and orders a grilled chicken sandwich and an order of fries. As she sits down to eat them, a University student approaches her and tells her that she is doing a research project for her microeconomics course, and would like to ask Jane a few quick questions. Jane agrees and the student asks what "score" (marginal utility) from 1 to 100 would she give as her satisfaction level with the first sandwich and the first order of fries? After eating that order, Jane is still hungry and orders a second chicken sandwich and another order of fries. Again, the student asks Jane to give her new scores. Since Jane has not eaten all day, she is hungry enough to order a third round of food and again gives "scores'r to the inquisitive student. Below is the University student's completed experiment tally sheet of Jane's marginal utility "scores'r and the calculation of her marginal utility per dollar, given that each sandwich costs $4.00, and each order of fries costs $2.00. Her budget is $20. The student filled in the shaded cells based on Jane's responses, then computed the values in the remaining cells. Using this information, answer the following questions: Student's completed experiment tally sheet. Available budget is $20. Price Price rnu of mu of (score) each (score) each Money Total Total from1 Money Order from1 spent Money Budget Order of to100 $4.00 spenton of t0100 $2.00 on Spent Remaining chicken mu mul$ Chicken Fries mu mul$ Fries Sandwich Sandwich 'lst 25 $2.00 $6.00 $14.00 2nd 10 $2.00 $12.00 $8.00 3rd 3rd 3 $2.00 $13.00 $2.00 4th 4th Utility Utility Total utility for 308 both Total spent on Chicken $12.00 Total spent on fries $6.00 $10.00 $2.00 Sandwiches a. Is Jane maximizing her utility? Explain your reasoning and show any calculations. b. If Jane is not maximizing her utility, remembering the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility, would she be better off to buy one less chicken sandwich and one more order of fries? Explain your reasoning and show any calculations. c. If Jane is not maximizing her utility with the original purchase combination, remembering the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility, would she be better off buying just one more order of fries? Explain your reasoning and show any calculations. cl. If Jane is not maximizing her utility with the original purchase, remembering the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility, would she be better off buying one less order of fries and one more chicken sandwich? Explain your reasoning and show any calculations. 2. Remembering the Learning Activity, in the year 107 WBCE (Way Before the Common Era) the Gondwanaland Chairman of Production reported that the gosum berry growers could meet an average demand of 700 barrels of gosum berries per month at an average a price of $70 per barrel. In the year 108 WBCE, the growers were plagued with a gosum berry bug infestation that reduced average output, causing production to fall to only 600 barrels per month, causing the price to rise to $84 per barrel. The following table shows the Chairman's report: Year (WBCE) Monthly barrels of gosum Price per barrel berries demanded | 'l 07 | 700 | $70 | 600 | 108 | 334 | a. Using the midpoint method, calculate the price elasticity of demand for Gondwanaland gosum berries. Explain what this price elasticity of demand means? b. Complete the table below by calculating what the monthly average total revenue is for year 107, what the monthly average total revenue is for year 108, and the change in average total monthly revenue for these two years. How have these numbers changed? Year (WBCE) Monthly barrels Price per barrel Change in Monthly average of gosum berries total revenue demanded average total monthly revenue 107 700 $70 103 500 $84 c. Using your answer to part a. above, how could you have predicted the change in total monthly revenue that you found in part b. above? 3. The Gondwanaland Chairman of Production reported that the new Altair chariots (most modern, horse drawn family chariot) had a PRlCE elasticity of 3 and an INCOME elasticity of 2. The supply of these Altair chariots is elastic. Evaluate the following statements and explain why you think they are true, or false. a. A 20% increase in the price of the Altair chariot will cause the quantity demanded to fall by an astounding 60%. b. An increase in Gondwanaland consumers' incomes will cause prices to rise, but the total quantity demanded will also increase. 4. The accompanying table shows the price and monthly demand for barrels of gosum berries in Gondwanaland. Price of gosum berries per barrel Native Demand for gosum berries per month $100 0 $90 100 $80 200 $70 300 $60 400 $50 500 $40 600 $30 700 $20 800 $10 900 $0 1000 a. Using the midpoint method (show your work), calculate the price elasticity of demand when the price of a barrel of gosum berries rises from $10 to $20. What kind of elasticity is this value that you computed for the price elasticity of demand and what does it mean for how demand will change based on a change in price within this price range? b. Using the midpoint method (show your work), calculate the price elasticity of demand when the price of a barrel of gosum berries rises from $70 to $80. What kind of elasticity is this value that you computed for the price elasticity of demand and what does it mean for how demand will change based on a change in price within this price range? c. Notice that the estimates from (a) and (b) above are different. Why do price elasticity of demand estimates change along the demand curve? 5. Matilda is downloading music and videos from an online site. She is currently buying three music downloads that cost $3 each and two video downloads that also cost $3 each. The table below indicates what she reports as the marginal utility of the last music download and of the last video download in this combination of purchases. Downloads Quantity Price per MU per download Download Music downloads 3 $3 60 Video downloads 2 $3 45 As an assignment for her Microeconomics course, Matilda used the marginal utilities that she gave to her 3rd music download and her 2"Id video download to complete the Experiment Tally Sheet below. Her available budget was $19.00. Pce mu of mu Price (score) of from each Money (score) each Money Downloads 1 to Downloads from 1 spent Total Total of 100 $3.00 on to100 $3.00 on Money Budget mul$ music videos Spent Remaining $3.00 $6.00 $13.00 $3.00 $12.00 $7.00 $15.00 $4.00 Total money spent on music Total money spent on $6.00 $15.00 $4.00 videos a. A consumer maximizes utility when the last dollar spent on any good generates the same satisfaction as the last dollar spent on every other good. ls Matilda maximizing her utility? Explain your answer. b. Should Matilda consume one more video download, to move her closer to her optimum utility? Explain your answer. 0. Should Matilda consume one less music download and one more video download, to move her closer to her optimum utility? Explain your answer. d. Should Matilda consume one more music download, to move her closer to her optimum utility? Explain your answer. 6. Brandon and his family often rent movies from the new internet movie streaming service, Xanadu. The table below shows Brandon's demand schedule for eight movie rentals that Brandon's family is interested in watching. Number of internet movie rentals Willingness to pay each rental 1st 37 2nd 36 3rd $5 4th $4 5th $3 5th $2 7th $1 8th $0 a. If the price of each movie rental from Xanadu is $3, how many movie rentals will Brandon buy and how much consumer surplus does Brandon receive? Explain your answer. b. If the price of each movie rental from Xanadu is $5, how many movie rentals will Brandon buy and how much consumer surplus does Brandon receive? Explain your answer. c. If the Xanadu online service offers as many movie rentals as the customer wants to download, all for a one-time fee of $25.00, how many movie rentals will Brandon download and how much consumer surplus will Brandon receive? Explain your answer. cl. If the Xanadu online service offers as many movie rentals as the customer wants to download, all for a one-time fee of $35.00, how many movie rentals will Brandon download and how much consumer surplus will Brandon receive? Explain your answer. e. If the Xanadu's market research showed that Brandon's demand represented what most of Xanadu's customers wanted, what would be the most that Xanadu could charge as a one- time fee for all the downloads that the customer wanted? 7. Newspaper vending machines are designed so that once you have paid for one paper; you have access to all the papers in the machine and could take multiple papers at a time. However, other vending machines dispense only one item (the item you bought). You do not have access to all the goods (sodas, candy, snacks, etc.) at one time. Using the concept of marginal utility, explain why these vending machines differ