Question
Answer Questions 5, 6, and 9 from the information given. 5. Calculate SCRPCs cost of capital when retained earnings is the source of common stock
Answer Questions 5, 6, and 9 from the information given.
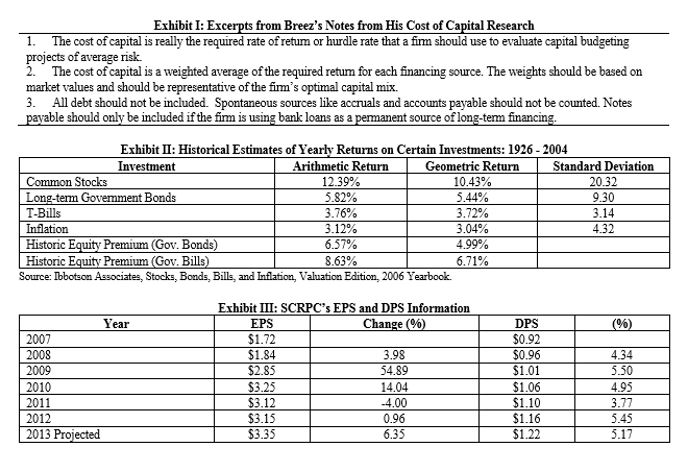
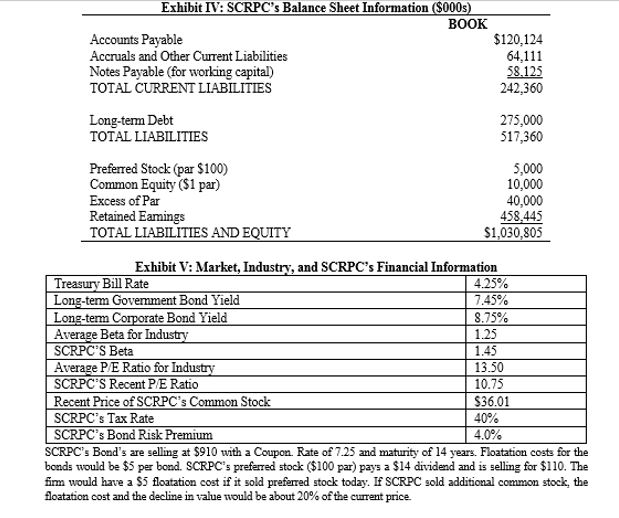
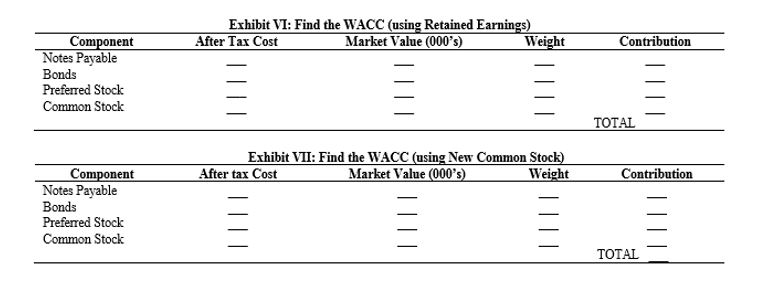
5. Calculate SCRPCs cost of capital when retained earnings is the source of common stock financing and the Gordon Model estimate is used. Use current market values of the financial instruments to determine the components weights (see Exhibit VI).
6. What is SCRPCs cost of capital when the firm has to issue new common stock and the Gordon Model estimate is used? (See Exhibit VII).
9. Should market values or book values be used in the estimation of a firms cost of capital. Defend your recommendation.
Answer Questions 5, 6, and 9 with the information given above.
5. Calculate SCRPCs cost of capital when retained earnings is the source of common stock financing and the Gordon Model estimate is used. Use current market values of the financial instruments to determine the components weights (see Exhibit VI).
6. What is SCRPCs cost of capital when the firm has to issue new common stock and the Gordon Model estimate is used? (See Exhibit VII).
9. Should market values or book values be used in the estimation of a firms cost of capital. Defend your recommendation.
Exhibit I: Excerpts from Breez's Notes from His Cost of Capital Research 1. The cost of capital is really the required rate of retum or hurdle rate that a fimm should use to evaluate capital budgeting projects of average risk 2. The cost of capital is a weighted average of the required retum for each financing source. The weights should be based on market values and should be representative of the fim's optimal capital mix. 3. All debt should not be included. Spontaneous sources like accruals and accounts payable should not be counted Notes payable should only be included if the fim is using bank loans as a permanent source of long-term financing. Exhibit II: Historical Estimates of Yearly Returns on Certain Investments: 1926 - 2004 Investment Arithmetic Return Geometric Return Standard Deviation Common Stocks 12.39% 10.43% 20.32 Long-term Government Bonds 5.82% 5.44% 9.30 T-Bills 3.76% 3.72% 3.14 Inflation 3.12% 3.04% 4.32 Historic Equity Premium (Gov. Bonds) 6.57% 4.99% Historic Equity Premium (Gov. Bills) 8.63% 6.71% Source: Ibbotson Associates, Stocks, Bonds, Bills, and Inflation, Valuation Edition, 2006 Yearbook. (%) Year 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Projected Exhibit III: SCRPC's EPS and DPS Information EPS Change (%) $1.72 $1.84 3.98 $2.85 54.89 $3.25 14.04 $3.12 -4.00 $3.15 0.96 $3.35 6.35 DPS $0.92 $0.96 $1.01 $1.06 $1.10 $1.16 $1.22 4.34 5.50 4.93 3.77 5.45 5.17 Exhibit IV: SCRPC's Balance Sheet Information ($000s) BOOK Accounts Payable $120,124 Accruals and Other Current Liabilities 64,111 Notes Payable (for working capital) 58.125 TOTAL CURRENT LIABILITIES 242,360 Long-term Debt 275,000 TOTAL LIABILITIES 517,360 Preferred Stock (par $100) 5,000 Common Equity ($1 par) 10,000 Excess of Par 40,000 Retained Eamings 458,445 TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY $1,030,805 Exhibit V: Market, Industry, and SCRPC's Financial Information Treasury Bill Rate 4.25% Long-term Government Bond Yield 7.45% Long-term Corporate Bond Yield 8.75% Average Beta for Industry 1.25 SCRPC'S Beta 1.45 Average P/E Ratio for Industry 13.50 SCRPC'S Recent P/E Ratio 10.75 Recent Price of SCRPC's Common Stock $36.01 SCRPC's Tax Rate 40% SCRPC's Bond Risk Premium 4.0% SCRPC's Bond's are selling at $910 with a Coupon. Rate of 7.25 and maturity of 14 years. Floatation costs for the bonds would be $5 per bond. SCRPC's preferred stock ($100 par) pays a $14 dividend and is selling for $110. The fimm would have a $5 floatation cost if it sold preferred stock today. If SCRPC sold additional common stock, the floatation cost and the decline in value would be about 20% of the current price Exhibit VI: Find the WACC (using Retained Earnings) After Tax Cost Market Value (000's) Weight Contribution Component Notes Payable Bonds Preferred Stock Common Stock TOTAL Exhibit VII: Find the WACC (using New Common Stock) After tax Cost Market Value (000's) Weight Contribution Component Notes Payable Bonds Preferred Stock Common Stock TOTAL Exhibit I: Excerpts from Breez's Notes from His Cost of Capital Research 1. The cost of capital is really the required rate of retum or hurdle rate that a fimm should use to evaluate capital budgeting projects of average risk 2. The cost of capital is a weighted average of the required retum for each financing source. The weights should be based on market values and should be representative of the fim's optimal capital mix. 3. All debt should not be included. Spontaneous sources like accruals and accounts payable should not be counted Notes payable should only be included if the fim is using bank loans as a permanent source of long-term financing. Exhibit II: Historical Estimates of Yearly Returns on Certain Investments: 1926 - 2004 Investment Arithmetic Return Geometric Return Standard Deviation Common Stocks 12.39% 10.43% 20.32 Long-term Government Bonds 5.82% 5.44% 9.30 T-Bills 3.76% 3.72% 3.14 Inflation 3.12% 3.04% 4.32 Historic Equity Premium (Gov. Bonds) 6.57% 4.99% Historic Equity Premium (Gov. Bills) 8.63% 6.71% Source: Ibbotson Associates, Stocks, Bonds, Bills, and Inflation, Valuation Edition, 2006 Yearbook. (%) Year 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Projected Exhibit III: SCRPC's EPS and DPS Information EPS Change (%) $1.72 $1.84 3.98 $2.85 54.89 $3.25 14.04 $3.12 -4.00 $3.15 0.96 $3.35 6.35 DPS $0.92 $0.96 $1.01 $1.06 $1.10 $1.16 $1.22 4.34 5.50 4.93 3.77 5.45 5.17 Exhibit IV: SCRPC's Balance Sheet Information ($000s) BOOK Accounts Payable $120,124 Accruals and Other Current Liabilities 64,111 Notes Payable (for working capital) 58.125 TOTAL CURRENT LIABILITIES 242,360 Long-term Debt 275,000 TOTAL LIABILITIES 517,360 Preferred Stock (par $100) 5,000 Common Equity ($1 par) 10,000 Excess of Par 40,000 Retained Eamings 458,445 TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY $1,030,805 Exhibit V: Market, Industry, and SCRPC's Financial Information Treasury Bill Rate 4.25% Long-term Government Bond Yield 7.45% Long-term Corporate Bond Yield 8.75% Average Beta for Industry 1.25 SCRPC'S Beta 1.45 Average P/E Ratio for Industry 13.50 SCRPC'S Recent P/E Ratio 10.75 Recent Price of SCRPC's Common Stock $36.01 SCRPC's Tax Rate 40% SCRPC's Bond Risk Premium 4.0% SCRPC's Bond's are selling at $910 with a Coupon. Rate of 7.25 and maturity of 14 years. Floatation costs for the bonds would be $5 per bond. SCRPC's preferred stock ($100 par) pays a $14 dividend and is selling for $110. The fimm would have a $5 floatation cost if it sold preferred stock today. If SCRPC sold additional common stock, the floatation cost and the decline in value would be about 20% of the current price Exhibit VI: Find the WACC (using Retained Earnings) After Tax Cost Market Value (000's) Weight Contribution Component Notes Payable Bonds Preferred Stock Common Stock TOTAL Exhibit VII: Find the WACC (using New Common Stock) After tax Cost Market Value (000's) Weight Contribution Component Notes Payable Bonds Preferred Stock Common Stock TOTALStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


