Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Answer the following questions regarding permutations and combinations. a. What is a permutation? b. What is a combination? c. What is the major distinction


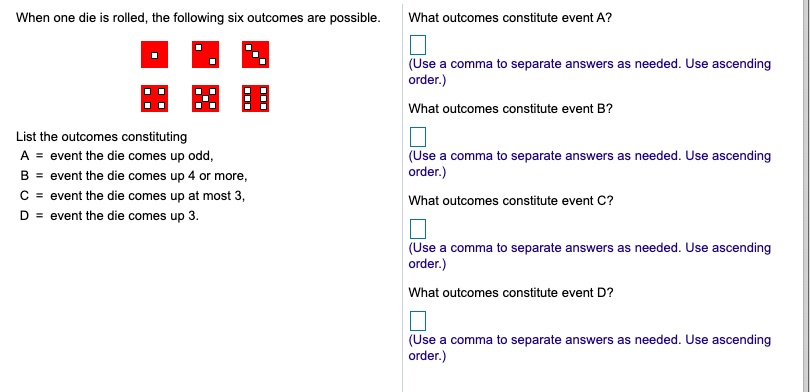
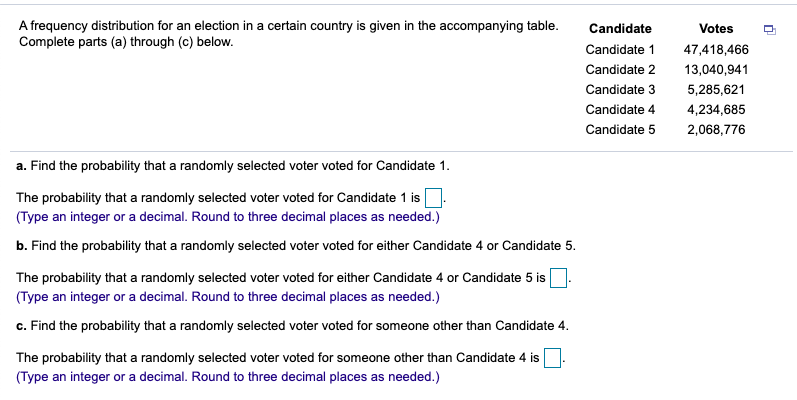

Answer the following questions regarding permutations and combinations. a. What is a permutation? b. What is a combination? c. What is the major distinction between the two? a. Choose the correct answer below. O A. A permutation of r objects from a collection of m objects is any unordered arrangement of r of the m objects. OB. A permutation of r objects from a collection of m objects is any ordered arrangement of r of the m objects. OC. A permutation is the product of the first k positive integers (counting numbers) and is denoted k!. OD. A permutation, NPn, is the number of possible samples of size n from a population of size N. b. Choose the correct answer below. O A. A combination, NC, is the number of possible samples of size n from a population of size N. O B. A combination of a counting number is obtained by successively multiplying it by the next smaller counting number until reaching 1. OC. A combination of r objects from a collection of m objects is any unordered arrangement of r of the m objects. OD. A combination of r objects from a collection of m objects is any ordered arrangement of r of the m objects. c. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Order matters in combinations but not in permutations. B. Order matters in permutations but not in combinations. C. More combinations of r objects from a collection of m objects can be made than permutations. D. Permutations can only be used when r is greater than 10. When one die is rolled, the following six outcomes are possible. List the outcomes constituting A = event the die comes up odd, B = event the die comes up 4 or more, C = event the die comes up at most 3, D = event the die comes up 3. What outcomes constitute event A? (Use a comma to separate answers as needed. Use ascending order.) What outcomes constitute event B? (Use a comma to separate answers as needed. Use ascending order.) What outcomes constitute event C? (Use a comma to separate answers as needed. Use ascending order.) What outcomes constitute event D? (Use a comma to separate answers as needed. Use ascending order.) A frequency distribution for an election in a certain country is given in the accompanying table. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. Find the probability that a randomly selected voter voted for Candidate 1. The probability that a randomly selected voter voted for Candidate 1 is. (Type an integer or a decimal. Round to three decimal places as needed.) b. Find the probability that a randomly selected voter voted for either Candidate 4 or Candidate 5. The probability that a randomly selected voter voted for either Candidate 4 or Candidate 5 is (Type an integer or a decimal. Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Find the probability that a randomly selected voter voted for someone other than Candidate 4. The probability that a randomly selected voter voted for someone other than Candidate 4 is (Type an integer or a decimal. Round to three decimal places as needed.) Candidate Candidate 1 Candidate 2 Candidate 3 Candidate 4 Candidate 5 Votes 47,418,466 13,040,941 5,285,621 4,234,685 2,068,776 Researchers collected information on the body parts of a new species of frog. The thumb length for the female frog has a mean of 6.97 mm and a standard deviation of 0.67 mm. Let x denote thumb length for a female specimen. a. Find the standardized version of x. b. Determine and interpret the z-scores for thumb lengths of 8.7 mm and 5.2 mm. Round your answers to two decimal places. a. Find the standardized version of x. Z= (Do not simplify. Use integers or decimals for any numbers in the expression. Do not round.) b. Determine and interpret the z-scores for thumb lengths of 8.7 mm and 5.2 mm. Round your answers to two decimal places. Determine and interpret the z-score for a thumb length of 8.7 mm. The z-score for a thumb length of 8.7 is. This is standard deviations (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine and interpret the z-score for a thumb length of 5.2 mm. The Z-score for a thumb length of 5.2 is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) This is standard deviations the mean thumb length. the mean thumb length.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.38 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a A perm utation is a way of arranging a set of objects in a particular order where the order matters A perm utation of r objects from a collection of ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


