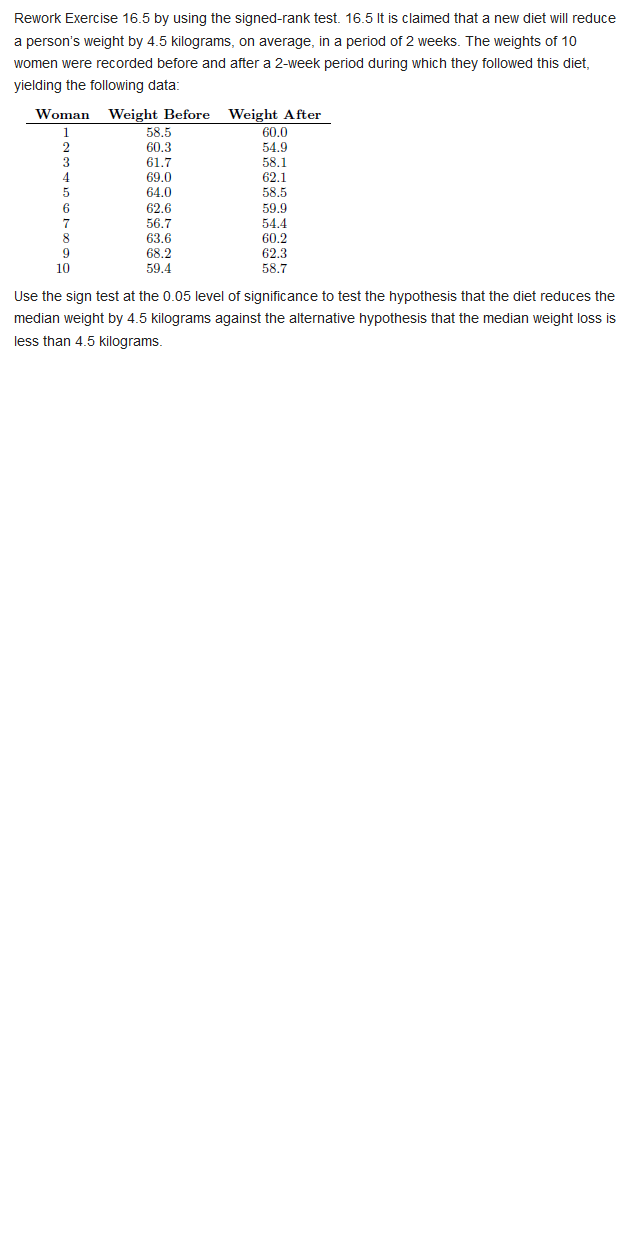
Answer these
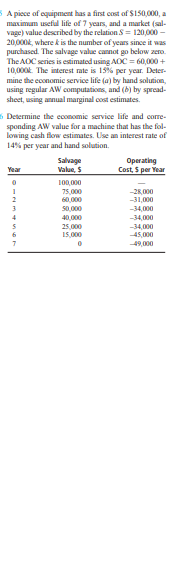
A piece of equipment has a first end of $150,000, a macsumana usefid life of 7 years, and a market (sal- vage) value described by the relation S = 120,000 - 2010004, where & is the number of years since it was purchased. The salvage value cannot go below zero. The AOC series is estimated using AOC = 601000 + 10,000k The interest rate is 15% per year. Deter- mine the economic service life (a) by hand solution, using regular AW computations, and (b) by spread- sheet, using annual marginal cost estimates. Determine the economic service life and come- sponding AW value for a machine that has the fol- lowing cash flow estimates. Use an interest rate of 14%% per year and hand solution. Salvage Operating Value, $ Cost, $ per Year 75 000 -31,030 -34,030 40 000 -34,030 25 000 -34,030 15 000 -45,030 -49 030In the opportunity cost approach to replacement analysis, what does the opportunity refer to? State what is meant by the cash flow approach in replacement analysis, and list two reasons why it is not a good idea to use this method. icement Study over a Specified Study Period ABB Communications is considering replacing equipment that had a first cost of $300,000 five years ago. The company CBD wants to know if the equipment should be replaced now or at any other time over the next 3 years to minimi the cost of producing mis sors. Since the pic it or the proposed equipment can be used for any or all of the 3-year period, one of the company's industrial engineers produced AW cost information for the defender and challenger as shown below. The values repre- sent the annual costs of the respective equipment if used for the indicated number of years. Determine when the defender should be replaced to minimize the cost to ABB for the 3-year study period using an interest rate of 10%6 per year. AW If Kept Stated Number of Number of Years, $ per Year Years Kept Defender Challenger -22,DOD -29,000 -24,DOD -27,DOD -25,00011.47 In conducting a replacement study, all of the follow- ing are correct viewpoints for the analyst except: (a) Consultant's (b) Owner's c Qursider's () Nonowner's 11.48 A sunk cost is the difference between: (4) The first cost and the salvage value (b) The market value and the salvage value c The first cost and the market value The book value and the market value 11:49 A truck was purchased 3 years ago for $45,000 and can be sold today for $24,000. The operating costs are $9000 per year, and it is expected to last 4 more years with a $3000 salvage value. A new truck, which will perform that same service, can be pur- chased for $50,000, and it will have a life of 10 years with operating costs of $28,000 per year and a $10,000 salvage value. The value that should be used as P for the presently owned vehicle in a replacement study is: (4) $45,000 (6) $5000 (3) $501000 () $24.000Define the following terms: bundle, contingent project, dependent project. State two assumptions made when doing capital ma- tioning using a PW analysis for unequal-life projects. For independent projects identified as A, B. C, D, E. F, and G, how many mutually exclusive bundles can be formed? For independent projects identified as W, X, Y, and Z, develop all of the mutually exclusive bundles. Projects X and Y perform the same function with different processes; both should not be selected I Five projects have been identified for possible implementation by a company that makes dry ice blasters-machines that propel tiny dry ice pel- lets at supersonic speeds so they flash-freeze and then lift grime, paint, rust, mold, asphalt, and\f