

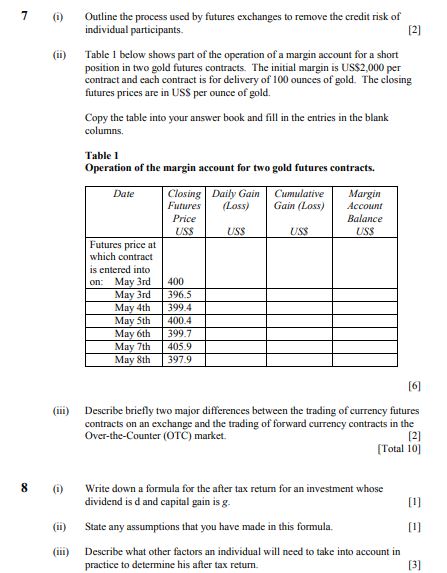
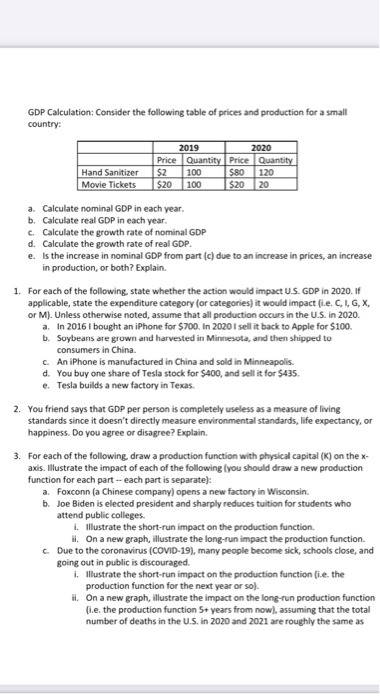
Answer,the following questions precisely.
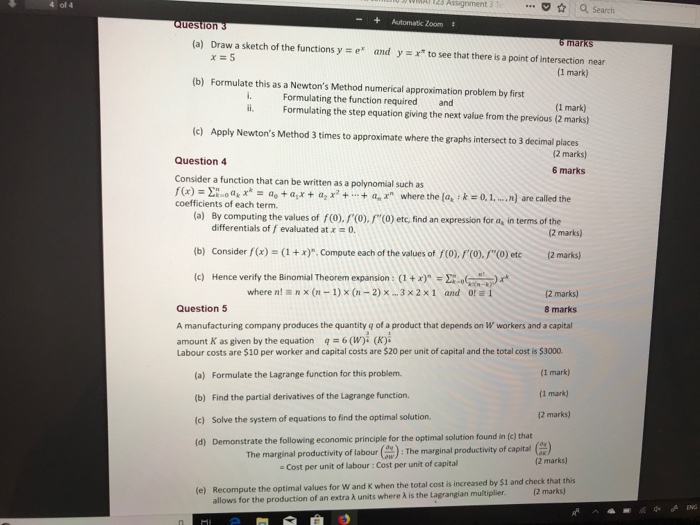
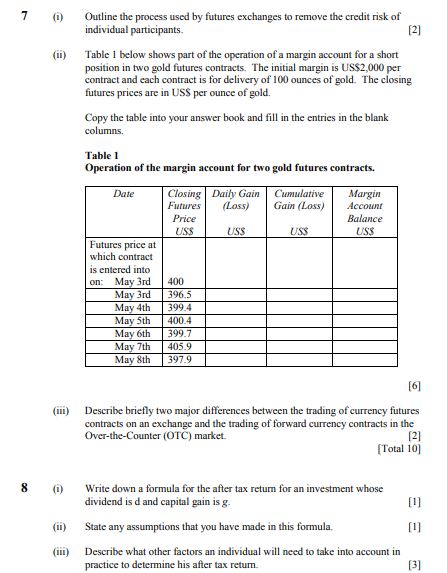
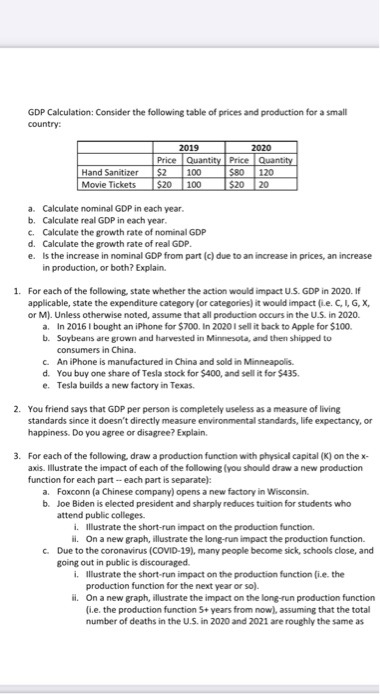
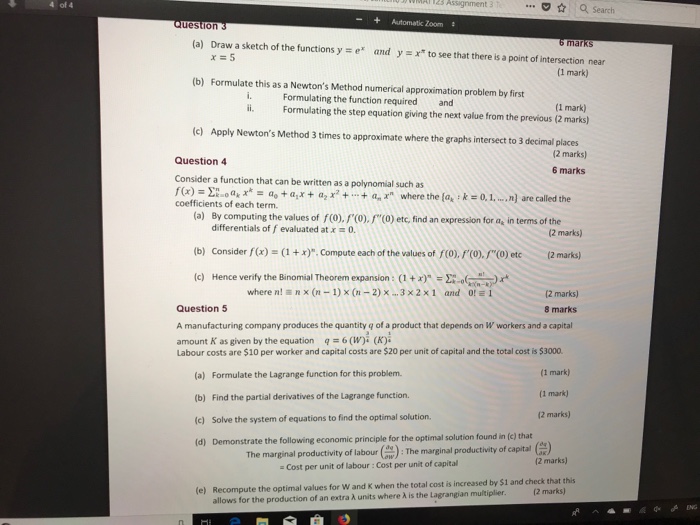
Assignment .: 1 Q search Question 3 Automatic Joom 6 marks (a) Draw a sketch of the functions y = er and y = x* to see that there is a point of intersection near [1 mark) (b) Formulate this as a Newton's Method numerical approximation problem by first i. Formulating the function required ii. and (1 mark) Formulating the step equation giving the next value from the previous (2 marks) (c) Apply Newton's Method 3 times to approximate where the graphs intersect to 3 decimal places (2 marks) Question 4 6 marks Consider a function that can be written as a polynomial such as f(x) = >lod, x* = do tax + a, x + + a, r" where the [a, : k = 0, 1, .. n] are called the coefficients of each term. (a) By computing the values of f(0), /'(0), /"(0) etc, find an expression for a, in terms of the differentials of f evaluated at x = 0. (2 marks) (b) Consider / (x) = (1 + x)". Compute each of the values of /(0), /'(0). /"(0) etc (2 marks) (c) Hence verify the Binomial Theorem expansion : (1 + )" =)()x* where n! = n x (n - 1) x (n - 2) x_.3 x 2x1 and 0! = 1 [2 marks] Question 5 8 marks A manufacturing company produces the quantity q of a product that depends on W workers and a capital amount K as given by the equation q =6 (W): (K). Labour costs are $10 per worker and capital costs are $20 per unit of capital and the total cost is $3000. (a) Formulate the Lagrange function for this problem. (1 mark) (b) Find the partial derivatives of the Lagrange function. (1 mark] (c) Solve the system of equations to find the optimal solution. (2 marks] [d) Demonstrate the following economic principle for the optimal solution found in [c) that The marginal productivity of labour () : The marginal productivity of capital () = Cost per unit of labour : Cost per unit of capital [2 marks] (e) Recompute the optimal values for W and & when the total cost is increased by $1 and check that this [2 marks) allows for the production of an extra A units where A is the Lagrangian multiplier.1. Consider the following short-run model: Y a, - b ( Re - F) a Y - 6. YY EX IM. aim Yt, where C is consumption at time t, It is investment, G, is government purchases, EX, and IM, are exports and imports, Y, is potential output, Y is short-run output, R, is the real interest rate, 7 is the marginal product of capital, and as, di, ag, der, dim, 61, and 62 are parameters. (a) Derive the equation for the IS-curve (that is, the relationship between short-run output and the real interest rate) when 61 6 [0, 1) and 62 2 0. (b) Draw the IS-diagram (that is, the diagram with the real interest rate on the vertical axis and short-run output on the horizontal axis) with two IS-curves. The first IS-curve is given by the answer to part a) when o, = 0 and 62 = 0. The second IS-curve is given by the answer to part a) when 0 61. Suppose the real interest rate increases. Show graphically what will happen to short-run output for both IS-curves. Carefully explain why short-run output is more sensitive to changes in the real interest rate in one of the models.Question 3. Answer the following questions about social insurance. a) Consider one of the social insurance programs we have studied. Present an argument as to why there are incomplete private insurance markets in this case. What is the likely (insurance) outcome in the absence of government intervention? b) The optimal social insurance problem is a balance between protection and distortion. Discuss each of these in the context of the unemployment compensation literature. What are we concerned about distorting? What are we protecting? What are the key elasticities that we need to measure to determine optimal UI benefits? How does each qualitatively affect the optimal UI benefit? Two of the key social insurance benefit programs in the US are disability insurance (DI) and social security (SS). Both programs are federal; therefore all persons face the same eligibility and benefit structure (e.g. no variation across states). Further, benefits are a function of prior earnings. c) Discuss the challenges for causal identification of the impact of social insurance (DI/SS) on labor supply given the program characteristics listed above. d) Suppose we estimate the impact of the social insurance program by regressing labor supply (4) on the DI or SS benefit (B) using cross sectional data (for example, I, = a + BX, + >B, + 8, ). Discuss the validity of this estimator and the sign of the possible bias for the parameter of interest (7 ). e) Describe an identification strategy used in the literature on DI or SS that you think provides the best alternative approach for estimating the impact of B on L. Focus your discussion on the identification strategy.7 Outline the process used by futures exchanges to remove the credit risk of individual participants. [2] Table I below shows part of the operation of a margin account for a short position in two gold futures contracts. The initial margin is US$2,000 per contract and each contract is for delivery of 100 ounces of gold. The closing futures prices are in USS per ounce of gold. Copy the table into your answer book and fill in the entries in the blank columns. Table 1 Operation of the margin account for two gold futures contracts. Date Closing Daily Gain Cumulative Margin Futures (Loss) Gain (Loss) Account Price Balance US USS USS USS Futures price at which contract is entered into on: May 3rd 400 May 3rd 396-5 May 4th 399 4 May 5th 400.4 May 6th 399 7 May 7th 405.9 May 8th 397.9 [6] (ili) Describe briefly two major differences between the trading of currency futures contracts on an exchange and the trading of forward currency contracts in the Over-the-Counter (OTC) market. [2] [Total 10] Write down a formula for the after tax return for an investment whose dividend is d and capital gain is g- [1] State any assumptions that you have made in this formula. (iii) Describe what other factors an individual will need to take into account in practice to determine his after tax return. [3]GDP Calculation: Consider the following table of prices and production for a small country: 2019 2020 Price Quantity Price Quantity Hand Sanitizer $2 100 580 120 Movie Tickets $20 100 520 20 a. Calculate nominal GDP in each year. b. Calculate real GDP in each year. c. Calculate the growth rate of nominal GDP d. Calculate the growth rate of real GDP. e. Is the increase in nominal GDP from part (c) due to an increase in prices, an increase in production, or both? Explain. 1. For each of the following, state whether the action would impact U.S. GDP in 2020. If applicable, state the expenditure category (or categories) it would impact fi.e. C, I, G, X, or MJ. Unless otherwise noted, assume that all production occurs in the U.S. in 2020. a, In 2016 I bought an iphone for $700. In 2020 1 sell it back to Apple for $100. b. Soybeans are grown and harvested in Minnesota, and then shipped to consumers in China. C. An iphone is manufactured in China and sold in Minneapolis. d. You buy one share of Tesla stock for $400, and sell it for $435. e. Tesla builds a new factory in Texas. 2. You friend says that GDP per person is completely useless as a measure of living standards since it doesn't directly measure environmental standards, life expectancy, or happiness. Do you agree or disagree? Explain. 3. For each of the following. draw a production function with physical capital (K) on the x- axis. Illustrate the impact of each of the following (you should draw a new production function for each part - each part is separate): a. Foxconn (a Chinese company) opens a new factory in Wisconsin. b. Joe Biden is elected president and sharply reduces tuition for students who attend public colleges. i. Illustrate the short-run impact on the production function. il. On a new graph, illustrate the long-run impact the production function. c. Due to the coronavirus (COVID-19), many people become sick, schools close, and going out in public is discouraged. i. Illustrate the short-run impact on the production function fie. the production function for the next year or sol. Il. On a new graph, illustrate the impact on the long-run production function [i.e. the production function 5+ years from now), assuming that the total number of deaths in the U.S. in 2020 and 2021 are roughly the same as