Any source can be used for this assignment. It doesn't have to be Wall Street Journal. 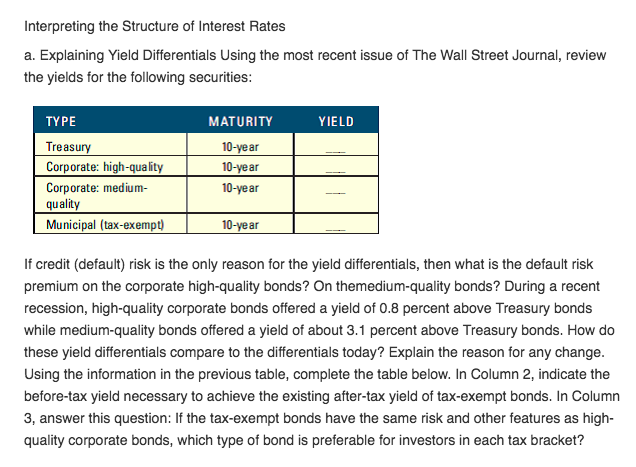
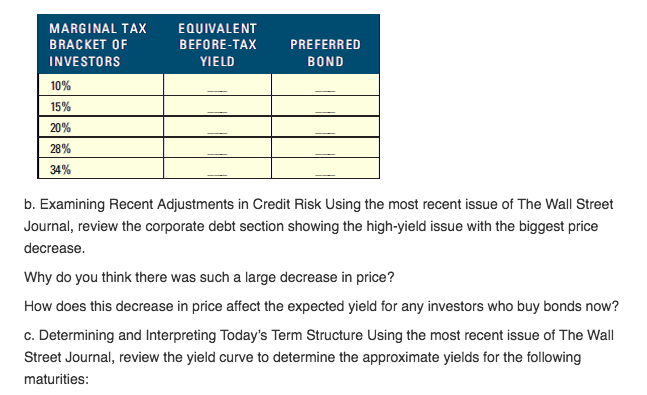
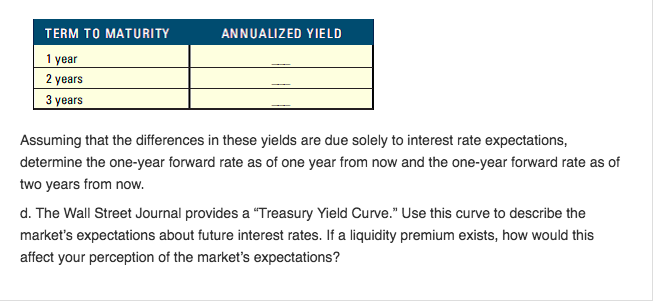
Interpreting the Structure of Interest Rates a. Explaining Yield Differentials Using the most recent issue of The Wall Street Journal, review the yields for the following securities YIELD MATURITY 10-year 10-year 10-year TY PE Treasury Corporate: high-quality Corporate: medium- quality Municipal (tax-exempt 10-year If credit (default) risk is the only reason for the yield differentials, then what is the default risk premium on the corporate high-quality bonds? On themedium-quality bonds? During a recent recession, high-quality corporate bonds offered a yield of 0.8 percent above Treasury bonds while medium-quality bonds offered a yield of about 3.1 percent above Treasury bonds. How do these yield differentials compare to the differentials today? Explain the reason for any change Using the information in the previous table, complete the table below. In Column 2, indicate the before-tax yield necessary to achieve the existing after-tax yield of tax-exempt bonds. In Column 3, answer this question: If the tax-exempt bonds have the same risk and other features as high- quality corporate bonds, which type of bond is preferable for investors in each tax bracket? Interpreting the Structure of Interest Rates a. Explaining Yield Differentials Using the most recent issue of The Wall Street Journal, review the yields for the following securities YIELD MATURITY 10-year 10-year 10-year TY PE Treasury Corporate: high-quality Corporate: medium- quality Municipal (tax-exempt 10-year If credit (default) risk is the only reason for the yield differentials, then what is the default risk premium on the corporate high-quality bonds? On themedium-quality bonds? During a recent recession, high-quality corporate bonds offered a yield of 0.8 percent above Treasury bonds while medium-quality bonds offered a yield of about 3.1 percent above Treasury bonds. How do these yield differentials compare to the differentials today? Explain the reason for any change Using the information in the previous table, complete the table below. In Column 2, indicate the before-tax yield necessary to achieve the existing after-tax yield of tax-exempt bonds. In Column 3, answer this question: If the tax-exempt bonds have the same risk and other features as high- quality corporate bonds, which type of bond is preferable for investors in each tax bracket









