Apply the "high-low" method in order to estimate the portion of this company's costs that are fixed, versus the portion that are variable. Normally the calculations for high-low use changes in activity levels - e.g., number of units produced - to perform high-low calculations. Use number of units produced/sold, use revenue dollars.
Herman Miller, Inc. Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income
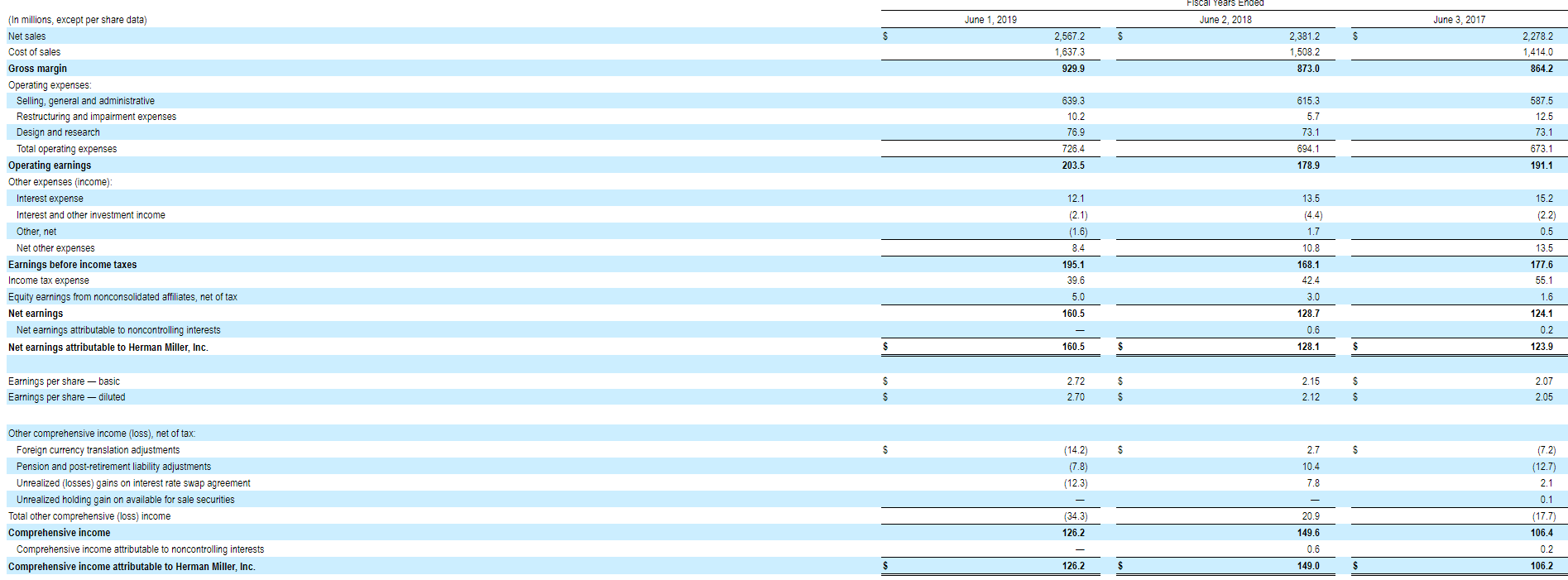
Fiscal Years Ended June 2, 2018 June 1, 2019 June 3, 2017 5 S 2,567 2 1,637.3 929.9 2,381.2 1,508.2 873.0 2,2782 1,414.0 864.2 639.3 10.2 76.9 726.4 203.5 615.3 5.7 73.1 694.1 178.9 587.5 12.5 73.1 673.1 191.1 (In millions, except per share data) Net sales Cost of sales Gross margin Operating expenses: Selling, general and administrative Restructuring and impairment expenses Design and research Total operating expenses Operating earnings Other expenses (income): Interest expense Interest and other investment income Other, net Net other expenses Earnings before income taxes Income tax expense Equity earnings from nonconsolidated affiliates, net of tax Net earnings Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests Net earnings attributable to Herman Miller, Inc. 33 12.1 (2.1) (1.6) 195.1 39.6 13.5 (4.4) 1.7 10.8 168.1 42.4 3.0 128.7 0.6 128.1 15.2 (2.2) 0.5 13.5 177.6 55.1 1.6 124.1 0.2 123.9 5.0 160.5 $ 160.5 S Earnings per share - basic Earnings per share diluted 2.725 2.70 S 2.15 2.12 $ $ 2.07 2.05 S S (14.2) (7.8) (12.3) 2.7 10.4 7.8 Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax Foreign currency translation adjustments Pension and post-retirement liability adjustments Unrealized (losses) gains on interest rate swap agreement Unrealized holding gain on available for sale securities Total other comprehensive (loss) income Comprehensive income Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests Comprehensive income attributable to Herman Miller, Inc. (7.2) (12.7) 2.1 0.1 (17.7) 106.4 0.2 106.2 (34.3) 126.2 20.9 149.6 0.6 126.2 149.0 Fiscal Years Ended June 2, 2018 June 1, 2019 June 3, 2017 5 S 2,567 2 1,637.3 929.9 2,381.2 1,508.2 873.0 2,2782 1,414.0 864.2 639.3 10.2 76.9 726.4 203.5 615.3 5.7 73.1 694.1 178.9 587.5 12.5 73.1 673.1 191.1 (In millions, except per share data) Net sales Cost of sales Gross margin Operating expenses: Selling, general and administrative Restructuring and impairment expenses Design and research Total operating expenses Operating earnings Other expenses (income): Interest expense Interest and other investment income Other, net Net other expenses Earnings before income taxes Income tax expense Equity earnings from nonconsolidated affiliates, net of tax Net earnings Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests Net earnings attributable to Herman Miller, Inc. 33 12.1 (2.1) (1.6) 195.1 39.6 13.5 (4.4) 1.7 10.8 168.1 42.4 3.0 128.7 0.6 128.1 15.2 (2.2) 0.5 13.5 177.6 55.1 1.6 124.1 0.2 123.9 5.0 160.5 $ 160.5 S Earnings per share - basic Earnings per share diluted 2.725 2.70 S 2.15 2.12 $ $ 2.07 2.05 S S (14.2) (7.8) (12.3) 2.7 10.4 7.8 Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax Foreign currency translation adjustments Pension and post-retirement liability adjustments Unrealized (losses) gains on interest rate swap agreement Unrealized holding gain on available for sale securities Total other comprehensive (loss) income Comprehensive income Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests Comprehensive income attributable to Herman Miller, Inc. (7.2) (12.7) 2.1 0.1 (17.7) 106.4 0.2 106.2 (34.3) 126.2 20.9 149.6 0.6 126.2 149.0







