Question: As a designer you are asked to evaluate three possible options for an on-chip write-through data cache. Some of the design options (associativity) and performance
As a designer you are asked to evaluate three possible options for an on-chip write-through data cache. Some of the design options (associativity) and performance consequences (miss rate, miss penalty) are described in the table below:
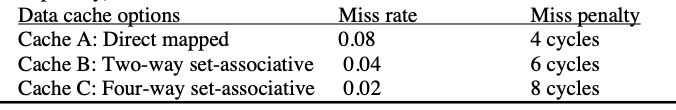
(a) Assume that load instructions have a CPI of 1.2 if they hit in the cache and a CPI of 1.2 + (miss penalty) otherwise. All other instructions have a CPI of 1.2. The instruction mix is such that 20% of instructions are loads. What is the CPI for each configuration (youll need to keep three decimal digits, i.e., compute the CPI as x.xxx)? Which cache would you choose if CPI is the determining factor?
(b) Assumenowthatifthedirect-mappedcacheisused,thecycletimeis20ns.If the two-way set-associative cache is used, the cycle time is 22 ns. If the four-way is used, the cycle time is 24 ns. What is the average time per instruction? Which cache would you choose if average time per instruction is the determining factor?
(c) In the case of the two-way set-associative cache, the replacement algorithm is LRU. In the case of the four-way set-associative cache, the replacement algorithm is such that the most recently used (MRU) line is not replaced; the choice of which of the other three is replaced is random and not part of the logic associated with each line in the cache. Indicate what bits are needed to implement the replacement algorithms for each line.
I don't have time please solve it as soon as possible
thank you
Data cache options Cache A: Direct mapped Cache B: Two-way set-associative Cache C: Four-way set-associative Miss rate 0.08 0.04 0.02 Miss penalty 4 cycles 6 cycles 8 cycles
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


