Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
As discussed in Chapter 21, the master budget assists a company in planning, directing, and controlling performance. The control function, or budgetary performance evaluation,
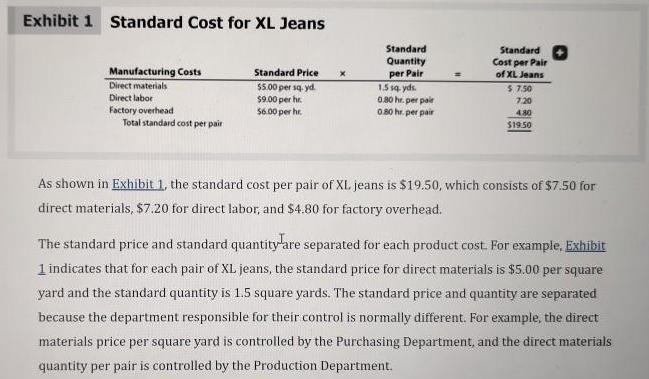

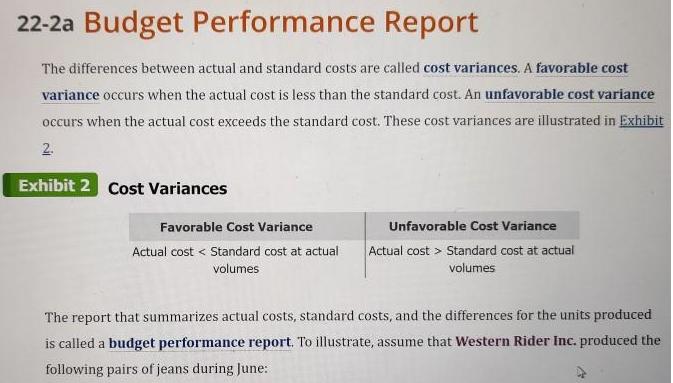
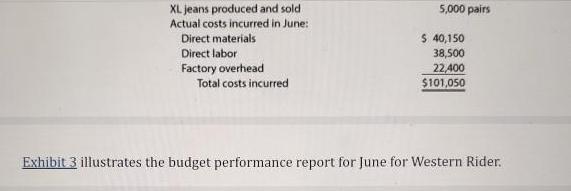
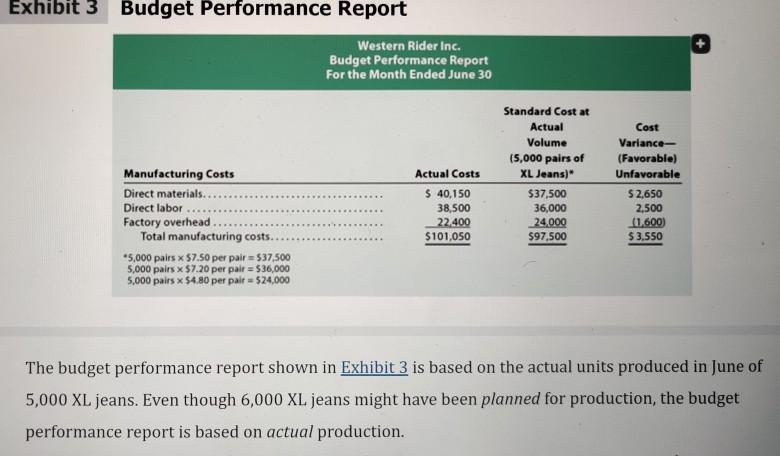
As discussed in Chapter 21, the master budget assists a company in planning, directing, and controlling performance. The control function, or budgetary performance evaluation, compares the actual performance against the budget. To illustrate, Western Rider Inc., a manufacturer of blue jeans, uses standard costs in its budgets. The standards for direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead are separated into the following two components: . Standard price Standard quantity Objective 2 The standard cost per unit for direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead is computed as follows: Standard Cost per Unit - Standard Price x Standard Quantity Western Rider's standard costs per unit for its XL jeans are shown in Exhibit 1. Exhibit 1 Standard Cost for XL Jeans Manufacturing Costs Direct materials Direct labor Factory overhead Total standard cost per pair Standard Price $5.00 per sq.yd. $9.00 per hr. $6.00 per hr Standard Quantity per Pair 1.5 sq yds. 0.80 hr.per pair 0.80 hr. per pair = Standard Cost per Pair of XL Jeans $7.50 7:20 4.80 $19.50 As shown in Exhibit 1, the standard cost per pair of XL. jeans is $19.50, which consists of $7.50 for direct materials, $7.20 for direct labor, and $4.80 for factory overhead. The standard price and standard quantity are separated for each product cost. For example, Exhibit 1 indicates that for each pair of XL jeans, the standard price for direct materials is $5.00 per square yard and the standard quantity is 1.5 square yards. The standard price and quantity are separated because the department responsible for their control is normally different. For example, the direct materials price per square yard is controlled by the Purchasing Department, and the direct materials quantity per pair is controlled by the Production Department. As illustrated in Chapter 21, the master budget is prepared based on planned sales and production. The budgeted costs for materials purchases, direct labor, and factory overhead are determined by multiplying their standard costs per unit by the planned level of production. Budgeted (standard) costs are then compared to actual costs during the year for control purposes. 22-2a Budget Performance Report The differences between actual and standard costs are called cost variances. A favorable cost variance occurs when the actual cost is less than the standard cost. An unfavorable cost variance occurs when the actual cost exceeds the standard cost. These cost variances are illustrated in Exhibit 2. Exhibit 2 Cost Variances Favorable Cost Variance Actual cost Standard cost at actual volumes Unfavorable Cost Variance Actual cost Standard cost at actual volumes The report that summarizes actual costs, standard costs, and the differences for the units produced is called a budget performance report. To illustrate, assume that Western Rider Inc. produced the following pairs of jeans during June: XL jeans produced and sold Actual costs incurred in June: Direct materials Direct labor Factory overhead Total costs incurred 5,000 pairs $ 40,150 38,500 22,400 $101,050 Exhibit 3 illustrates the budget performance report for June for Western Rider. Exhibit 3 Budget Performance Report Manufacturing Costs Direct materials... Direct labor Factory overhead Total manufacturing costs. *5,000 pairs x $7.50 per pair= $37,500 5,000 pairs x $7.20 per pair = $36,000 5,000 pairs x $4.80 per pair - $24,000 Western Rider Inc. Budget Performance Report For the Month Ended June 30 Actual Costs $ 40,150 38,500 22,400 $101,050 Standard Cost at Actual Volume (5,000 pairs of XL Jeans)* $37,500 36,000 24,000 $97,500 Cost Variance- (Favorable) Unfavorable $2,650 2,500 (1,600) $3,550 The budget performance report shown in Exhibit 3 is based on the actual units produced in June of 5,000 XL jeans. Even though 6,000 XL jeans might have been planned for production, the budget performance report is based on actual production. Why might firms use nonfinancial performance measures? What measures might a hospital use? Target? Chase Bank? City Colleges of Chicago? Select one of the above listed types of businesses and describe the inputs, activities, and outputs as described on page 1051 in your text. I expect you to respond to the posted question with a minimum 250 word response AND interact with your fellow students' thoughts and ideas by posting an additional 2 posts adding your thoughts and insights to what they had to say. Saying "good job" or "I agree" would not count toward this grade. Please spread your interactions out throughout the week. I cannot grant full points if you post one reply after the other on a single day.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.39 Rating (174 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Before going to discuss about why any firms uses its nonfinancial measures let we discuss about what ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


