Question
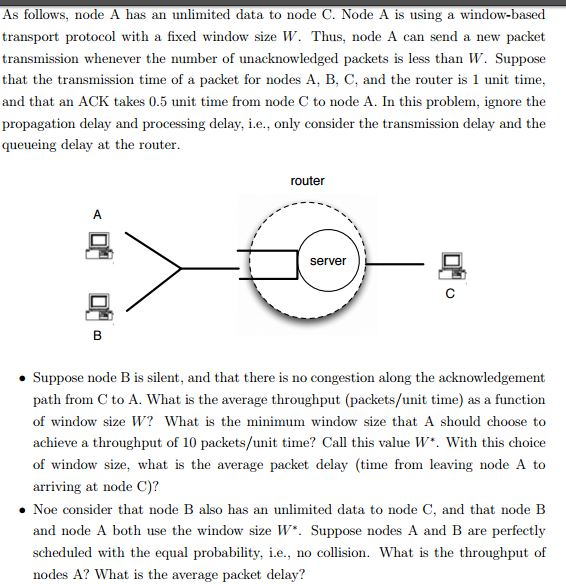
As follows, node A has an unlimited data to node C. Node A is using a window-based transport protocol with a fixed window size W.
As follows, node A has an unlimited data to node C. Node A is using a window-based transport protocol with a fixed window size W. Thus, node A can send a new packet transmission whenever the number of unacknowledged packets is less than W. Suppose that the transmission time of a packet for nodes A, B, C, and the router is 1 unit time, and that an ACK takes 0.5 unit time from node C to node A. In this problem, ignore the propagation delay and processing delay, i.e., only consider the transmission delay and the queueing delay at the router.
Now consider that node B also has an unlimited data to node C, and that node B and node A both use the window size W . Suppose nodes A and B are perfectly scheduled with the equal probability, i.e., no collision. What is the throughput of nodes A? What is the average packet delay?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


