Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Assess bps management of its investment and strategic alliances in Russia. Why is the TNK- BP partnership experiencing so much internal conflict? What can BP



- Assess bp’s management of its investment and strategic alliances in Russia. Why is the TNK- BP partnership experiencing so much internal conflict? What can BP do to salvage the situation in Russia? Do you agree with the BP’s decision to block a TNK - BP cooperative arrangement with Rosneft
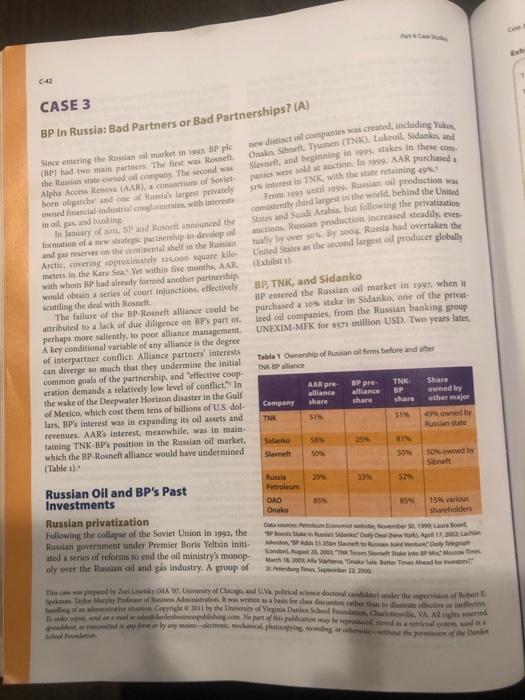
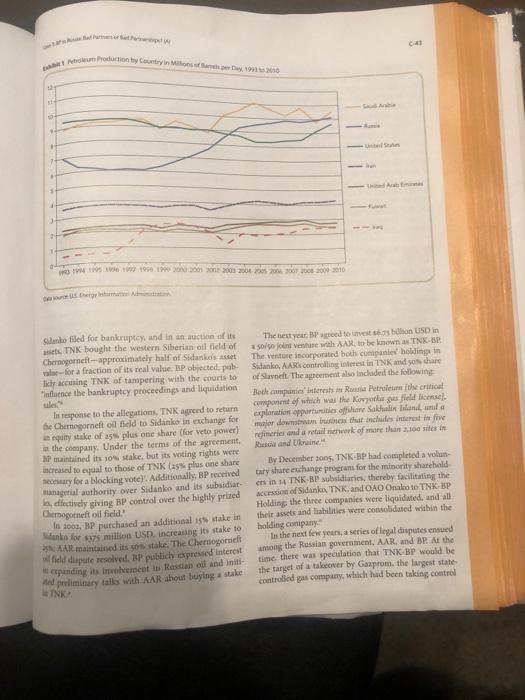
C-42 CASE 3 BP In Russia: Bad Partners or Bad Partnerships? (A) Since entering the Russian oil market in 1997. BP plc (BP) had two main partners. The first was Rosneft. the Russian state-onened oll company. The second was Alpha Access Renova (AAR), a consortium of Soviet- born oligarchs and one of Russia's largest privately owned financial-industrial conglomerates, with interests in oil, gas, and banking new distinct oil companies was created, including Yukos, Onako, Sibneft, Tyumen (TNK), Lukeoil, Sidanko, and Slavneft, and beginning in 1995, stakes in these com panies were sold at auction. In 1999. AAR purchased a 51% interest in TNK, with the state retaining 49% From 1993 until 1999, Russian oil production was consistently third largest in the world, behind the United States and Saudi Arabia, but following the privatization auctions, Russian production increased steadily, even tually by over so%. By 2004. Russia had overtaken the United States as the second largest oil producer globally In January of 2011, BP and Rosneft announced the formation of a new strategic partnership to develop oil and gas reserves on the continental shelf in the Russian Arctic, covering approximately 125,000 square kilo- meters in the Kara Sea Yet within five months, AAR, with whom BP had already formed another partnership, would obtain a series of court injunctions, effectively scuttling the deal with Rosneft. (Exhibit 1). BP, TNK, and Sidanko BP entered the Russian oil market in 1997, when it purchased a 10% stake in Sidanko, one of the privat- ired oil companies, from the Russian banking group UNEXIM-MFK for $571 million USD. Two years later, Table 1 Ownership of Russian oil firms before and after TNK BP alliance The failure of the BP-Rosneft alliance could be attributed to a lack of due diligence on BP's part of. perhaps more saliently, to poor alliance management. A key conditional variable of any alliance is the degree of interpartner conflict: Alliance partners interests can diverge so much that they undermine the initial common goals of the partnership, and "effective coop- eration demands a relatively low level of conflict." In the wake of the Deepwater Horizon disaster in the Gulf of Mexico, which cost them tens of billions of US dol- lars, BP's interest was in expanding its oil assets and revenues. AAR's interest, meanwhile, was in main- taining TNK-BP's position in the Russian oil market, which the BP-Rosneft alliance would have undermined (Table 1). Share AAR pre alliance share BP pre- alliance share TNK- BP owned by other major share Company TNK 51% 51% 49% owned by Russian state Sidanko 25% 81% Slavnelt 50% 50% owned by Sibneft Russia Petroleum 52% Russian Oil and BP's Past Investments 85% OAD Onako 85% 15% various shareholders Russian privatization Following the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1992, the Russian government under Premier Boris Yeltsin initi- ated a series of reforms to end the oil ministry's monop- oly over the Russian oil and gas industry. A group of Data Petroleum Econon website, November 30, 1999 Laura Board BP Booty Stuke in Rusus Sidanko Daily Deal (New York, April 17, 2002: Lach Johoton SP Ad $1.358n Slavnet to Russian Joint Venture Daily Telegraph London, August 20, 2001 TK Tosses Shavneft Stake to BP Mx Moscow T March 18, 2008 Aa Startseva, "Onako Sale Better Times Ahead for Investors St. Pshing Res, September 22, 2000 This case was perpared by Zur Letky (MA , University of Chicags, and Va political science doctoral candidate) under the superstion of Robert E Spekum Take Marghby Proleer of assess Administration. It was we as a basis five class discussion rather than to astrate effective or ineffectiv hling of an alcanistrative station Copyright 2011 by the Unnersity of Virginia Darden School Foundation, Charlottesville, VA All rights reserved De ondern end an email to salendardensplishing.com No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, word road or red in any form or by any means-lectronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise without the permission of the Darden Cap Exh 1 C-42 CASE 3 BP In Russia: Bad Partners or Bad Partnerships? (A) Since entering the Russian oil market in 1997. BP plc (BP) had two main partners. The first was Rosneft. the Russian state-onened oll company. The second was Alpha Access Renova (AAR), a consortium of Soviet- born oligarchs and one of Russia's largest privately owned financial-industrial conglomerates, with interests in oil, gas, and banking new distinct oil companies was created, including Yukos, Onako, Sibneft, Tyumen (TNK), Lukeoil, Sidanko, and Slavneft, and beginning in 1995, stakes in these com panies were sold at auction. In 1999. AAR purchased a 51% interest in TNK, with the state retaining 49% From 1993 until 1999, Russian oil production was consistently third largest in the world, behind the United States and Saudi Arabia, but following the privatization auctions, Russian production increased steadily, even tually by over so%. By 2004. Russia had overtaken the United States as the second largest oil producer globally In January of 2011, BP and Rosneft announced the formation of a new strategic partnership to develop oil and gas reserves on the continental shelf in the Russian Arctic, covering approximately 125,000 square kilo- meters in the Kara Sea Yet within five months, AAR, with whom BP had already formed another partnership, would obtain a series of court injunctions, effectively scuttling the deal with Rosneft. (Exhibit 1). BP, TNK, and Sidanko BP entered the Russian oil market in 1997, when it purchased a 10% stake in Sidanko, one of the privat- ired oil companies, from the Russian banking group UNEXIM-MFK for $571 million USD. Two years later, Table 1 Ownership of Russian oil firms before and after TNK BP alliance The failure of the BP-Rosneft alliance could be attributed to a lack of due diligence on BP's part of. perhaps more saliently, to poor alliance management. A key conditional variable of any alliance is the degree of interpartner conflict: Alliance partners interests can diverge so much that they undermine the initial common goals of the partnership, and "effective coop- eration demands a relatively low level of conflict." In the wake of the Deepwater Horizon disaster in the Gulf of Mexico, which cost them tens of billions of US dol- lars, BP's interest was in expanding its oil assets and revenues. AAR's interest, meanwhile, was in main- taining TNK-BP's position in the Russian oil market, which the BP-Rosneft alliance would have undermined (Table 1). Share AAR pre alliance share BP pre- alliance share TNK- BP owned by other major share Company TNK 51% 51% 49% owned by Russian state Sidanko 25% 81% Slavnelt 50% 50% owned by Sibneft Russia Petroleum 52% Russian Oil and BP's Past Investments 85% OAD Onako 85% 15% various shareholders Russian privatization Following the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1992, the Russian government under Premier Boris Yeltsin initi- ated a series of reforms to end the oil ministry's monop- oly over the Russian oil and gas industry. A group of Data Petroleum Econon website, November 30, 1999 Laura Board BP Booty Stuke in Rusus Sidanko Daily Deal (New York, April 17, 2002: Lach Johoton SP Ad $1.358n Slavnet to Russian Joint Venture Daily Telegraph London, August 20, 2001 TK Tosses Shavneft Stake to BP Mx Moscow T March 18, 2008 Aa Startseva, "Onako Sale Better Times Ahead for Investors St. Pshing Res, September 22, 2000 This case was perpared by Zur Letky (MA , University of Chicags, and Va political science doctoral candidate) under the superstion of Robert E Spekum Take Marghby Proleer of assess Administration. It was we as a basis five class discussion rather than to astrate effective or ineffectiv hling of an alcanistrative station Copyright 2011 by the Unnersity of Virginia Darden School Foundation, Charlottesville, VA All rights reserved De ondern end an email to salendardensplishing.com No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, word road or red in any form or by any means-lectronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise without the permission of the Darden Cap Exh 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Assess BPs management of its investments and strategic alliances in Russia Being the 2nd largest producer of oil since 2004 Russia presents a lucrativ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


