

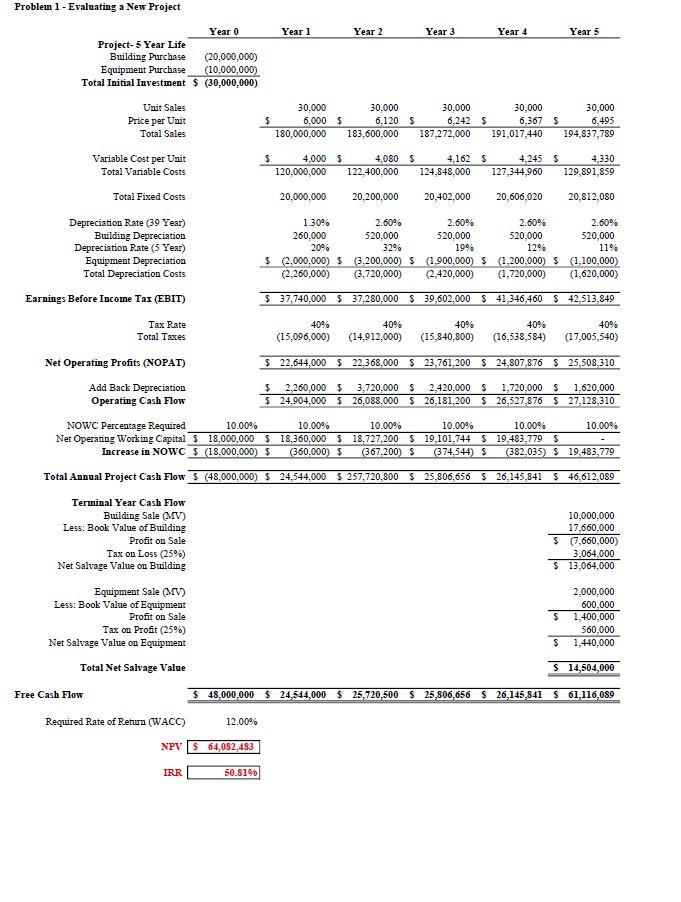
Assignment 4 Estimating Cash Flows Instruction: Please submit your assignment as an attachment by midnight on the due date Solve all problems in the Excel file provided. Problem 1 Regency Integrated Chips (RIC), a large Nashville-based technology company is evaluating a new project to manufacture a new chip. a. The project's estimated economic life is 5 years. b. RIC's marketing vice-president believes that annual sales would be 30,000 units if the units were priced at $6,000 each. RIC expects no growth in unit sales, and it believes that the unit price will rise by 3 percent each year. C. The engineering department has reported that the project will require additional manufacturing space, and RIC currently has an option to purchase an existing building, at a cost of $20 million, which would meet this need. The building would be bought and paid for on December 31 of Year 0, and for depreciation purposes, it would fall into the MACRS 39-year class. The annual depreciation rate for the five years of economic life of the project would be: Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 1.3% 2.6% 2.6% 2.6% 2.6% d. The necessary equipment would be purchased, installed, and paid for on December 31 of Year 0. The equipment would fall into the MACRS 5-year class, and it would cost $10 million, including transportation and installation. The annual depreciation rate for the five years of economic life of the project would be: Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 20% 32% 19% 12% 11% e. f. At the end of the project, the building is expected to have a market value of $10 million and the equipment is expected to have a market value of $2 million. The production department has estimated that variable manufacturing costs would be $4000 per unit, and that fixed overhead costs, excluding depreciation would be $20 million a year. They expect variable costs to rise by 3 percent per year, and fixed costs to rise by 2 percent per year. Depreciation expense would be determined in accordance with MACRS rates. g. RIC must have an amount of NOWC on hand equal to 10 percent of the upcoming year's sales. h. RIC's marginal tax rate is 25 percent, its cost of capital is 12 percent, and it assumes that all operating cash flows occur at the end of the year. Evaluate the project using the NPV rule and the IRR rule. Problem 2 You have been asked by the president of the Farr Construction Company to evaluate the proposed acquisition of a new earth mover. The mover's basic price is $220,000, and it would cost another $30,000 to modify it for special use. Assume that the mover falls into the MACRS 5-year class, it would be sold after 4 years for $60,000, and it would require an increase in net operating working capital (spare parts inventory) of $10,000. The earth mover would have no effect on revenues, but it is expected to save the firm $52,000 per year in before-tax operating costs, mainly labor. The firm's marginal federal-plus-state tax rate is 25 percent and the project's cost of capital is 10 percent. Evaluate the project using the NPV rule and the IRR rule. Problem 3 ABC Inc. wishes to buy new machinery that would cost $166,000, but it would lead to increased output, higher sales, and higher costs. Moreover, the firm would receive $100,000 after taxes for the old machine. The new machine would result in sales of $120,000 per year versus old sales of $70,000, and the new costs would be $40,000 versus old costs of $20,000. Finally, the old machine was being depreciated at the rate of $10,000 per year, but the new machine would have $30,000 of annual depreciation. The marginal tax rate is 25 percent and WACC is 10 percent. Based on these figures, and assuming the new and old machines both have a life of four years, find the incremental cash flows. Problem 1 - Evaluating a New Project Year 0 Project- 5 Year Life Building Purchase (20,000,000) Equipment Purchase (10,000,000) Total Initial Investment $ (30,000,000) Unit Sales 30,000 6,495 $ Price per Unit Total Sales 180,000,000 183,600,000 187,272,000 191,017,440 194,837,789 Variable Cost per Unit S 4,000 120,000,000 4.080 122,400,000 4,162 S 4,245 124,848,000 127,344,960 4,330 129,891,859 Total Variable Costs Total Fixed Costs 20,000,000 20,200,000 20,402,000 20,606,020 20,812,080 Depreciation Rate (39 Year) 2.60% 2.60% 2.60% 2.60% 1.30% 260,000 20% 520,000 520,000 520,000 520,000 32% 19% 12% Building Depreciation Depreciation Rate (5 Year) Equipment Depreciation Total Depreciation Costs $ (2,000,000) $ (3,200,000) S (1,900,000) $ (2,260,000) (3,720,000) (2,420,000) 11% (1,200,000) S (1,100,000) (1,720,000) (1,620,000) Earnings Before Income Tax (EBIT) $ 37,740,000 $37,280,000 $ 39,602,000 $ 41,346,460 $ 42,513,849 40% 40% Tax Rate Total Taxes 40% 40% (15,096,000) (14,912,000) (15,840,800) (16,538,584) 40% (17,005,540) Net Operating Profits (NOPAT) $ 22,644,000 $22,368,000 $ 23,761,200 $ 24,807,876 $ 25,508,310 Add Back Depreciation Operating Cash Flow $ 2,260,000 $ 3,720,000 $ $24.904.000 $ 26,088,000 $ 2,420,000 $1,720,000 $ 1,620,000 26,181,200 $ 26,527,876 $ 27,128,310 10.00% NOWC Percentage Required 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% Net Operating Working Capital $ 18,000,000 $18,360,000 $18,727,200 $ 19,101,744 $ 19,483,779 $ Increase in NOWC $ (18,000,000) $ (360,000) $ (367,200) $ (374,544) $ (382,035) $ 19,483,779 Total Annual Project Cash Flow (48,000,000) $ 24,544,000 $257,720,800 $25,806,656 $ 26,145,841 $ 46,612,089 Terminal Year Cash Flow Building Sale (MV) Less: Book Value of Building 10,000,000 17,660,000 Profit on Sale $ (7,660,000) 3,064,000 Tax on Loss (25%) Net Salvage Value on Building $ 13,064,000 Equipment Sale (MV) Less: Book Value of Equipment Profit on Sale 2,000,000 600,000 S 1,400,000 560,000 Tax on Profit (25%) Net Salvage Value on Equipment S 1,440,000 Total Net Salvage Value S 14,504,000 $ 48,000,000 $24,544,000 $ 25,720,500 $25,806,656 $ 26,145,841 $ 61,116,089 Required Rate of Return (WACC) 12.00% NPV $ 64,082,483 IRR 50.81% Free Cash Flow $ Year 1 30,000 6,000 $ $ Year 2 30,000 6,120 $ Year 3 30,000 6,242 S Year 4 30,000 6,367 S $ Year 5 Problem 2 - Evaluating a Cost Saving Project Acquisition - 5 Year Life Earth Mover ?? Installation Costs ?? Total Initial Investment $ Savings in Costs Depreciation Rate (5 Year) Total Depreciation Costs Earnings Before Income Tax (EBIT) Tax Rate Total Taxes Net Operating Profits (NOPAT) Add Back Depreciation Operating Cash Flow Net Operating Working Capital ?? Increase in NOWc ?? Total Annual Project Cash Flow ?? Terminal Year Cash Flow Machine Sale Less: Book Value of Machine Profit on Sale Tax on Profit (25%) Net Salvage Value on Equipment ?? Required Rate of Return (WACC) ?? NPV ?? IRR ?? Free Cash Flow Year 0 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Year 1 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? 33 ?? ?? Year 2 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Year 3 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? 3 33 ?? 3.3 33 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Year 4 Problem 3 - Evaluating a Replacement Project Year 0 Acquisition - 5 Year Life New Machinery ?? Sale - Old Machine ?? Total Initial Investment ?? New Sales Old Sales Change in Sales New Costs Old Costs Change in Costs New Depreciation Old Depreciation Change in Depreciation Earnings Before Income Tax (EBIT) Tax Rate Total Taxes Net Operating profits (NOPAT) Add Back Depreciation Operating Cash Flow Net Operating Working Capital Increase in NOWC Total Annual Project Cash Flow ?? Required Rate of Return (WACC) ?? NPV ?? IRR ?? Free Cash Flow ?? ?? ?? 22 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Year 1 ?? 333 333 333 333 333 333 333 ?? ?? ?? 333 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Year 2 ?? ?? ?? ?? 22 72 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Year 3 ?? ?? ?? ?? 38 3 ?? ?? ?? Year 4 NOT NEEDED NOT NEEDED NOT NEEDED NOT NEEDED Assignment 4 Estimating Cash Flows Instruction: Please submit your assignment as an attachment by midnight on the due date Solve all problems in the Excel file provided. Problem 1 Regency Integrated Chips (RIC), a large Nashville-based technology company is evaluating a new project to manufacture a new chip. a. The project's estimated economic life is 5 years. b. RIC's marketing vice-president believes that annual sales would be 30,000 units if the units were priced at $6,000 each. RIC expects no growth in unit sales, and it believes that the unit price will rise by 3 percent each year. C. The engineering department has reported that the project will require additional manufacturing space, and RIC currently has an option to purchase an existing building, at a cost of $20 million, which would meet this need. The building would be bought and paid for on December 31 of Year 0, and for depreciation purposes, it would fall into the MACRS 39-year class. The annual depreciation rate for the five years of economic life of the project would be: Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 1.3% 2.6% 2.6% 2.6% 2.6% d. The necessary equipment would be purchased, installed, and paid for on December 31 of Year 0. The equipment would fall into the MACRS 5-year class, and it would cost $10 million, including transportation and installation. The annual depreciation rate for the five years of economic life of the project would be: Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 20% 32% 19% 12% 11% e. f. At the end of the project, the building is expected to have a market value of $10 million and the equipment is expected to have a market value of $2 million. The production department has estimated that variable manufacturing costs would be $4000 per unit, and that fixed overhead costs, excluding depreciation would be $20 million a year. They expect variable costs to rise by 3 percent per year, and fixed costs to rise by 2 percent per year. Depreciation expense would be determined in accordance with MACRS rates. g. RIC must have an amount of NOWC on hand equal to 10 percent of the upcoming year's sales. h. RIC's marginal tax rate is 25 percent, its cost of capital is 12 percent, and it assumes that all operating cash flows occur at the end of the year. Evaluate the project using the NPV rule and the IRR rule. Problem 2 You have been asked by the president of the Farr Construction Company to evaluate the proposed acquisition of a new earth mover. The mover's basic price is $220,000, and it would cost another $30,000 to modify it for special use. Assume that the mover falls into the MACRS 5-year class, it would be sold after 4 years for $60,000, and it would require an increase in net operating working capital (spare parts inventory) of $10,000. The earth mover would have no effect on revenues, but it is expected to save the firm $52,000 per year in before-tax operating costs, mainly labor. The firm's marginal federal-plus-state tax rate is 25 percent and the project's cost of capital is 10 percent. Evaluate the project using the NPV rule and the IRR rule. Problem 3 ABC Inc. wishes to buy new machinery that would cost $166,000, but it would lead to increased output, higher sales, and higher costs. Moreover, the firm would receive $100,000 after taxes for the old machine. The new machine would result in sales of $120,000 per year versus old sales of $70,000, and the new costs would be $40,000 versus old costs of $20,000. Finally, the old machine was being depreciated at the rate of $10,000 per year, but the new machine would have $30,000 of annual depreciation. The marginal tax rate is 25 percent and WACC is 10 percent. Based on these figures, and assuming the new and old machines both have a life of four years, find the incremental cash flows. Problem 1 - Evaluating a New Project Year 0 Project- 5 Year Life Building Purchase (20,000,000) Equipment Purchase (10,000,000) Total Initial Investment $ (30,000,000) Unit Sales 30,000 6,495 $ Price per Unit Total Sales 180,000,000 183,600,000 187,272,000 191,017,440 194,837,789 Variable Cost per Unit S 4,000 120,000,000 4.080 122,400,000 4,162 S 4,245 124,848,000 127,344,960 4,330 129,891,859 Total Variable Costs Total Fixed Costs 20,000,000 20,200,000 20,402,000 20,606,020 20,812,080 Depreciation Rate (39 Year) 2.60% 2.60% 2.60% 2.60% 1.30% 260,000 20% 520,000 520,000 520,000 520,000 32% 19% 12% Building Depreciation Depreciation Rate (5 Year) Equipment Depreciation Total Depreciation Costs $ (2,000,000) $ (3,200,000) S (1,900,000) $ (2,260,000) (3,720,000) (2,420,000) 11% (1,200,000) S (1,100,000) (1,720,000) (1,620,000) Earnings Before Income Tax (EBIT) $ 37,740,000 $37,280,000 $ 39,602,000 $ 41,346,460 $ 42,513,849 40% 40% Tax Rate Total Taxes 40% 40% (15,096,000) (14,912,000) (15,840,800) (16,538,584) 40% (17,005,540) Net Operating Profits (NOPAT) $ 22,644,000 $22,368,000 $ 23,761,200 $ 24,807,876 $ 25,508,310 Add Back Depreciation Operating Cash Flow $ 2,260,000 $ 3,720,000 $ $24.904.000 $ 26,088,000 $ 2,420,000 $1,720,000 $ 1,620,000 26,181,200 $ 26,527,876 $ 27,128,310 10.00% NOWC Percentage Required 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% Net Operating Working Capital $ 18,000,000 $18,360,000 $18,727,200 $ 19,101,744 $ 19,483,779 $ Increase in NOWC $ (18,000,000) $ (360,000) $ (367,200) $ (374,544) $ (382,035) $ 19,483,779 Total Annual Project Cash Flow (48,000,000) $ 24,544,000 $257,720,800 $25,806,656 $ 26,145,841 $ 46,612,089 Terminal Year Cash Flow Building Sale (MV) Less: Book Value of Building 10,000,000 17,660,000 Profit on Sale $ (7,660,000) 3,064,000 Tax on Loss (25%) Net Salvage Value on Building $ 13,064,000 Equipment Sale (MV) Less: Book Value of Equipment Profit on Sale 2,000,000 600,000 S 1,400,000 560,000 Tax on Profit (25%) Net Salvage Value on Equipment S 1,440,000 Total Net Salvage Value S 14,504,000 $ 48,000,000 $24,544,000 $ 25,720,500 $25,806,656 $ 26,145,841 $ 61,116,089 Required Rate of Return (WACC) 12.00% NPV $ 64,082,483 IRR 50.81% Free Cash Flow $ Year 1 30,000 6,000 $ $ Year 2 30,000 6,120 $ Year 3 30,000 6,242 S Year 4 30,000 6,367 S $ Year 5 Problem 2 - Evaluating a Cost Saving Project Acquisition - 5 Year Life Earth Mover ?? Installation Costs ?? Total Initial Investment $ Savings in Costs Depreciation Rate (5 Year) Total Depreciation Costs Earnings Before Income Tax (EBIT) Tax Rate Total Taxes Net Operating Profits (NOPAT) Add Back Depreciation Operating Cash Flow Net Operating Working Capital ?? Increase in NOWc ?? Total Annual Project Cash Flow ?? Terminal Year Cash Flow Machine Sale Less: Book Value of Machine Profit on Sale Tax on Profit (25%) Net Salvage Value on Equipment ?? Required Rate of Return (WACC) ?? NPV ?? IRR ?? Free Cash Flow Year 0 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Year 1 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? 33 ?? ?? Year 2 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Year 3 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? 3 33 ?? 3.3 33 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Year 4 Problem 3 - Evaluating a Replacement Project Year 0 Acquisition - 5 Year Life New Machinery ?? Sale - Old Machine ?? Total Initial Investment ?? New Sales Old Sales Change in Sales New Costs Old Costs Change in Costs New Depreciation Old Depreciation Change in Depreciation Earnings Before Income Tax (EBIT) Tax Rate Total Taxes Net Operating profits (NOPAT) Add Back Depreciation Operating Cash Flow Net Operating Working Capital Increase in NOWC Total Annual Project Cash Flow ?? Required Rate of Return (WACC) ?? NPV ?? IRR ?? Free Cash Flow ?? ?? ?? 22 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Year 1 ?? 333 333 333 333 333 333 333 ?? ?? ?? 333 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Year 2 ?? ?? ?? ?? 22 72 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Year 3 ?? ?? ?? ?? 38 3 ?? ?? ?? Year 4 NOT NEEDED NOT NEEDED NOT NEEDED NOT NEEDED












