Assist in solving the following problems
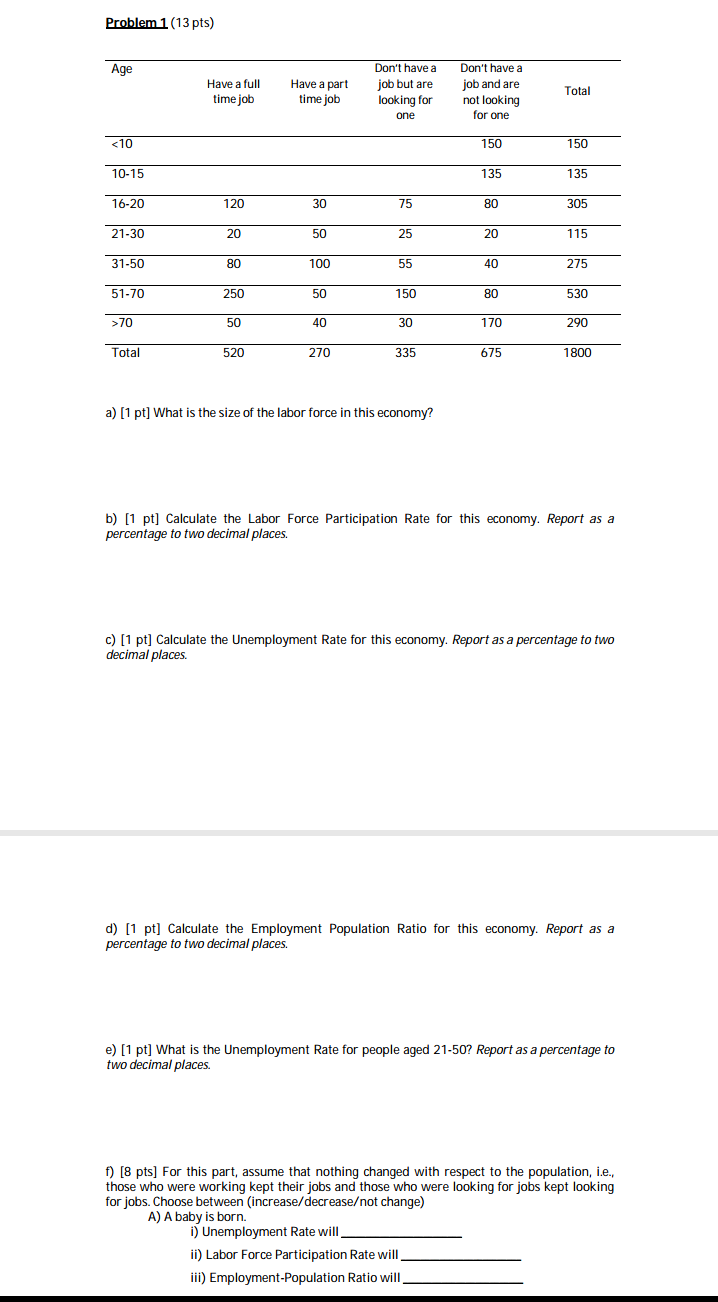
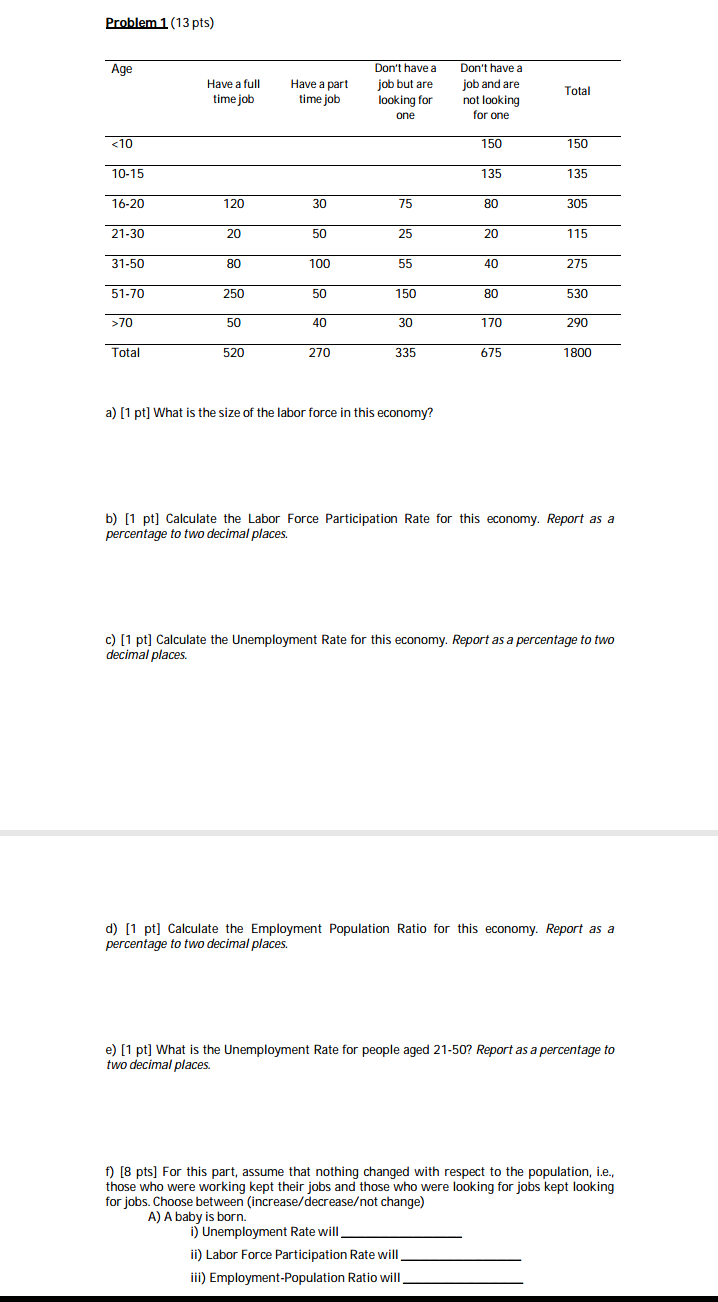
EXERCISES Fen CHAPTER 13 Ext-wise 13.1 (a) What is the distinction between growth in potential GDP and growth in per capita real GDP? [b] Why is this distinction important to an evaluation of the relationship between economic growth and growth in standards of living? (c) Which grows more rapidly. potential GDP or per capita real lGDP? Exercise 13.2 Consider two countries with the same level of potential GDP, say $100 billion, today. Suppose potential GDP grows at an annual rate of 3.5 percent (0.035) in one country and 3.25 percent (0.0325) in the second country. Based on this information: (a) What do you predict for the percentage difference in potential GDP between the two coun- tries 10 years in the future? (b) 20 years in the future? [Note that the growth rates will compound to determine real GDP according to the following formula: 1", = Y(l + growth rate)'.] Exercise 13.3 Suppose you have the following information about an economy: Average annual rates ofgrowth from 1993 to 2008: Potential GDP 3.5% Labour force 2.1% Capital stock 3.0% Share of labour income in national income: 18. Using growth accounting, nd the contribution to the annual growth in potential GDP that came from: (a) Growth in labour force [b] Growth in capital stock (c) Improved productivity as measured by the Solow residual. Exercise 13.4 If technology were constant while labour force grew at a rate of 2.5% a year, capital stock grew at 1.5% per year and the share of labour income in national income was T0%, how fast would potential GDP grow? Exercise 13.5 Suppose you have the following information for two economies: 350 I Economic growth Camry A Country B Average annual i. Labour fume 2.5% 4.0% growth rates: ii. Capital stock 3.5% 3.5% Lah-mrr incomm'nmiuml income: 2'3 233 (a) Assuming a constant state of technology, which of these two countries will have the faster rate of growth in total real GDP? [b] Which of the two countries will have the faster rate of growth in per capita real GDP? (c) What differences, if any, do you see in the growth rates of the capital to labour ratios in the two countries? (d) Explain the reasons for the differences in growth rates you have found. Problem 4 (15 pts) You are given data on the following variables in an economy: Government spending 300 Planned investment 200 Net exports 50 Autonomous taxes 250 Income tax rate 0.1 Marginal propensity to consume 0.5 a) [2 pts] Consumption (C) is 600 when income (Y) is equal to 1500. Solve for autonomous consumption. b) [4 pts] Solve for the equilibrium level of output in the following two scenarios: i) there is an income tax t=0.1, ii) there is no income tax in the economy. Denote these two variables by Y" w and Y" wo respectively. c) [2 pts] In the economy with an income tax of 10%, what is the budget balance of the government? d) [3 pts] Solve for the change in net exports that would bring the equilibrium output level in the economy with the income tax to the level of Y"we that you found in part b. Specify both the magnitude of the change and whether it is an increase or a decrease. What would be the new level of net exports after this change? e) [4 pts] Suppose that we would like to achieve the same goal (as in part d) by changing the level of autonomous taxes instead of that of net exports. So, net exports remain at 50 and the level of autonomous taxes changes instead. Find the necessary magnitude of the change and specify whether autonomous taxes would have to increase or decrease. What would be the new level of autonomous taxes that accomplishes this goal?Problem 3 (10 pts) You have the following information on 3 countries: Soccerland, Handeggland and Neverland Soccerland Handeggland Neverland GDP in the beginning 5000 1000 2000 of 2013 Growth rate per year 5% 8% 10% a) [1 pt] How long will it take until Soccerland's GDP increases by 75%? b) [2 pts] How long will it take until Soccerland and Handeggland have the same GDP? c) [2 pts] Soccerland's population is not happy that, eventually, Handeggland is going to have higher GDP than their country. They feel that they are a much better country, so they are going to work harder to ensure that Handeggland will never catch up with Soccerland. If Soccerland new growth rate is constant every year, what is the minimum growth rate that ensures that Soccerland will always have a higher GDP than Handeggland? d) [5 pts] Neverland's ambition is to host the World Cup. At the beginning of 2013, its GDP was 2,000 and it was growing at 10% a year. Moreover, it will keep this pace until it hosts the World Cup. In order to host such a big event, Neverland's GDP must be at least 6,000. After the moment it reaches that GDP level, it will host the World Cup in the beginning of the next year available for the event (remember that the World Cup takes place every four years, in the years: 2014, 2018, 2022, etc.) During the year that Neverland hosts the World Cup, their GDP will grow at 75%. Then, everything returns to normal, and their GDP will keep growing at 10% a year forever onwards. i) (3 pts) When will Neverland's GDP reach 20,000?Problem 2 (10 pts) Consider Country X with a GDP level of 210,000 and a growth rate of 5% in 2013 (calculated at the end of year 2013). The experts predict that the growth of the economy of Country X will gradually slow down in the coming years. More precisely, they foresee the following growth rates for the future: 2013 -2016 5% 2016 -2019 3% 2019 - on 1% Hint: The list above should be read as saying that, for instance, 'the growth rate from the end of 2013 until the end of 2016 will be 5%, then from the end of 2016 until the end of 2019 it will be 3%' and so on. a) [5 pts] Assuming that the predictions of the experts listed above are accurate, when in the future will Country X's GDP double compared to the GDP level of 2013? b) [3 pts] What would your answer for the question in part a be if the growth rate from 2019 and on was in fact -1%? Explain your reasoning carefully. c) [2 pts] Consider now the more optimistic scenario in which the economy does not slow down and the current growth rate of 5% remains constant in the coming years. How long will it take for the GDP level to double in this scenario? Express your answer in two forms: i) in number of years, ii) as a fraction of your answer in part a.Problem 1 (13 pts) Age Don't have a Don't have a Have a full Have a part job but are job and are Total time job time job looking for not looking one for one