Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Assume that in order to achieve reliable data transfer, we use negative acknowledge- ments (NAKs) instead of acknowledgements (ACKs). The protocol works as follows:

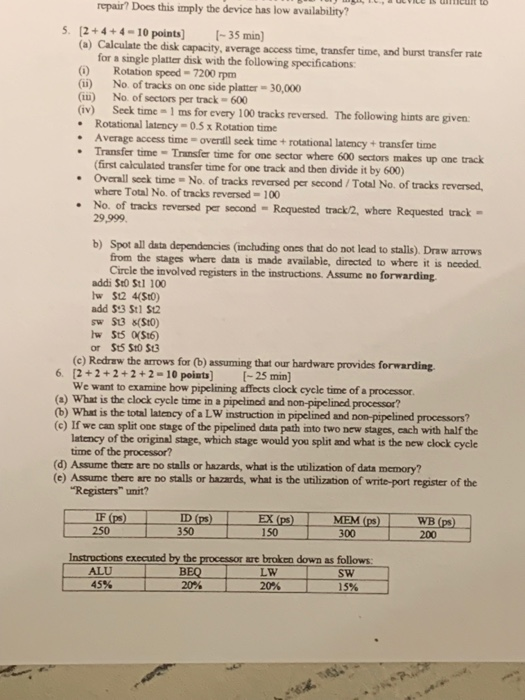
Assume that in order to achieve reliable data transfer, we use negative acknowledge- ments (NAKs) instead of acknowledgements (ACKs). The protocol works as follows: When receiver detects a gap in the sequence numbers, a NAK is sent. Sender uses time-out. - Both NAK and timeout result in retransmission. Argue that this protocol achieves reliable data transfer or not. Also, assume that the sender has a lot of data to transfer and the end-to-end connection experiences few losses. Compare the NAK-only protocol with the NAK-free protocol that we discussed in class. repair? Does this imply the device has low availability? 5. [2+4+4-10 points] [-35 min) (a) Calculate the disk capacity, average access time, transfer time, and burst transfer rate for a single platter disk with the following specifications: (1) (ii) (II) (iv) No. of sectors per track - 600 Seek time=1 ms for every 100 tracks reversed. The following hints are given: Rotational latency-0.5 x Rotation time . Average access time overall seek time + rotational latency + transfer time Rotation speed-7200 rpm No. of tracks on one side platter - 30,000 . . Transfer time-Transfer time for one sector where 600 sectors makes up one track (first calculated transfer time for one track and then divide it by 600) Overall seek time= No. of tracks reversed per second / Total No. of tracks reversed, where Total No. of tracks reversed - 100 No. of tracks reversed per second Requested track/2, where Requested track - 29,999. . b) Spot all data dependencies (including ones that do not lead to stalls). Draw arrows from the stages where data is made available, directed to where it is needed. Circle the involved registers in the instructions. Assume no forwarding. addi $t0 St1 100 lw $12 4($10) add $13 St1 S12 sw S13 ($10) lw $t5 0($16) or S15 S10 $13 (c) Redraw the arrows for (b) assuming that our hardware provides forwarding. 6. [2+2+2+2+2-10 points] [-25 min] We want to examine how pipelining affects clock cycle time of a processor. (a) What is the clock cycle time in a pipelined and non-pipelined processor? (b) What is the total latency of a LW instruction in pipelined and non-pipelined processors? (c) If we can split one stage of the pipelined data path into two new stages, each with half the latency of the original stage, which stage would you split and what is the new clock cycle time of the processor? (d) Assume there are no stalls or hazards, what is the utilization of data memory? (e) Assume there are no stalls or hazards, what is the utilization of write-port register of the "Registers" unit? IF (ps) 250 ID (ps) 350 A cult to EX (ps) 150 MEM (ps) 300 Instructions executed by the processor are broken down as follows: ALU BEQ LW 45% 20% 20% SW 15% WB (ps) 200
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


