Question
At the start of the strategy-making process, a company's senior managers must struggle with the issue of what directional path the company should take and
At the start of the strategy-making process, a company's senior managers must struggle with the issue of what directional path the company should take and whether its market positioning and future performance prospects could be improved by changing the company's product offerings, the markets in which it participates, the customers it caters to and/or the technologies it employs. Top management's views about the company's long-term direction and future product-customer-market-technology focus constitute a strategic vision for the company.
A clearly articulated strategic vision communicates management's aspirations to stakeholders about "where we are going" and helps steer the energies of company personnel in a common direction. For instance, Henry Ford's vision of a car in every garage had power because it captured the imagination of others, aided internal efforts to mobilize the Ford Motor Company's resources, and served as a reference point for gauging the merits of the company's strategic actions.
Well-conceived visions are distinctive and specific to a particular organization; they avoid generic, feel-good statements such as "We will become a global leader and the first choice of customer's in every market we choose to serve"?which could apply to any of hundreds of organizations. And they are not the product of a committee charged with coming up with an innocuous but well-meaning one-sentence vision that wins consensus approval from various stakeholders. Nicely worded vision statements with no specifics about the company's product-market-customer-technology focus fall well short of what it takes for a vision to measure up.
For a strategic vision to function as a valuable managerial tool, it must provide understanding of what management wants its business to look like and give managers a reference point in making strategic decisions. It must say something definitive about how the company's leaders intend to position the company beyond where it is today.
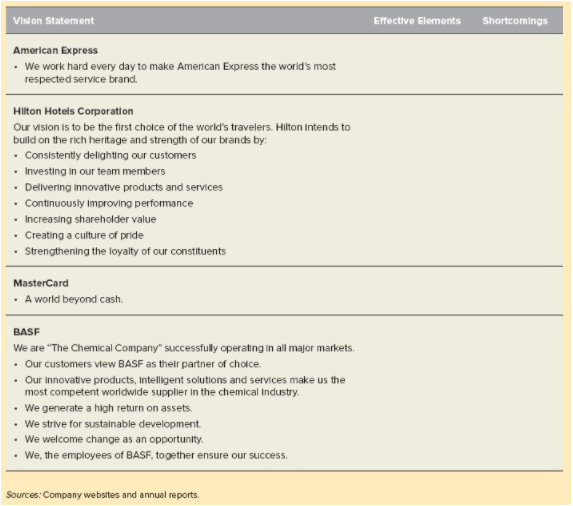
Table 2.1 presents the "Dos and Don'ts" of wording a vision statement. Illustration Capsule 2.1 provides examples of the strategic visions of several companies with a critique of each, including effective elements and shortcomings.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


