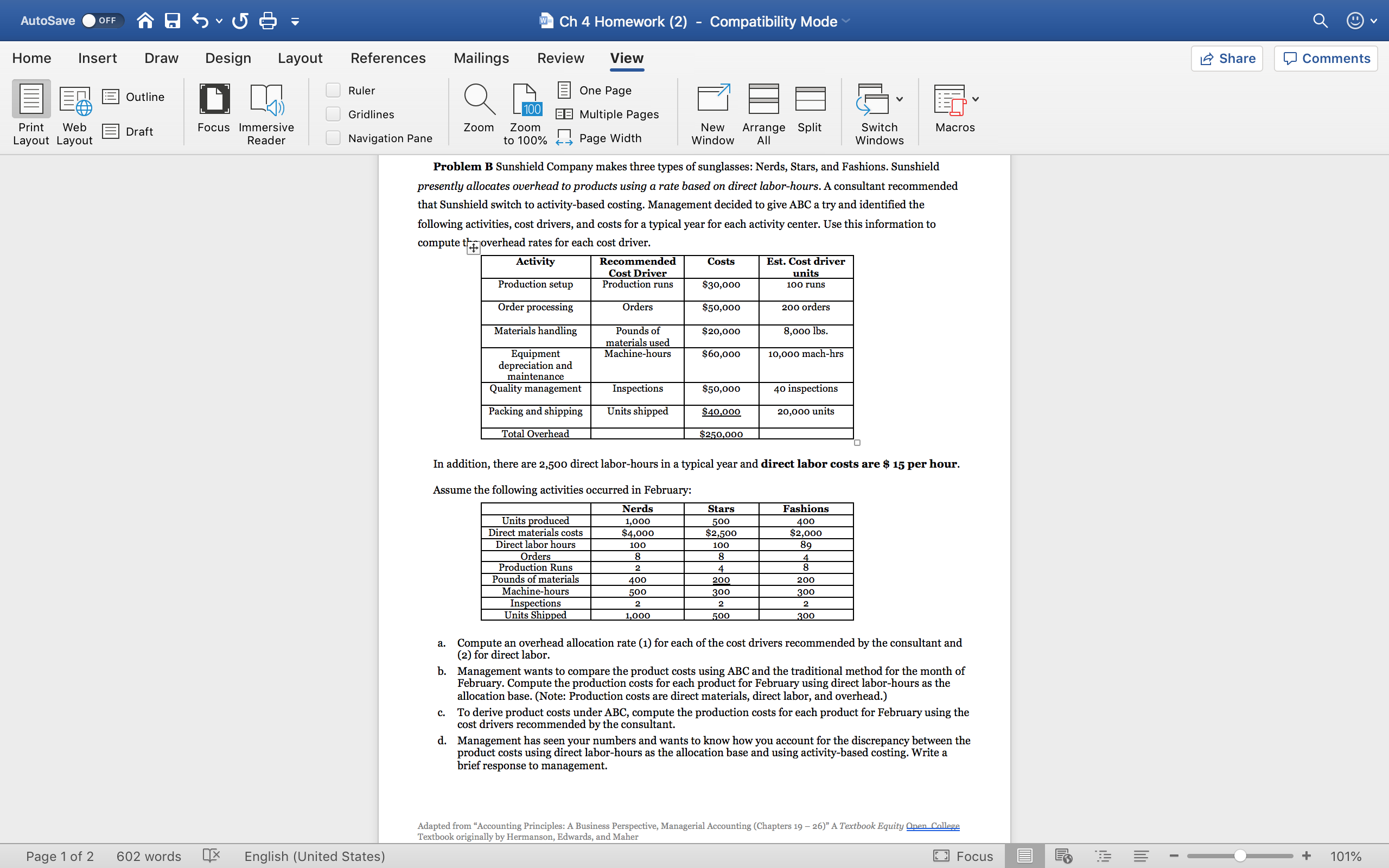
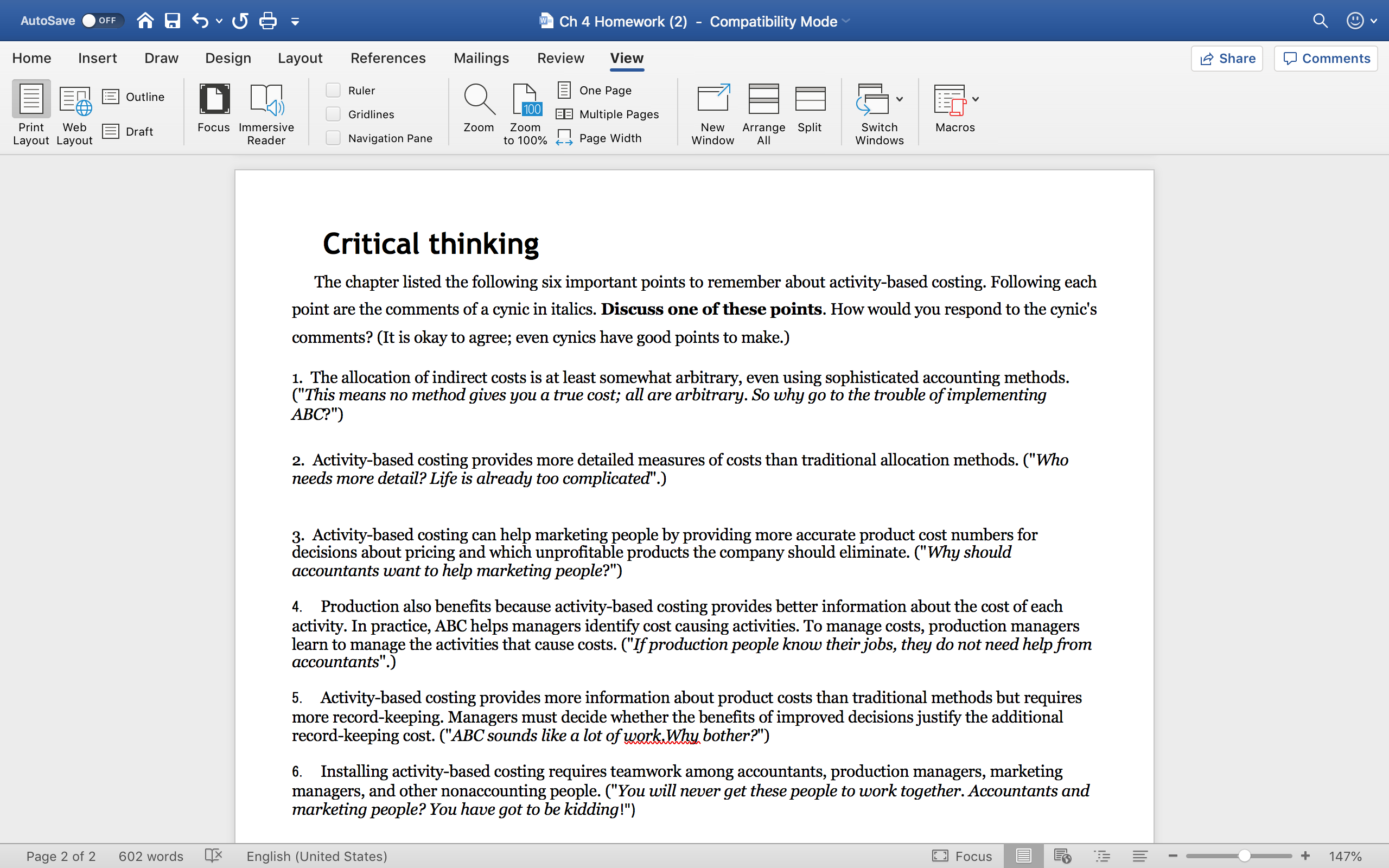
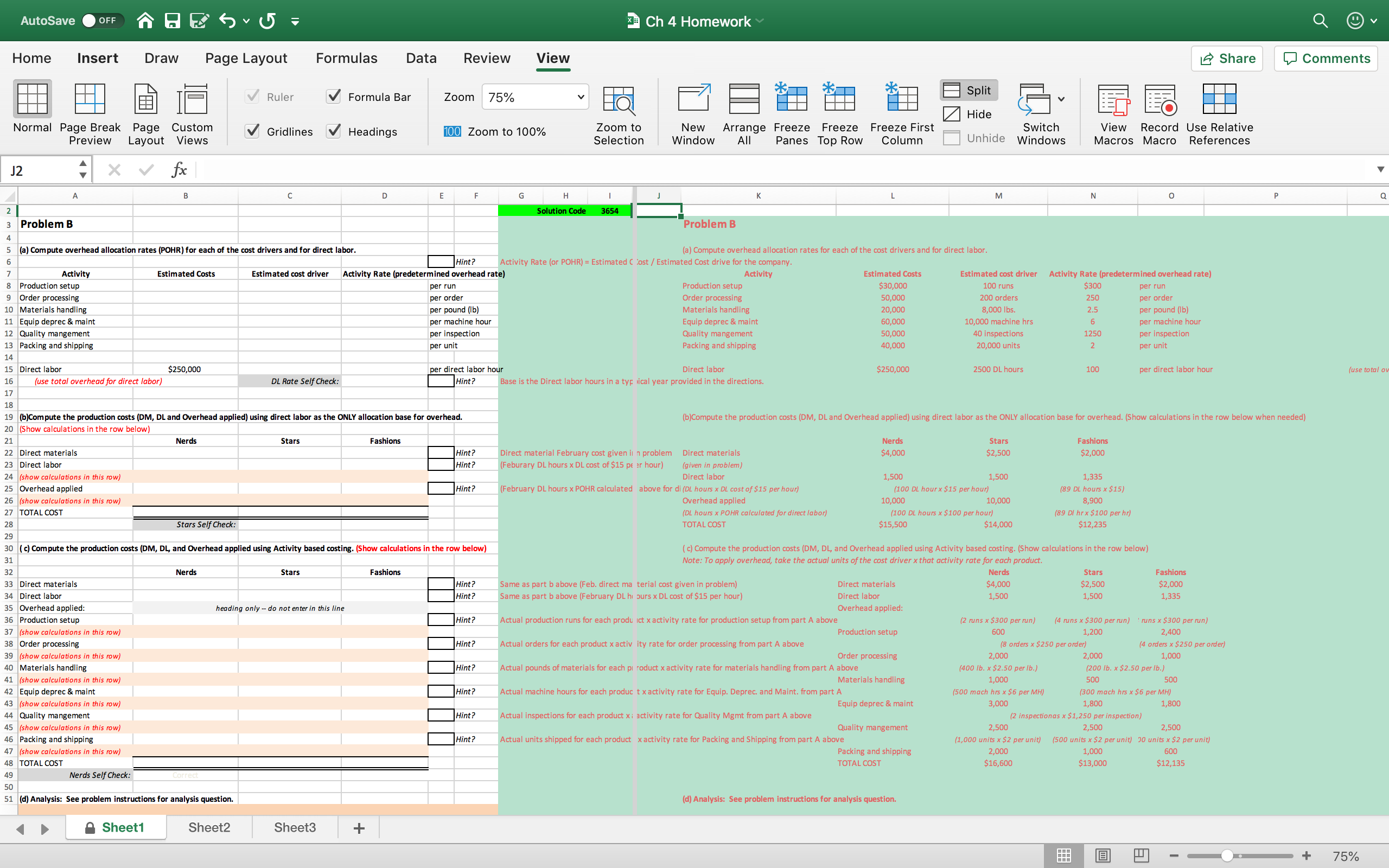
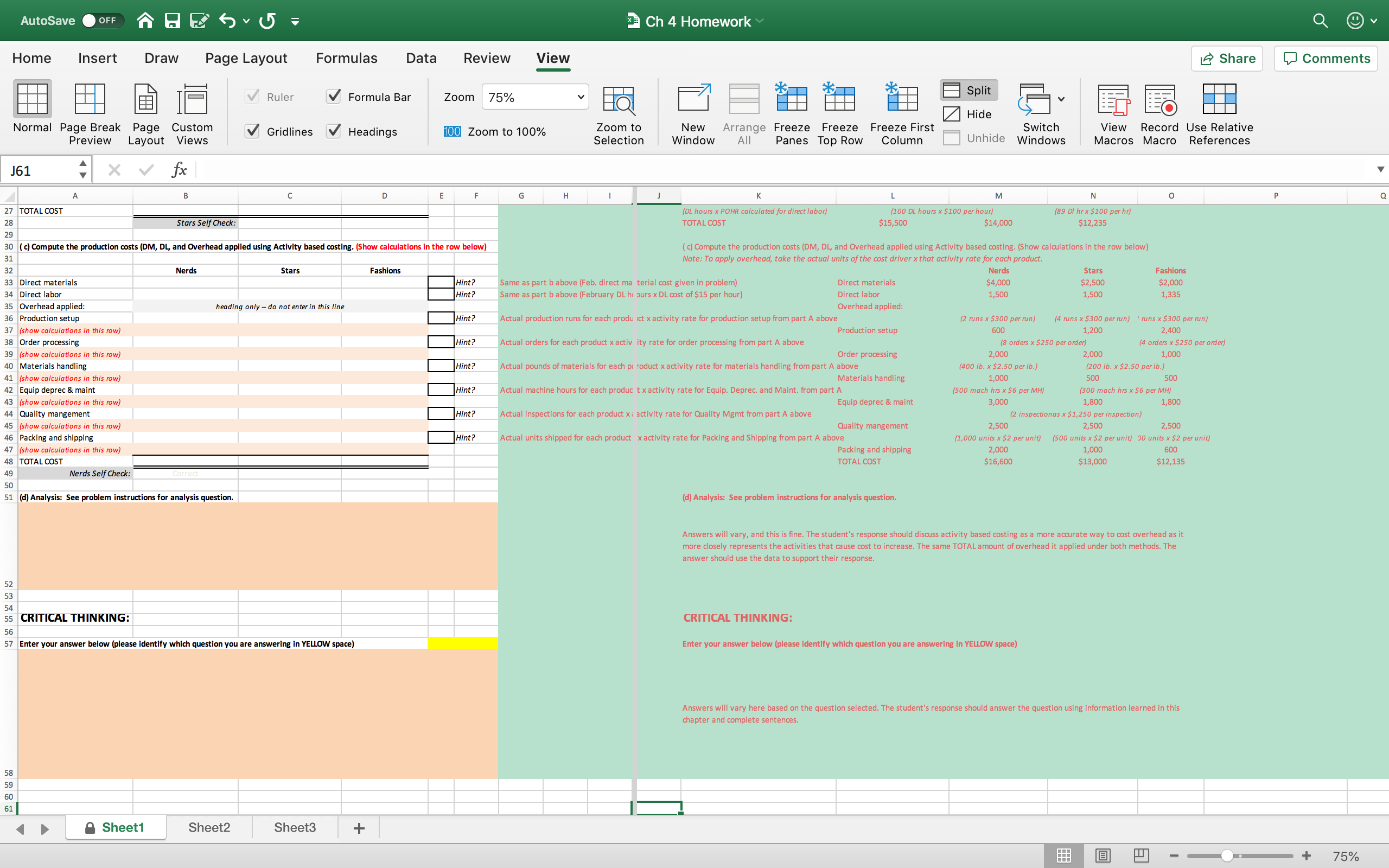
AutoSave OFF Ch 4 Homework (2) - Compatibility Mode Q v Home Insert Draw Design Layout References Mailings Review View Share Comments Outline Ruler One Page Print Web Focus Immersive Gridlines Zoom Zoom BE Multiple Pages New Arrange Split Switch Macros Layout Layout Draft Reader Navigation Pane to 100% Page Width Window All Windows Problem B Sunshield Company makes three types of sunglasses: Nerds, Stars, and Fashions. Sunshield presently allocates overhead to products using a rate based on direct labor-hours. A consultant recommended that Sunshield switch to activity-based costing. Management decided to give ABC a try and identified the following activities, cost drivers, and costs for a typical year for each activity center. Use this information to compute try overhead rates for each cost driver. Activity Recommended Costs Est. Cost driver Cost Driver units Production setup Production runs $30,000 oo runs Order processing Orders $50,000 200 orders Materials handling Pounds of $20,000 ,ooo Ibs materials used Equipment Machine-hours $60,000 10,000 mach-hrs depreciation and maintenance Quality management Inspections $50,000 40 inspections Packing and shipping Units shipped $40,000 20,000 units Total Overhead $250,000 In addition, there are 2,500 direct labor-hours in a typical year and direct labor costs are $ 15 per hour. Assume the following activities occurred in February: Nerds Stars Fashions Units produced 1,000 500 400 Direct materials costs $4,000 $2,500 $2,000 Direct labor hours 100 100 89 Orders 8 Production Runs 2 8 Pounds of materials 400 200 Machine-hours 200 500 300 300 Inspections 2 Units Shipped 2 1,000 500 300 a. Compute an overhead allocation rate (1) for each of the cost drivers recommended by the consultant and (2) for direct labor. b. Management wants to compare the product costs using ABC and the traditional method for the month of February. Compute the production costs for each product for February using direct labor-hours as the allocation base. (Note: Production costs are direct materials, direct labor, and overhead.) To derive product costs under ABC, compute the production costs for each product for February using the cost drivers recommended by the consultant. d. Management has seen your numbers and wants to know how you account for the discrepancy between the product costs using direct labor-hours as the allocation base and using activity-based costing. Write a brief response to management. Adapted from "Accounting Principles: A Business Perspective, Managerial Accounting (Chapters 19 - 26)" A Textbook Equity Open College Textbook originally by Hermanson, Edwards, and Maher Page 1 of 2 602 words X English (United States) Focus E + 101%AutoSave .orr Q E (j v (5 : "3 Ch4Homework (2) Compatibility Mode Home Insert Draw Design Layout References Mailings Review View a Share G Comments i' 1 _ i 5 gr! Em. U'I - Q {a E One-Page 4' g '3' 5:1 v ;: . E75 L 4 (1)) Gridlines .MulliplePages ' Print Web E Draft Focus lmmersive _ > Zoom Zoom '_' ' New Arrange Split Switch Macros Layout Layout Reader P NaVIQENOH Pane 7100'. 49 Page Wldth Window All Windows Critical thinking The chapter listed the following six important points to remember about activity-based costing. Following each point are the comments of a cynic in italics. Discuss one of these points. How would you respond to the cynic's comments? (It is okay to agree; even cynics have good points to make.) 1. The allocation of indirect costs is at least somewhat arbitrary, even using sophisticated accounting methods. ("This means no method gives you a true cost; all are arbitrary. So why go to the trouble of implementing ABC'") 2. Activity-based costing provides more detailed measures of costs than traditional allocation methods. ("Who needs more detail? Life is already too complicated") 3. Activity-based costing can help marketing people by providing more accurate product cost numbers for decisions about pricing and which unprotable products the company should eliminate. ("Why should accountants want to help marketing people?") 4. Production also benets because activity-based costing provides better information about the cost of each activity. In practice, ABC helps managers identify cost causing activities. To manage costs, production managers learn to manage the activities that cause costs. ("If production people know their jobs, they do not need help from accountants".) 5. Activitybased costing provides more information about product costs than traditional methods but requires more record-keeping. Managers must decide whether the benets of improved decisions justify the additional record-keeping cost ("ABC sounds like a lot of mm bother?") 6. Installing activitybased costing requires teamwork among accountants, production managers, marketing managers, and other nonacoounting people. ("You will never get these people to work together. Accountants and marketing people? You have got to be kidding!") Page20t2 602 words [13' English (United States) D Focus n has TE 5 - V + 147% AutoSave OFF Ch 4 Homework Q v Home Insert Draw Page Layout Formulas Data Review View Share Comments Ruler Formula Bar Zoom 75% Split Hide FO Normal Page Break Page Custom Gridlines Headings 100 Zoom to 100% Zoom to New Arrange Freeze Freeze Freeze First Switch View Record Use Relative Preview Layout Views Selection Window All Panes Top Row Column Unhide Windows Macros Macro References J2 X V fx C D E G H M N Solution Code 3654 Problem B Problem B (a) Compute overhead allocation rates (POHR) for each of the cost drivers and for direct labor. Hint ? (a) Compute overhead allocation rates for each of the cost drivers and for direct labor Activity Rate (or POHR) = Estimated Cost / Estimated Cost drive for the company. Activity Estimated Costs Estimated cost driver Activity Rate (predetermined overhead rate) Activity Estimated Costs Estimated cost driver Activity Rate (predetermined overhead rate) Production setup per run Production setup $30,000 100 runs $300 per run Order processing per order Order processing 50,000 200 orders 250 per order 10 Materials handling per pound (Ib) Materials handling 20,000 8,000 Ibs. 2.5 per pound (1b) 11 Equip deprec & maint per machine hour Equip deprec & maint 60,000 10,000 machine hrs 6 per machine hour Quality mangement per inspection Quality mangement 50,000 40 inspections 1250 per inspection 13 Packing and shipping per unit Packing and shipping 40,000 20,000 units per unit 14 15 Direct labor $250,000 per direct labor hour Direct labor $250,000 2500 DL hours 100 per direct labor hour (use total 16 17 (use total overhead for direct labor) DL Rate Self Check: Hint? Base is the Direct labor hours in a typ iical year provided in the directions. 18 19 (b)Compute the production costs (DM, DL and Overhead applied) using direct labor as the ONLY allocation base for overhead. (b)Compute the production costs (DM, DL and Overhead applied) using direct labor as the ONLY allocation base for overhead. (Show calculations in the row below when needed) 20 (Show calculations in the row below) 21 Nerds Stars Fashions Nerds Stars Fashions 22 Direct materials Hint ? Direct material February cost given in n problem Direct materials $4,000 $2,500 $2,000 23 Direct labor Hint? Feburary DL hours x DL cost of $15 pt :r hour) (given in problem) 24 (show calculations in this row) Direct labor 1,500 1,500 1,335 25 Overhead applied Hint ? (February DL hours x POHR calculated above for di (DL hours x DL cost of $15 per hour) (100 DL hour x $15 per hour) (89 DL hours x $15) 26 (show calculations in this row) Overhead applied 10,000 10,000 8,900 27 TOTAL COST (DL hours x POHR calculated for direct labor) (100 DL hours x $100 per hour) (89 DI hr x $100 per hr) 28 Stars Self Check: TOTAL COST $15,500 $14,000 $12,235 29 30 ( c) Compute the production costs (DM, DL, and Overhead applied using Activity based costing. (Show calculations in the row below) ( c) Compute the production costs (DM, DL, and Overhead applied using Activity based costing. (Show calculations in the row below) 31 Note: To apply overhead, take the actual units of the cost driver x that activity rate for each product. 32 Nerds Stars Fashions Nerds Stars Fashions 33 Direct materials Hint? Same as part b above (Feb. direct ma terial cost given in problem) Direct materials $4,000 $2,500 $2,00 34 Direct labor Hint? Same as part b above (February DL hi ours x DL cost of $15 per hour) Direct labor 1.500 1,500 1,335 35 Overhead applied: heading only - do not enter in this line Overhead applied: 36 Production setup Hint ? Actual production runs for each produ ict x activity rate for production setup from part A above (2 runs x $300 per run) (4 runs x $300 per run) ' runs x $300 per run) 37 (show calculations in this row) Production setup 600 1,200 2,400 38 Order processing Hint? Actual orders for each product x activ ity rate for order processing from part A above (8 orders x $250 per order) (4 orders x $250 per order) 39 (show calculations in this row) Order processing 2,000 2,000 1,000 40 Materials handling Hint ? Actual pounds of materials for each pi roduct x activity rate for materials handling from part A above (400 lb. x $2.50 per lb.) (200 lb. x $2.50 per lb.) 41 (show calculations in this row) Materials handling 1,000 500 500 42 Equip deprec & maint Hint? Actual machine hours for each produc t x activity rate for Equip. Deprec. and Maint. from part A (500 mach hrs x $6 per MH) 300 mach hrs x $6 per MH) 43 (show calculations in this row) Equip deprec & maint 3,000 1,800 1,800 44 Quality mangement Hint ? Actual inspections for each product xi activity rate for Quality Memt from part A above (2 inspectionas x $1,250 per inspection) 45 (show calculations in this row) Quality mangement 2,500 2,500 2,500 46 Packing and shipping Hint ? Actual units shipped for each product x activity rate for Packing and Shipping from part A above (1,000 units x $2 per unit) (500 units x $2 per unit) 20 units x $2 per unit) 47 (show calculations in this row) Packing and shipping 2,000 1,000 600 48 TOTAL COST TOTAL COST $16,600 $13,000 $12,135 49 Nerds Self Check: 50 51 (d) Analysis: See problem instructions for analysis question. (d) Analysis: See problem instructions for analysis question. A Sheet1 Sheet2 Sheet3 + + 75%AutoSave OFF Ch 4 Homework Q v Home Insert Draw Page Layout Formulas Data Review View Share Comments Ruler Formula Bar Zoom 75% Split Hide FO Normal Page Break Page Custom Preview Layout Views Gridlines Headings 100 Zoom to 100% Zoom to New Arrange Freeze Freeze Freeze First Switch View Record Use Relative Selection Window All Panes Top Row Column Unhide Windows Macros Macro References J61 X V fx G H I M N 0 27 TOTAL COST DL hours x POHR calculated for direct labor) (100 DL hours x $100 per hour) (89 DI hr x $100 per hr) 28 Stars Self Check: TOTAL COST $15,500 $14,000 $12,235 29 30 ( c) Compute the production costs (DM, DL, and Overhead applied using Activity based costing. (Show calculations in the row below) ( c) Compute the production costs (DM, DL, and Overhead applied using Activity based costing. (Show calculations in the row below) 31 Note: To apply overhead, take the actual units of the cost driver x that activity rate for each product 32 Nerds Stars Fashions Nerds Stars Fashions 33 Direct materials |Hint Same as part b above (Feb. direct ma terial cost given in problem) Direct materials $4,000 $2,500 $2,000 34 Direct labor Hint ? Same as part b above (February DL hi purs x DL cost of $15 per hour) Direct labor 1,500 1,500 1,335 35 Overhead applied heading only - do not enter in this line Overhead applied: 36 Production setup Hint? Actual production runs for each produ ict x activity rate for production setup from part A above (2 runs x $300 per run) (4 runs x $300 per run) ' runs x $300 per run) 37 (show calculations in this row) Production setup 600 1,200 2,400 38 Order processing Hint ? Actual orders for each product x activ ity rate for order processing from part A above (8 orders x $250 per order) (4 orders x $250 per order) 39 (show calculations in this row) Order processing 2,000 2,000 1,000 40 Materials handling Hint ? Actual pounds of materials for each pi roduct x activity rate for materials handling from part A above (400 lb. x $2.50 per lb.) (200 lb. x $2.50 per lb.) 41 (show calculations in this row) Materials handling 1,000 500 500 42 Equip deprec & maint Hint? Actual machine hours for each produc t x activity rate for Equip. Deprec. and Maint. from part A (500 mach hrs x $6 per MH) (300 mach his x $6 per MH) 13 (show calculations in this row) Hint Equip deprec & maint 3,000 1,800 1 ,800 44 Quality mangement Actual inspections for each product xi activity rate for Quality Memt from part A above (2 inspectionas x $1, 250 per inspection) 45 (show calculations in this row) Hint ? Quality mangement 2,500 2,500 2,500 46 Packing and shipping Actual units shipped for each product x activity rate for Packing and Shipping from part A above (1,000 units x $2 per unit) (500 units x $2 per unit) 10 units x $2 per unit) 47 (show calculations in this row) Packing and shipping 2,000 1,000 600 48 TOTAL COST TOTAL COST $16,600 $13,000 $12,135 49 Nerds Self Check: 50 51 (d) Analysis: See problem instructions for analysis question. (d) Analysis: See problem instructions for analysis question. Answers will vary, and this is fine. The student's response should discuss activity based costing as a more accurate way to cost overhead as it more closely represents the activities that cause cost to increase. The same TOTAL amount of overhead it applied under both methods. The answer should use the data to support their response. 52 54 55 CRITICAL THINKING: CRITICAL THINKING: 56 57 Enter your answer below (please identify which question you are answering in YELLOW space) Enter your answer below (please identify which question you are answering in YELLOW space) Answers will vary here based on the question selected. The student's response should answer the question using information learned in this chapter and complete sentences. 58 60 61 Sheet1 Sheet2 Sheet3 + + 75%