Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
b) Calculate the gravimetric stoichiometric air/fuel ratio for a type of fuel with the gravimetric mixture given in Table Q2 below. Assume that the
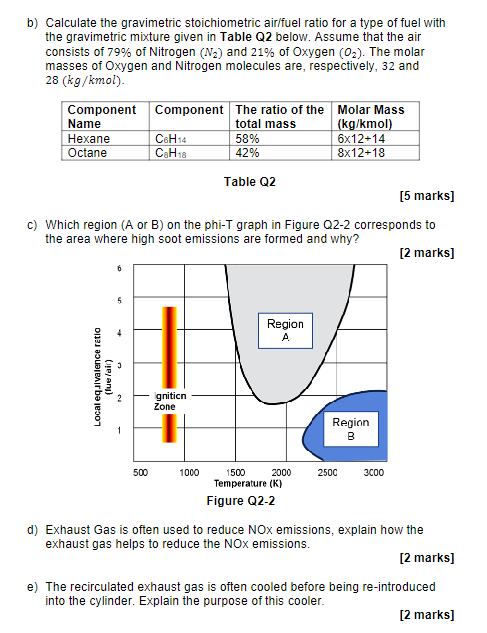
b) Calculate the gravimetric stoichiometric air/fuel ratio for a type of fuel with the gravimetric mixture given in Table Q2 below. Assume that the air consists of 79% of Nitrogen (N) and 21% of Oxygen (0). The molar masses of Oxygen and Nitrogen molecules are, respectively, 32 and 28 (kg/kmol). Component Name Hexane Octane Local equivalence ratio (lue/air) 6 5 N Component 500 C6H14 C8H18 [5 marks] c) Which region (A or B) on the phi-T graph in Figure Q2-2 corresponds to the area where high soot emissions are formed and why? [2 marks] gnition Zone The ratio of the Molar Mass total mass 1000 58% 42% Table Q2 Region A 1500 Temperature (K) Figure Q2-2 (kg/kmol) 6x12+14 8x12+18 2000 Region 2500 00 3000 d) Exhaust Gas is often used to reduce NOx emissions, explain how the exhaust gas helps to reduce the NOx emissions. [2 marks] e) The recirculated exhaust gas is often cooled before being re-introduced into the cylinder. Explain the purpose of this cooler. [2 marks]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
b To calculate the gravimetric stoichiometric airfuel ratio we need to determine the mass ratio of air to fuel that provides the stoichiometric condition We can use the molar masses of nitrogen N and ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


